Introduction to Nuclear Chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Mass of individual particles vs. mass of entire atom
answer
Individual particles more
question
Binding energy
answer
E=mc^2 Energy that holds atom together Loss of mass converted to binding energy when creating atom
question
Neutron function
answer
Glue that holds nucleus together by filling in space to prevent protons from crashing into each other
question
Radioactivity
answer
Natural process by which some atoms spontaneously disintegrate, emitting both particles and energy as they transform into different, more stable atoms. Also called radioactive decay
question
Why does radioactive decay occur?
answer
Because unstable isotopes tend to transform into stable isotopes
question
Energetic stuff about radioactivity
answer
Negative delta G Thermodynamically favorable Nothing about speed
question
Radiation
answer
Particles or energy released during decay
question
Energy of radiation
answer
E=hc/wavelength
question
Shortest to longest wave types
answer
Gamma, x-ray, UV, visible, IR
question
Primordial vs. cosmogenic when formed
answer
P - Formed during or very soon after universe creation C - synthesized through high E cosmic radiation interacting with certain nuclei or through decay of primordial
question
Half lives - Primordial vs. cosmogenic
answer
Primordial - either stable or very long Cosmogenic - vary greatly
question
Naturally always remaking ______ nuclei
answer
Cosmogenic
question
3 reasons nuclei unstable
answer
Consider in order: Too big Odd/even protons vs. neutrons Ratio of neutrons/protons
question
Nuclei size threshold for size
answer
83
question
Nuclei threshold for naturally occurring
answer
92
question
Which 2 radioactive and not naturally occuring
answer
Tc and Pm 43 and 61
question
Most stable when referring to even/odd neutrons and protons and why
answer
Most stable is even for both because nuclear particles like to pair up similar to electrons
question
Ratio of neutrons to protons
answer
If Z 1.1 If Z>20 then should be 1.4 --> 1.6
question
Gamma decay
answer
Occurs if nucleus is in excited state Will emit gamma ray
question
Which type of radiation always accompanies nuclear reaction?
answer
Gamma
question
If atom is too big, which type of decay
answer
Alpha decay
question
If ratio of neutrons to protons too high, which kind of decay?
answer
Beta emission
question
If ratio of neutrons to protons too low what happens?
answer
If Z20, then electron capture
question
Electron capture accompanied by
answer
X ray radiation
question
What happens during electron capture?
answer
Nucleus literally pulls inner core e- into the nucleus...causes relaxation of higher energy orbital...relaxation gives off X-ray
question
Positron
answer
or B+
question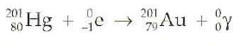
Electron capture
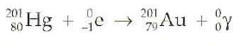
answer
+ X-ray



