Integrated Pest Management Midterm – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is a pest?
answer
a pest is any organism that interferes with the activities and desires of humans
question
Name 3 arthropod classes
answer
1. Arachnida; Ex. spiders 2. Crustacea; Ex. crabs 3. Diplopoda; Ex. millipedes 4. Chilopoda; Ex. centapedes 5. Insecta or Hexopoda (insects)
question
3 characteristics of invasive plants
answer
1. Introduced from other regions 2. Show a tendency to spread out of control. 3. Outcompete native plants, producing a monoculture that discourages the growth of other plant varieties.
question
2 types of insect development
answer
no metamorphosis gradual metamorphosis
question
What is a weed bud bank and what is its typical longevity?
answer
A budbank is the total accumulated meristems (buds) on vegetative reproductive structures of weeds such as nutsedges, johnsongrass and field bindweed. Each bud can make a new plant. Typical longevity of a budbank 2 to 10 years.
question
2 ways weeds can disseminate to new locations
answer
wind passing through the digestive tracts of herbivores and omnivores.
question
What are pheromones?
answer
A pheromone is a chemical an animal produces which changes the behavior of another animal of the same species (animals include insects)
question
What pest organisms can enter a state of cryptobiosis when suitable environmental conditions deteriorate?
answer
nematodes
question
What does it mean when an arthropod pest is said to have a delayed voltine seasonal cycle?
answer
life cycle requires more than 1 year for completion
question
What is the definition of IPM?
answer
IPM is a sustainable approach to managing pests by combining biological, cultural, physical and chemical tools in a way that minimizes economic, health, and environmental risks."
question
What does the term monitoring mean as used in IPM efforts and list 2 benefits of this activity
answer
Monitoring means capturing samples of pest organisms in order to record phenological timelines and extrapolate pest populations in an agroecosystem. 1. Monitoring provides information on spatial patterns of pests so that any pest management actions will be more accurately targeted. 2. Monitoring provides information on population size and thus can influence the decision to take action or not, such as whether to spray or not to spray.
question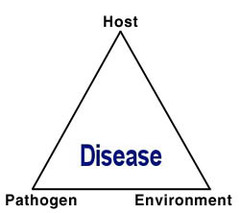
What is the disease pyramid?

answer
the existence of a disease caused by a biotic agent absolutely requires the interaction of a susceptible host, a virulent pathogen, and an environment favorable for disease development (1,6). Conversely, plant disease is prevented upon elimination of any one of these three causal components.
question
What is a facultative saprophyte?
answer
an organism that is usually parasitic but may live as a saprophyte having the ability to be a parasite.
question
What is cultural control?
answer
making the environment less suitable for the pests
question
how are cultural tactics different from physical and mechanical tactics?
answer
all cultural control tactics are mediated through the crop or crop environment, such as changes to the microclimate or crop canopy
question
Do cultural controls affect pest directly or indirectly
answer
indirectly
question
are cultural controls fast acting or slow acting?
answer
slow acting
question
Are cultural controls good for a sudden infestation?
answer
no, for taht you need direct controls like chemical spraying
question
how do cultural controls work? do they eliminate the pest?
answer
Cultural controls seek to keep the pest below the economic injury level
question
do cultural controls change the ecosystem carryign capacity for the pest?
answer
no
question
can a pest bounce back if cultural controls are relaxed to a economically damaging level?
answer
yes
question
Can cultural controls be stopped and started as needed or do they need to be continuous
answer
cultural controls need to be continuous
question
Do cultural controls require high inputs?
answer
no they generally require low inputs and have minimal environmental impact
question
Do cultural controls need sophisticated equipment?
answer
no
question
What resources to cultural controls require most?
answer
extra expertise and time on the part of managers, more human training needed
question
Are cultural controls often specific to a region?
answer
yes
question
How can pests enter a crop? 7 things
answer
1. animals 2. equipment 3 soil 4. in the crop seed itself 5. weeds 6. nematodes 7. insects
question
how can animals put pest in a crop?
answer
they can transport weeds, nematodes, pathogens, insects and mites on their bodies
question
how can equipment put pests in a crop field?
answer
on the tires or tools, equipment needs to be cleaned before moved to a new place, all surfaces with plant or soil debris
question
Do farmers generally have a good practice of cleaning their equipment or not?
