Exam #2 Chapters 5-11 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Define tissue.
answer
a set of cells with similar appearance and function together in an organ
question
What are the 4 primary tissue classes?
answer
Epithelial, Connective, Nervous, Muscular
question
Describe Epithelial tissue
answer
tissue composed of closely spaced cells that cover organ surfaces, form glands, and protect, secrete and absorb
question
Where can you find epidermis?
answer
Digestive tract, liver, glands
question
Describe Connective tissue
answer
more matrix than cell volume, specialized to support, bind and protect organs
question
What are some organs made of connective tissue?
answer
tendons, ligaments, cartilage, bone, blood
question
Describe Nervous tissue
answer
contains excitable cells specialized for rapid transmission of coded information to other cells
question
Give an example of an organ with nervous tissue
answer
brain, nerves, spinal cord
question
Describe Muscular tissue
answer
tissue composed of elongated, excitable muscle cells, specialized for contraction.
question
What are some of the functions of Epithelial tissue?
answer
Secretion, Protection, absorption, filtration, sensation
question
True or False: There are blood vessels in epithelia
answer
False
question
Does Epithelial Tissue have a high mitosis rate?
answer
Yes
question
What membrane lies between epithelium and the underlying connective tissue
answer
Basement membrane
question
What are the 4 kinds of Simple Epithelia?
answer
Simple Squamous, Simple Cuboidal, simple columnar, pseudostratified
question
Describe Simple Squamous cells
answer
thin and scaly
question
Describe simple cuboidal cells
answer
cube shaped, tight packing, glandular functions,
question
describe simple columnar cells
answer
tall and narrow, consists of goblet cells
question
describe psuedostratified columnar cells
answer
not all cells reach surface, also consists of goblet cells
question
What are the 4 kinds of Stratified epithelia?
answer
Stratified squamous(keritanized & non keritanized), stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar(rare), transitional
question
Exfoliation/Desquamation:
answer
separation from the surface
question
Keratinized/cornified
answer
found in epidermis, covered w/ a layer of compact dead squamous cells filled w/ keratin & packed w/ water repellent glycolipid
question
Non keratinized
answer
no layer of dead cells, moist, slippery, abrasion resistant
question
What does ectoderm develop into?
answer
nervous system & skin glands, epidermis, some blood vessels
question
What does endoderm develop into?
answer
lining of lungs and glands of the gut
question
What tissue lines the trachea?
answer
pseudostratified columnar epithelial
question
Ligament
answer
bone to bone
question
Tendon
answer
muscle to bone
question
Osteocytes
answer
cells that make up bones
question
Chondrocytes
answer
cells in lacunae of cartilage
question
Difference between secretion and excretion:
answer
secreted materials have a physiological function and excretion removes waste from body
question
What does Mesoderm develop into?
answer
dermis of skin, muscle, blood, connective tissue
question
Where does gas exchange occur?
answer
Capillaries
question
Where does filtration occur?
answer
Glomerular capsule
question
Where are some places you can find simple squamous epithelium?
answer
alveoli, blood vessels, serous membrane of organs, glomerular capsule
question
What structure holds cells to basement membrane
answer
desmosomes
question
Endothelial Functions:
answer
hormonal functions, contraction, inflammation and permeability, clot prevention
question
Simple Squamous Epithelium lining all blood vessels consists of what cells
answer
Endothelial cells
question
Simple cuboidal epithelium functions:
answer
protection, secretion and reabsorption
question
This tissue secretes digestive enzymes and helps with nutrient absorption
answer
Simple Columnar Epithelium
question
Function of goblet cells:
answer
make mucus to lubricate passage of materials
question
What tissues have cilia and goblet cells?
answer
Simple Columnar Epithelium, Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
question
Why would cilia be important in the airway?
answer
Push bacteria out of lungs
question
what are some places on the body are covered by Stratified Squamous Epithelium-nonkeratinized
answer
vagina, mouth, anus, esophogus
question
Why would the lower urinary tract and part of umbilical cord consist of transitional epithelium?
answer
Transitional Epithelium allows tissues to stretch better
question
Embryogenesis:
answer
development of tissues and organs
question
Are connective tissues derived from Mesoderm, Ectoderm, or Endoderm?
