IB Biology Topic 2 : Molecular Biology
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
How many bonds can carbon make
answer
carbon can make four covalent bonds
question
Four most common compounds
answer
- carbon -hydrogen -nitrogen -oxygen
question
what is life based on
answer
carbon compounds
question
metabolism
answer
metabolism- chemical processes in the body, synthesis & breakdown of substances in living organisms. anabolism- the synthesis of complex molecules (simple to complex) (condensation reaction) catabolism- the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler macromolecules (hydrolysis)
question
Importance of the artificial creation of urea
answer
vitalism - states that organic compounds can come from living things, so the creation on urea in a lab disproved this
question
international problems with water
answer
Water is not readily available to all countries. And even within countries there are distribution problems
question
What does polar and non polar mean?
answer
polar means that there is a positive and negative charge and its an equal sharing of electrons, while non-polar means that there is an unequal sharing
question
what kind bonds do water molecules make with each other
answer
hydrogen bonds
question
Hydrogen Bonds
answer
Hydrogen bonds are the weakest because they are positive
question
Covalent Bonds
answer
covalent bonds are strongest because they share a pair of electrons.
question
Properties of Water
answer
Water molecules are polar (forms hydrogen bonds), because of the pull of electrons towards oxygen. Cohesion - when water sticks to itself. Allows surface tension to occur. Adhesion- when water sticks to to other substances. The ability for water to stick to the xylem of plants allows it to be transported throughout the plant. Thermal properties- water has the highest heat capacity of all liquids and so it takes a lot of energy before it will change temperature. It also has a high boiling point because it takes a lot of energy to break hydrogen bonds. This is helpful in sweating b/c the energy provided by the body causes one to sweat - hence the cooling affect.
question
Hydrophobic
answer
- not attracted to water - insoluble in water
question
Hydrophilic
answer
- attracted to water - dissolves well in water - form molecular bonds with water molecules
question
What are the four main macromolecules?
answer
-lipids -carbohydrates -nucleic acids -proteins
question
Carbohydrates
answer
- Sugars - Made of of C, H, and O - main functions are quick energy, storage, raw/structural material - Monosaccharides, disaccharides, polyssacharides
question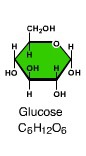
Monosaccharides

answer
- sugars that consist of a single sub-unit (monomer) - only contains carbon, hydrogen & oxygen with a ration of 1:2:1 eg. glucose (C6H12O6) and fructose
question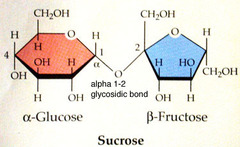
Disaccharides

answer
- a pairs of monosaccharides linked together by condensation eg. maltose ( glucose + glucose - used for food when plants break down their starch stores), lactose ( glucose + galactose - nursing and milk), sucrose ( fructose + glucose - table sugar)
question
Polysaccharides
answer
- complex carbohydrates - chain of many monosaccharides - extremely soluble so a good source of quick energy eg. starch, glycogen, chitin, and cellulose
question
How are sugars classified?
answer
the number of carbons
question
Lipids
answer
- carbon compounds - non polar hydrophobic organic molecules Types of lipids: - triglycerides (eg. fats & oils) - phosopholipids - steroids (eg. testosterone & estrogen)
question
Function of lipids
answer
- twice as much energy as carbohydrates but a slower release - insulation - framework for cell membrane
question
Health risks for trans/saturated fat
answer
- Trans fats increase the "bad" cholesterol which raises the risks of coronary heat disease. - Diets that are high in trans-fat unnecessarily increase the chance that you will consume more than your body needs, because they are energy dense.
question
BMI Equation
answer
bmi = weight of body / (height in meters ^2)
question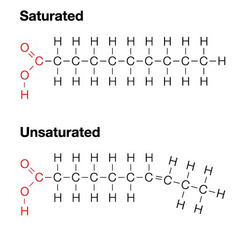
Fatty Acids

answer
Types: - Saturated: All atoms in the chain are connected by single bonds - Unsaturated: chain contains one or more double bonds - Monounsaturated: only one double bond - Polyunsaturated: two or more double bonds - Cis-unsaturated: H bonded to C on the same side of the double bond - Trans-unsaturated: H bonded to C on different sides of the double bond.
question
Polypeptides
answer
- chain of amino acids - the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is coded for by a gene. The DNA sequence determines the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide. - a protein consists of either a single or multiple polypeptides linked together.
question
Denaturation
answer
proteins have a delicate structure that can be damaged by substances or conditions: this is called denaturation - heat causes denaturation - change in pH causes denaturation
question
Function of proteins
answer
wide range of functions Eg: - Rubisco is an enzyme that catalyses the photosynthesis reaction - Insulin is a hormone that lowers the body's blood glucose concentration
question
Enzymes
answer
- biological catalysts - they speed up chemical reactions and metabolism - a reactant is an enzyme catalysed reaction called a substrate -substrates bind to the active site of the enzyme and the products are released.
question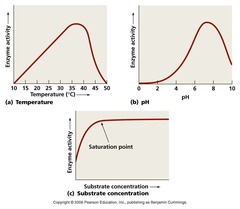
Factors affecting enzymes

answer
1) Temperature - temperature increases enzyme activity - when temperatures are high, enzymes are denatured and stop working. 2) pH - enzyme activity decreases pH decreases from optimum. - above a certain pH, the a;lalinity denatures the enzyme 3) Substrate concentration - at low substrate concentrations enzyme activity increases steeply - at high substrate concentrations, most of the active sites are occupied.
question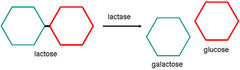
Production of lactose free milk (for lactose intolerant people)

answer
- lactose is the sugar in milk - it can be hydrolysed into glucose and galactose by the enzyme lactase
question
DNA

answer
- nucleic acid - consist of nucleotides - nucleotide: sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base (bases: adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine)
question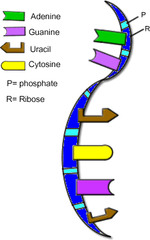
RNA

answer
- single stranded (DNA is double stranded) - thymine is replaced by uracil
question
Proteome
answer
the combination of all proteins in an organism, everyone's is unique
question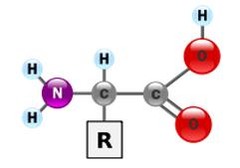
Amino acids

answer
have a central carbon atom with 4 different atoms linked to it: - R group (R) - amine group (N - Hx2) - carboxyl group (C=o, C-OH) - hydrogen atom (H)
question
Peptide bonds
answer
bonds that link amino acids to form polypeptides. you take way the OH and one of te H's from the H2 of the amine group
question
primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary
answer
1. order of amino acids 2. reactions with amino acids near each other 3. reacts with farther apart amino acids, the reaction of the R groups which them determines the quaternary structure 4. arrangement of multiple proteins
question
The importance of the R group
answer
This group determines the function of the protein and thus instructs how the it will interact with other amino acids ( which instructs how the amino acid chains are folded)
question
Activation energy
answer
the energy it takes to begin a reaction
question
Active site
answer
the place where the substrate binds to the enzyme; where the reaction occurs