answer
no
question
how can soil transport pests?
answer
soil can contain lots of insect eggs, pathogens, fungi and weed seeds
question
how can crop seeds transmit pests?
answer
infected transplants, infected seed, infected propagule material.
question
can viruses ever be seed borne?
answer
yes
question
how do you ensure that seeds or propagule material is not infected
answer
get certified disease free material
question
is grain and grass crop seed infected with weed seeds?
answer
yes
question
What kind of planting materials are nematodes expecially a problem for?
answer
nematodes are particularly problematic with corms, bulbs and tubers
question
How much of a problem is contamination of seed by insects?
answer
less of a problem, can be traeted by treating seeds with insecticides or fumigants
question
How about insects in cuttings or roots used in vegetative propagation?
answer
Insects are more of a problem in vegetative propagation, for example lepidopterous borer larvae in sugar cane pieces
question
What is a limitation of certified seed?
answer
it is more expensive
question
What is the role of sanitation in agriculture?
answer
removing crop and other plant debris that may be harboring pests, decreasing likelihood of pest carryover from season to season
question
how does sanitation conflict with no-till farming?
answer
no-till leaves a ground cover, but this can create shelter for pests
question
Does sanitation have any application to weed management?
answer
no
question
example of overwintering pathogens
answer
apple scab on the dead leaves overwintering around an apple tree
question
what is the key IPM tactic for apple scab fungus on the leaves?
answer
till the leaves into the ground or add nitrogen fertilizer to speed leaf decomposition to decrease apple scab inoculum
question
where does brown rot disease of peaches overwinter?
answer
on infected fruit mummies on the ground
question
What is done with palms infected with red ring of coconut?
answer
they are cut down and burned to ensure that weevil vectors do not emerge from the diseased bole and infect new palms
question
What non-insect pest animals are take shelter under debris?
answer
mollusks snails and slugs
question
How is the navel orange worm pest controlled in almonds?
answer
the mummy or sticktight nuts must be removed from trees and from the ground because they contain the pupae of the navel orange worm
question
What is the main control tactic for cotton insect pests?
answer
destruction of the stubble by cultivation or plowing
question
how are overwintering corn borers killed?
answer
by shredding the corn stalks
question
how are overwintering codling moths killed on pear trees
answer
left over fruit is collected and destroyed.
question
What is the most important factor for controlling pest mammals such as squirrels, gophers, and field mice?
answer
removing vegetative cover
question
what are disadvantages to sanitation
answer
conflicts wtih no-till, that is the only disadvantage
question
what are host free periods?
answer
times where the host crop or alternative crop is not planted so there is no host for the pest
question
where are host free periods not possible?
answer
where the climate keeps host plants or alternative host plants growing all the time because overlapping crops permits the pest to move to each succeeding crop
question
which pests or pathogens is the host free period most important for?
answer
host free most important for controlling fastidious pathogens vectored by arthropods, including phytoplasmas, some bacteria and all viruses
question
how long is needed for host free periods to stop viruses?
answer
a few weeks
question
what is the host free month for lettuce mosaic virus in Salinas valley?
answer
December
question
What does the timescale for host free periods for nematode control depend on?
answer
the death rate of nematodes without a host, usually several years rather than a few weeks as for viruses.
question
What kind of nematodes are able to live for 6 to 10 years and why?
answer
cyst-nematodes, as eggs in cysts for 10 years or more
question
what can long host free periods select for in nematodes?
answer
nematode races taht are longer lived and can survive long rotations
question
what is the cotton free period in the Central Valley in California?
answer
January to March
question
What an obligate alternative host?
answer
a second host that is needed for a pathogen to survive, such as the cereal rust fungus
question
Is "host free periods" relevatn to weed management?
answer
no, but weeds can provide alternative hosts to pathogens or insects
question
What is a major problem in host free periods for nematodess
answer
controlling alternative hosts in neighboring areas
question
why is the control of alternative hosts a double edged sword in relation to arthropod management?
answer
because those alternative hosts may also be hosting beneficial insects
question
What is area wide insect management?
answer
controlling insects on vegetation external to crop fields
question
What is the obligate alternative host for lettuce root aphids?
