Gastritis and Gastric Cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Most common cause of chronic gastritis? What sort of therapy is making this increasingly less common?
answer
H. Pylori Triple therapy for H. pylori
question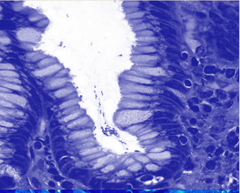
Biopsy in H. Pylori?

answer
Gram negative slender curved rods Hyperemic mucosa Lymphocytes Plasma cells Warthrin Silver stain
question
Simpler way to confirm H. pylori presence or eradication?
answer
Urease breath test Antigen in stool
question
Three risks associated with H. Pylori chronic gastritis? Which one is common to Autoimmune gastritis?
answer
1. Ulceration 2. MALT lymphoma - Post germinal centre B cells in marginal zone 3. Intestinal metaplasia (common to autoimmune gastritis, risk for gastric adenocarcinoma).
question
WHat is triple therapy?
answer
Clarithromycin Amoxycillin omeprazole to eradicate H pylori
question
Autoimmune gastritis occurs in the what and what of the stomach?
answer
Fundus and body
question
H. Pylori gastritis occurs in the what of the stomach?
answer
antrum.
question
What is the most common cause of duodenal ulcer? Second most common cause?
answer
H. pylori Zollinger Ellinson-Syndrome / gastrinoma
question
Why does pain caused by duodenal ulcers improve with meals?
answer
Because the duodenum begins to make protective substances in preparation for a meal that neutralize incoming stomach acid.
question
What type of duodenal gland becomes hypertrophied in a duodenal ulcer? Why?
answer
Brunner's glands Because they usually produce mucous and alkalinizing substances.
question
Complications of posterior duodenal ulcer rupture (2)?
answer
Acute pancreatitis Gastroduodenal artery rupture.
question
Where are Foveolar cells located? WHat do they do?
answer
They are located on the surface layer of teh gastric mucosa. They produce neutralizing mucous.
question
Causes of acute gastritis?
answer
Loss of prostaglandins due to NSAID use ISchemia (Burns, shock) Increased intracranial pressure Increased acid production
question
How does increased ICP cause acute gastritis?
answer
Causes vagal stimulation, release of acetylcholine, which stimulates acid release from the parietal cell.
question
What are the three substances that have receptors for inducing acid production from the parietal cell?
answer
Gastrin Histamine Acetylcholine
question
What type of hypersensitivity is autoimmune gastritis, mediated by what type of cell?
answer
Type 4, by T cells
question
What type of antibodies are created as a result of autoimmune destruction of parietal cells?
answer
Antibodies against IF Antibodies against Parietal cells.
question
What are three consequences of fundal of body chronic gastritis?
answer
1. Chronic inflammation may lead to intestinal metaplasia, predisposing to gastric carcinoma 2. Achlorhydria causes antral G cell hyperplasia, increased gastrin 3. Loss of IF causes Pernicious anemia.
question
Difference in pain features between duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer?
answer
Duodenal ulcer - relieved by eating, gastric ulcer worsened by eating.
question
Where are most gastric ulcers located? What structure is nearby here with what risk?
answer
Less curvature of the antrum. The left gastric artery.
question
Causes of gastric ulcer (3).
answer
1. H pylori 2. NSAIDs 3. Gastric carcinoma.
question
Risk factors for gastric adenocarcinoma. WHat cell type? aka? Where does it occur?
answer
1. Intestinal metaplasia 2. SMoked foods 3. Blood type A. Columnar epthelial cells. Intestinal type. Lesser curvature the stomach.
question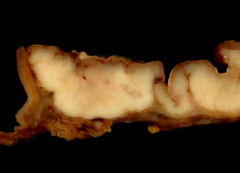
Diffuse cell gastric cancer. Pathological features on gross section?

answer
Thickening of the stomach wall, rhinitis plastica, desmoplasia.
question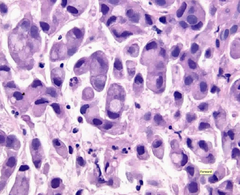
Pathological features of X cancer on histology? Name of cell? Name of tissue change? What happens to the nuclei?

answer
Signet ring cells diffusely infiltrate gastric wall. Nucleus is pushed off to edge by mucin produced by tumor cells.
question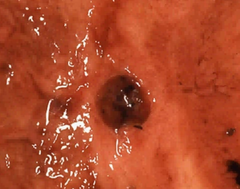
Features of benign gastric ulcers?

answer
SMALL. Punched out. Margins not raised.
question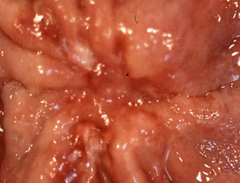
Features of cancerous gastric ulcers?

answer
Large, irregular, heaped up margins, NOT punched out.
question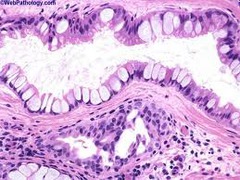
Uh oh, mucous containing goblet cells in the stomach? Causes?

answer
Intestinal metaplasia H. pylori, autoimmune gastritis.
question
Presenting signs of gastric carcinoma (4)? When does it present? Special features and why?
answer
Weight loss, early satiety, anemia, abdominal pain. Late. Acanthosis nigricans. Don't know. Lesser-Trelat sign. Many actinic keratoses seen on body.
question
What is characteristic lymph node site for gastric cancer? Which side?
answer
Supraclavicular node. Left. Virchow's node.
question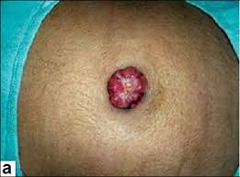
Classic site of met for intestinal type gastric cancer? NAme? Which type of gastric cancer does this again please?

answer
Sister Mary Joseph nodule. Periumbilical region. The intestinal type, aka adenocarcinoma.
question
Classic site of met for diffuse type of cancer? Which side? NAme? So which type of cell would be in this type of tumor?
answer
Ovaries. bilateral. sneaky! Krukenberg tumor. Signet ring cell.
question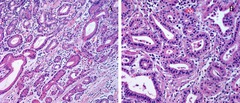
Cellular features of gastric intestinal type adenocarcinoma? What factors determine survival rate (2).

answer
Well formed columnar or cuboidal cells in glands. 1) Degree of invasion through the vessel wall, 2) regional lymph node involvement.



