Financial Accounting – CH 1 & 2 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Four Principal Activities of Business Firms:
answer
1.Establishing goals and strategies 2.Obtaining financing 3.Making investments 4.Conducting operations
question
What are the 2 sources Financing comes from?
answer
1. Owners 2. Creditors
question
Investments are made in the following:
answer
1. Land, buildings, equipment 2. Patents, licenses, contractual rights 3. Stock and bonds of other organizations 4. Inventories 5. Accounts Receivable
question
What are the 4 areas for conducting operations?
answer
1. Purchasing 2. Marketing 3. Production 4. Administration
question
What are the 4 commonly used conventions in financial statements?
answer
1. The accounting period 2. The number of reporting periods 3. The monetary amounts 4. The terminology and level of detail in the financial statements
question
Common Financial Reporting Conventions, Accounting Period
answer
The length of time covered by the financial statements. (The most common interval for external reporting is the fiscal year).
question
Common Financial Reporting Conventions, Number of reporting periods
answer
The number of reporting periods included in a given financial statement presentation, Both U.S. GAAP and IFRS require firms to include results for multiple reporting periods in each report.
question
Common Financial Reporting Conventions, Monetary amounts
answer
This includes measuring units, like thousands, millions, or billions, and the currency, such as dollars ($), euros (€), or Swedish kronor (SEK)
question
Common Financial Reporting Conventions, Terminology and level of detail in the financial statements
answer
U.S. GAAP and IFRS contain broad guidance on what the financial statements must contain, but neither system completely specifies the level of detail or the names of accounts. Therefore, some variation occurs.
question
Characteristics of a Balance Sheet
answer
A Balance Sheet: 1. is also known as a statement of financial position; 2. provides information at a point in time; 3. lists the firm's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity and provides totals and subtotals; and 4. can be represented as the Basic Accounting Equation. Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity
question
Accounting Equation Components
answer
1. Assets 2. Liabilities 3. Share Holder's Equity
question
Assets
answer
Assets are economic resources with the potential to provide future economic benefits to a firm. Examples: Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventories, Buildings, Equipment, intangible assets (like Patents)
question
Liabilities
answer
Liabilities are creditors' claims for funds, usually because they have provided funds, or goods and services, to the firm. Examples: Accounts Payable, Unearned Income, Notes Payable, Buildings, Accrued Salaries
question
Shareholders' Equity
answer
Shareholders' Equity shows the amounts of funds owners have provided and, in parallel, their claims on the assets of a firm. Examples: Common Stock, Contributed Capital, Retained Earnings
question
What are the separate sections on a Balance Sheet (Balance sheet classification)
answer
1. Current assets represent assets that a firm expects to turn into cash, or sell, or consume within approximately one year from the date of the balance sheet (i.e., accounts receivable and inventory). 2. Current liabilities represent obligations a firm expects to pay within one year (i.e., accounts payable and salaries payable). 3. Non-current assets are typically held and used for several years (i.e., land, buildings, equipment, patents, long-term security investments). 4. Noncurrent liabilities and shareholders' equity are sources of funds where the supplier of funds does not expect to receive them all back within the next year.
question
Income Statement
answer
1. Sometimes called the statement of profit and loss by firms applying IFRS 2. Provides information on profitability 3. May use the terms net income, earnings, and profit interchangeably 4. Reports amounts for a period of time 5. Typically one year 6. Is represented by the Basic Income Equation: Net Income = Revenues - Expenses
question
Revenues
answer
(also known as sales, sales revenue, or turnover, a term used by some firms reporting under IFRS) measure the inflows of assets (or reductions in liabilities) from selling goods and providing services to customers.
question
Expenses
answer
measure the outflow of assets (or increases in liabilities) used in generating revenues.
question
Relationship between the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement
answer
1. The income statement links the balance sheet at the beginning of the period with the balance sheet at the end of the period. 2. Retained Earnings is increased by net income and decreased by dividends.
question
Statement of Cash Flows
answer
The statement of cash flows (also called the cash flow statement) reports information about cash generated from or used by: 1. operating, 2. investing, and 3. financing activities during specified time periods. The statement of cash flows shows where the firm obtains or generates cash and where it spends or uses cash.