answer
poplar trees
question
how do alternative hosts relate to vertebrate animals?
answer
alternative hosts can serve as food for ground squirrels and meadow mice Removal of noncrop host vegetation for reducing populatiosn
question
what is the major limitation of alternative host removal?
answer
depends on implementation at the regional level
question
How does rotation work as a cultural control?
answer
it changes the associated pest complex
question
What can make rotation to non-host crops ineffective?
answer
if alternative host weeds are permitted to grow
question
How can rotation help control weeds?
answer
an herbicide can be used in a rotation crop that could not be used in the previous crop
question
Which two root parasitic weeds are controlled by rotation to non-host crops?
answer
root parasitic weeds in the genera striga and orobanche
question
What kind of pest is rotation the standard recommendation for?
answer
nematodes to manage sugar beet cyst nematode
question
how often can sugar beets be planted on soil infested with sugar beet cyst nematodes
answer
not more often than every three or four years
question
What can negate the effects of crop rotation for nematode control?
answer
weeds in the crops, because some nematodes have wide host ranges Pigweed in corn can maintain root-knot nematodes even though corn is not a host
question
how is rotation for insect pests?
answer
rotation works for insect pests with a non-mobile soil dwelling stage in their life cycle
question
How is rotation used with corn and soybeans for the corn root worm
answer
2 year rotation to soybeans almost eliminates the corn rootworm
question
How did the western corn rootworm adapt to rotation?
answer
Western corn rootworm evolved strains that spend 2 years diapausing eggs in soil and other strains have adapted to ovipositing in soybean fields.
question
What can an incorrect choice of crop sequence result in?
answer
an elevated insect problem, such as wireworms in potatoes following red clover or sweet clover
question
what is the major limitation of rotation?
answer
the best crop for pest management reasons may not be the the best crop economically
question
why do lots of midwest farmers not us a corn-soybean rotatioN?
answer
because the risk of corn rootworm is outweighed by the price of corn -- the risk is worth it
question
what is an advantage of fallow rotation?
answer
pest control tactics can be used that are not feasible when crops are present, such as tillage and desiccation
question
how does fallow reduce weed seedbanks?
answer
light tillage to kill each flush of seedlings or deplete underground root reserves of perennials
question
what is the limitation of fallowing?
answer
no money is made
question
How are planting dates used as a cultural control?
answer
The pest can be avoided or the pest impact can be reduced
question
What factors in usnig planting dates as a cultural control 3 factors?
answer
1. Climatic region 2. type of crop 3. Nature of the pest
question
how cn planting dates reduce pathogen problems?
answer
1. avoid seasons where pathogen vector activity peaks 2./ maximize crop and growth rates in relation to pathogen activity 3. avoid seasons when pathogen inoculum is at its greatest
question
How can planting dates help fight weed infestations?
answer
it is possible to time planting of a crop that favors the crop growth and not the weed growth. Planting cereals in the spring can minimize impact of downy brome, wild oats and other weed grasses taht grew during the winter because htye can be killed before the crop is planted
question
Why is alfalfa planted in late winter in Central Valley California?
answer
to escape summer and winter weeds
question
What does poikilothermic mean?
answer
A poikilotherm is an organism whose internal temperature varies considerably
question
how can changing planting dates reduce nematode problems
answer
nematodes less active in cool soil, plant in cool soil
question
how is planting date used for sugar beet against sugar beet cyst nematode?
answer
Sugar beets planted early spring allows for beets to establish but discourages nematode attack until after beets have grown somewhat
question
How were carrots protected from root-knot nematode in California with planting dates?
answer
Carrots were planted in the fall in CA to reduce galling and forking damage by root-knot nematodes
question
What is phenology?
answer
Phenology is the study of periodic plant and animal life cycle events and how these are influenced by seasonal and interannual variations in climate.
question
How are plants and pest insects related with phenology?
answer
many host specific insects require perfect synchronization of their life cycles with the life cycles of the host plant.
question
How are sugar beet plantings timed in the Central Valley California?
answer
sugar beets are planted only after the annual flights of the green peach aphid to avoid transmission of yellows viruses
question
what factors are conflicting in planting dates for sugar beets?