answer
Mesoderm
question
Name the 10 types of connective tissue.
answer
Dense Regular CT, Dense Irregular CT, Areolar CT, Reticular CT, Adipose, Hyalin Cartilage, Elastic Cartilage, Fibrocartilage, Bone, Blood
question
How is connective tissue spacing different from that of epithelial cells?
answer
cells occupy less space and usually aren't in direct contact w/eachother
question
What tissues are categorized as Dense CT?
answer
Dense Regular CT, Dense Irregular CT
question
What tissues are categorized as Loose CT?
answer
Areolar CT, Reticular CT, Adipose
question
What types of tissues are called fibrous or fibroconnective?
answer
Dense Irregular CT, Dense Regular CT, Areolar CT, Reticular CT, Adipose CT
question
What are the 3 types of cartilage?
answer
Hyalin, Elastic, Fibrocartilage
question
What tissue appears in ligaments and tendons and looks like it's lined in perfect rows.
answer
Dense Regular CT
question
What tissue is arranged in different directions and allows skin to be pulled on from different directions without tearing?
answer
Dense Irregular CT
question
What tissue is found under basement membranes and is rich in collagen?
answer
Areolar CT
question
What organ is Reticular CT found in?
answer
Spleen
question
Where can you find chondrocytes?
answer
Lacunae
question
What tissue connects the ribs to the sternum and can be found on the end of your nose?
answer
Hyalin Cartilage
question
What tissue contains more elastin, less collagen and is found in the ear?
answer
Elastic Cartilage
question
What tissue makes up the discs in the spine and is made of collagen?
answer
Fibrocartilage
question
What tissue is made of osteocytes
answer
bone
question
What CT is fluid?
answer
Blood,erythrocytes, lymphocytes, platelets
question
Erythrocytes:
answer
red blood cells
question
Fibril:
answer
overlapping collagen fibers
question
What tissue is turned to bone as an adult?
answer
Hyalin cartilage
question
Perichondrium surrounds what?
answer
Cartilage
question
What do osteoblasts do?
answer
build bone
question
What do osteoclasts do?
answer
erode bone
question
True or False: Nuclei in dense regular ct are located between fibers
answer
True
question
True or False: smooth muscle is striated
answer
false
question
True or False: You can't grow more muscle cells, but they can grow in size
answer
True
question
What do desmosomes attach together?
answer
cells to cells
question
True or False: Endocrine glands release hormones into blood
answer
true
question
Where and how do exocrine glands release hormones?
answer
Out of body via glands
question
Name some functions of CT
answer
binding of organs, support, physical protection, immune protection, movement, storage, heat production, transport
question
Describe Fibroblasts:
answer
large cells that produce fibers ; ground substance in CT
question
What fibers are created by fibroblasts?
answer
collagen, elastic fibers, reticular fibers
question
Describe collagen:
answer
most abundant protein, tough, flexible, resists stretching, white color, functions out of the cell
question
What is"stronger than steel by weight"?
answer
collagen
question
Describe Elastic fibers:
answer
stretchy, yellow color, found in skin, lungs ; arteries
question
What causes age lines in our skin?
answer
lack of elastic fibers
question
Describe Reticular fibers:
answer
thin collagen fibers coated w/ glycoprotein
question
The spleen and lymph nodes are formed by what fiber?
answer
Reticular fibers
question
Are there any blood vessels in collagen?
answer
No
question
What tissue does this description match: loose organized fibers, abundant blood vessels, seemingly a lot of empty space, mostly collagen fibers, varies in density, contains all CT cells types and all CT fibers?
answer
Areolar CT
question
What tissue does this description match: reticular fibers, fibroblasts, forms lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow?
answer
Reticular CT
question
What tissue does this description match: collagen fibers are closely packed, fibers are parallel to each other, found in tendons, ligaments, fibroblasts and few blood vessels?
answer
Dense Regular CT
question
In which tissue are adipocytes abundant?
answer
Adipose Tissue
question
What tissue does this description match: thick bundles of collagen running in random directions, found in dermis, kidneys spleen, leaves little room for cells and ground substance?