question
Classification of Cash Flows
answer
1. Operations: cash from customers less cash paid in carrying out the firm's operating activities 2. Investing: cash paid to acquire noncurrent assets less amounts from any sale of noncurrent assets 3. Financing: cash from issues of long-term debt or new capital less dividends
question
The Relationship of the Statement of Cash Flows to the Balance Sheet and Income Statement
answer
-The statement of cash flows explains the change in cash between the beginning and the end of the period, and separately displays the changes in cash from operating, investing, and financing activities. -In addition to sources and uses of cash, the statement of cash flows shows the relationship between net income and cash flow from operations.
question
Statement of Shareholders' Equity
answer
This statement displays components of shareholders' equity, including common shares and retained earnings, and changes in those components.
question
Other Items in Annual Reports
answer
Financial reports provide additional explanatory material in the schedules and notes to the financial statements.
question
Who are the 4 main groups of people involved with the Financial Reporting Process
answer
1. Managers and governing boards of reporting entities. 2. Accounting standard setters and regulatory bodies. 3. Independent external auditors. 4. Users of financial statements.
question
What is the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)?
answer
An agency of the federal government, that has the legal authority to set acceptable accounting standards and enforce securities laws.
question
What is the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)?
answer
a private-sector body comprising five voting members, to whom the SEC has delegated most tasks of U.S. financial accounting standard-setting.
question
GAAP
answer
1. Common terminology includes the pronouncements of the FASB (and its predecessors) in the compilation of accounting rules, procedures, and practices known as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). 2. Recently, the FASB launched its codification project which organizes all of U.S GAAP by topic (for example, revenues), eliminates duplications, and corrects inconsistencies.
question
FASB board members make standard-setting decisions guided by a conceptual framework that addresses:
answer
1. Objectives of financial reporting. 2. Qualitative characteristics of accounting information including the relevance, reliability, and comparability of data. 3. Elements of the financial statements. 4. Recognition and measurement issues.
question
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
answer
Concerns over the quality of financial reporting have led, and continue to lead, to government initiatives in the United States. Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 established the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB), which is responsible for monitoring the quality of audits of SEC registrants.
question
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
answer
-The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) is an independent accounting standard-setting entity with 14 voting members from a number of countries. Standards set by the IASB are International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). -The FASB and IASB Boards are working toward converging their standards, based on an agreement reached in 2002 and updated since then.
question
Auditor's Opinion
answer
Firms whose common stock is publicly traded are required to get an opinion by an independent auditor who: 1.Assesses the effectiveness of the firm's internal control system for measuring and reporting business transactions 2.Assesses whether the financial statements and notes present fairly a firm's financial position, results of operations, and cash flows in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles
question
Basic Accounting Conventions and Concepts
answer
1. Materiality is the qualitative concept that financial reports need not include items that are so small as to be meaningless to users of the reports. 2. The accounting period convention refers to the uniform length of accounting reporting periods. 3. Interim reports are often prepared for periods shorter than a year. However, preparing interim reports does not eliminate the need to prepare an annual report.
question
Cash vs. Accrual Accounting
answer
Cash basis A firm measures performance from selling goods and providing services as it receives cash from customers and makes cash expenditures to providers of goods and services. Accrual basis A firm recognizes revenue when it sells goods or renders services and recognizes expenses in the period when the firm recognizes the revenues that the costs helped produce.
question
What Is an Account? How Do You Name Accounts?
answer
-An account represents an amount on a line of a balance sheet or income statement (i.e., cash, accounts receivable, etc.). -There is not a master list to define these accounts since they are customized to fit each specific business's needs. -Accountants typically follow a conventional naming system for accounts, which increases communication.
question
Current assets and current liabilities (Balance Sheet Classifications)
answer
Receipt or payment of assets that the firm expects will occur within one year or one operating cycle.
question
Noncurrent assets and noncurrent liabilities (Balance Sheet Classifications)
answer
Firm expects to collect or pay these more than one year after the balance sheet date.