answer
yellows virus date versus nematode date
question
how is timing used to foil the boll weevil for cotton? 3 things
answer
1. Cotton planted early 2. Short season variety 3. Defoliated early before boll weevil populations reach damaging levels
question
When is late planting a good idea?
answer
to let overwintering insects starve to death
question
What are the limitations of manipulating the planting date?
answer
1. missing the best market price 2. weather conditions may prevent early planting 3. pest evolved with crop; conditions unfavorable for pest are often unfavorable for the crop
question
What does crop density help with?
answer
weeds
question
How can higher densities help with pathogen problems? How can they hurt?
answer
Seedling diseases can be offset with higher seeding rate. however, higher density can also lead to more spread of diseases
question
What kind of crops is density for weed control most significant?
answer
broadcast crops such as cereal and alfalfa
question
How does reducing row spacing and closing the canopy sooner impact arthropod management?
answer
Predators prefer to hunt pest insects under a closed canopy. Also, pest insects such as corn earworm moths often prefer to oviposit in open canopy fields
question
how can density help with vertebrates?
answer
seedling densities can offset damage from birds
question
Limitations of density solution
answer
1 Higher cost of seed 2. crop density that is above optimum for root crops such as carrots and sugar beets can reduce marketable yields
question
what is the advantage of priming or pregerminating the crop relative to pest insects and pathogens?
answer
reduces the time the crop is exposed to pests associated with stand establishment
question
what is the advantage of priming or pregerminating the crop relative to weeds?
answer
rapid germination and emergence allows a crop to establish faster than weeds
question
what is a limitation of priming seed?
answer
seed becomes more difficult to handle, if the radicle has emerged it must not be broken off it is expensive compared to conventional seeding
question
what is the advantage of deep planting? disadvantages?
answer
birds can't get the seed. however, seedlings are weaker and emerge slower which is a problem for other reasons
question
Advantages of transplanting?
answer
1. more uniform crop stand 2. reduced seed cost 3. earlier harvest for market and avoiding late season pests
question
Transplants in regard to diseases of germinating seeds?
answer
transplatns are beyond diseases of germinating seed such as damping off.
question
disadvantage of transplanting?
answer
can damage the roots, opening up entries for pathogens mechanical spread of virus such as tobacco mosaic virus
question
advantages of transplanting over nematodes
answer
delays nematode infection, larger plants better able to sustain nematode attack
question
advantage of transplanting over weeds
answer
1 transplanted crop is much larger than germinating weeds and thus has a competitive advantage. 2 also allow for piling soil into crop row for weed management 3. transplanted crops can be grown without use of herbicides 4. trifluralin herbicide can be used on transplanted tomatoes but not on direct seeded tomatoes
question
transplantation regards mollusks/arthropods
answer
established root systems and top growth reduces damage from cutworms and slugs
question
limitations of transplanting
answer
labor intensive/need greenhouse/not for root crops
question
what two aspects of soil can be changed for cultural control?
answer
moisture and pH
question
how can moisture of soil affect pest management?
answer
drown the pests or dry them out, such as with rice cultivation
question
how can altering pH of soil help?
answer
alter ability of microorganisms to survive and attack the host
question
Pathogens -- soil moisture
answer
wet soil can increase pathogen attack, many soil borne pathogens have a motile stage in their lifecycle such as the zoospores of Phytophthora needs free water to swim to the host
question
soil pH -- pathogens
answer
changing the soil pH can change the suitability for of soil environment for many microbial organisms clubroot pathogen only infects if soil is below pH of 7.0 (acidic)
question
how is potato scab streptomyces affected by soil pH?
answer
acidifying the soil to pH of 5.0 controls potato scab
question
soil moisture - weeds
answer
some weeds such as canary grass and wild oats do better in wet soil
question
can soil compaction favor weeds? how
answer
yes, knotweed and some spurges can grow well in compacted soil while crops do not thrive in it
question
moisture -- nematodes
answer
nematodes can be drowned
question
how does pH affect sorghum?
answer
acidic soil extends the whorl stage of sorghum, which benefits the armyworm which eats the whorl stage of sorghum
question
what kind of fertilization is best for pest managmeent
answer
optimally fertilized crops resist pests the best
question
overfertilization and pathogens and weeds
answer
overfertilized crops are very lush -- increase pathogens and weeds