question
Duality Effects of the Balance Sheet Equation (Assets = Liabilites + Shareholders' Equity)
answer
Any single event or transaction will have one of the following four effects or some combination of these effects: 1.INCREASE an asset and INCREASE either a liability or shareholders' equity. 2.DECREASE an asset and DECREASE either a liability or shareholders' equity. 3.INCREASE one asset and DECREASE another asset. 4.INCREASE one liability or shareholders' equity and DECREASE another liability or shareholders' equity.
question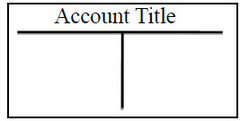
T-Accounts

answer
A T-account is a device or convention for organizing and accumulating the accounting entries of transactions that affect an individual account, such as Cash, Accounts Receivable, Bonds Payable, or Additional Paid-in Capital.
question
Journal Entries

answer
While T-accounts are useful to help analyze how individual transactions flow and accumulate within various accounts, journal entries formalize the reasoning that supports the transaction. The attached standardized format indicates the accounts and amounts, with debits on the first line and credits (indented) on the second line:
question
Revenue or Sales: (Common Income Statement Terms)
answer
Assets received in exchange for goods sold and services rendered.
question
Cost of Goods Sold: (Common Income Statement Terms)
answer
The cost of products sold.
question
Selling, General, and Administrative (SG&A): (Common Income Statement Terms)
answer
Costs incurred to sell products/services as well as costs of administration.
question
Research and Development (R&D) Expense: (Common Income Statement Terms)
answer
Costs incurred to create/develop new products, processes, and services.
question
Interest Income: (Common Income Statement Terms)
answer
Income earned on amounts lent to others or from investments in interest-yielding securities.
question
Important Account Differences
answer
1. Balance sheet accounts are permanent accounts in the sense that they remain open, with nonzero balances, at the end of the reporting period. 2. In contrast, income statement accounts are temporary accounts in the sense that they start a period with a zero balance, accumulate information during the reporting period, and have a zero balance at the end of the reporting period.
question
The Financial Statement Relationships can be summarized as:

answer
-After preparing the end-of-period income statement, the accountant transfers the balance in each temporary revenue and expense account to the Retained Earnings account. -This procedure is called closing the revenue and expense accounts. After transferring to Retained Earnings, each revenue and expense account is ready to begin the next period with a zero balance.
question
Posting
answer
1. After each transaction is recognized by a journal entry, the information is transferred in the accounting system via an activity known as posting. 2. The balance sheet ledger accounts (or permanent accounts) where these are posted begin each period with a balance equal to the ending balance of the previous period. 3.The income statement ledger accounts (or temporary accounts) have zero beginning balances.
question
Adjusting Entries
answer
There are some journal entries that are not triggered by a transaction or exchange. -Rather, journal entries known as adjusting entries, result from the passage of time at the end of an accounting period or are used to correct errors (more commonly known as correcting entries).
question
Four Basic Types of Adjusting Entries
answer
1.Unearned Revenues 2.Accrued Revenues 3.Prepaid Expenses 4.Accrued Expenses
question
Closing Process
answer
1. After adjusting and correcting entries are made, the income statement can be prepared. 2. Once completed, it is time to transfer the balance in each temporary revenue and expense account to the Retained Earnings account. This is known as the closing process. 3. Each revenue account is reduced to zero by debiting it and each expense account is reduced to zero by crediting it. 4. The offset account—Retained Earnings—is credited for the amount of total revenues and debited for the amount of total expenses. 5. Thus, the balance of ending Retained Earnings for a period shows the difference between total revenues and total expenses.
question
Preparation of the Balance Sheet
answer
1. After the closing process is completed, the accounts with nonzero balances are all balance sheet accounts. 2. We can use these accounts to prepare the balance sheet as at the end of the period. 3. The Retained Earnings account will appear with all other balance sheet accounts and now reflects the cumulative effect of transactions affecting that account.
question
Final Step in Preparing Financial Statements: The Cash Flow Statement
answer
1. The statement of cash flows describes the sources and uses of cash during a period and classifies them into operating, investing, and financing activities. 2. It provides a detailed explanation for the change in the balance of the Cash account during that period. 3. Two approaches can be used to prepare this statement: Direct and Indirect