answer
Dense Irregular CT
question
Leukocytes:
answer
white blood cells
question
Do anucleate red blood cells have a nucleus?
answer
No
question
When white blood cells divide too fast you have this disease:
answer
leukemia
question
What do lipoproteins carry?
answer
cholestoral
question
What proteins remove pathogens?
answer
immunoglobins
question
What breaks down clots?
answer
Plasmin
question
What does fibrinogen do?
answer
helps clot
question
Are platelets a cellular component?
answer
no
question
What do these items make up: heparin, salts/minerals, glycosaminoglycan, chondroitin sulfate, heparin, hyaluronic acid of joints?
answer
Ground Substance
question
What jello-like substance is a shock absorber, insulates and fills space around cells?
answer
Ground substance
question
Which type of fat is more abundant?
answer
White(can be called yellow too)
question
Which type of fat can be described as a single, large, globule of triglyceride?
answer
White Fat
question
Which type of fat stores lipid in multiple globules rather than 1 large one?
answer
Brown fat
question
6% of a baby's weight is made up of what?
answer
Brown fat
question
Which fat has an abundance of blood vessels and generates heat?
answer
Brown fat
question
Which fat provides thermal insulation, & cushions and anchors organs?
answer
White fat
question
What do Chondroblasts produce?
answer
Cartilage
question
Which cartilage is made up of collagen, chondroitin sulfate, and a proteoglycan core?
answer
hyalin cartilage
question
What fibrous sheath are all bones wrapped in?
answer
Periosteum
question
Osseous tissue
answer
bone
question
What limits the healing rate of broken bones?
answer
How fast nutrients can get to the cell
question
Which bone has a hollow space filled with red or yellow marrow?
answer
Spongy bone
question
What is the ground substance in blood known as?
answer
Blood plasma
question
What cells are "excitable"?
answer
myocytes & neurons
question
True or false: depolariztion can be used to promote changes in intracellular function?
answer
true
question
Do "excitable cells create a self-propagating wave of depolarization that moves across the plasma membrane?
answer
yes
question
What tissue consists of excitable neurons and non-excitable supportive cells?
answer
Nervous Tissue
question
Name 4 parts of a neuron.
answer
Dendrite, soma, axon, synapse
question
What is the function of a dendrite?
answer
Carries info to the nucleus
question
Where does the nucleus of a neuron sit?
answer
soma
question
Describe the axon of a neuron.
answer
single, long extension from cell body
question
What part of a neuron allows information to move from cell to cell?
answer
Synapse
question
Why do neurons need supportive glial cells?
answer
they quicken reactions, maintain neurons
question
True or false: there are more neurons than glial cells
answer
false
question
What tissue is derived from the primordial ectoderm?
answer
Neural tissue
question
True or false: Neural tissue is composed of two types of cell.
answer
True, neurons and glial cells
question
Define Synaptic Transmission:
answer
mechanism that permits a neuron to send its action potential to a second cell
question
Define Synaptic cleft:
answer
space between the presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic neuron
question
What cell type produces the extracellular protein collagen?
answer
Fibroblast
question
Negative charges and a loose fitting amino acid sequence allow what type of connective tissue fibers to stretch?
answer
Elastin
question
True or False: The ectodermal layer is the embryonic source of blood?
answer
False: mesoderm creates blood
question
True or False: striations in muscle tissue allow for contractions
answer
true
question
Which muscle type has multiple nuclei within a myofiber?
answer
skeletal
question
Which muscle types have striations?
answer
Cardiac & skeletal
question
Which muscle type has intercalated discs?
answer
Cardiac
question
True or False: Cardiac muscle can have 1 or 2 nuclei in each cell?
answer
true
question
Are fibroblasts inbetween collagen fibers in dense regular ct?
answer
yes
question
Which muscle type comes in sheets and has only 1 nuclei per cell?
answer
Smooth muscle
question
What filaments allow muscle to be shortened?
answer
actin and mysoin
question
Which muscle type is voluntary?
answer
skeletal
question
Which muscle types are involuntary?
answer
cardiac, smooth
question
Which muscle types have multiple mitochondria and have a short period of contraction?
answer
Skeletal and cardiac
question
Which muscle type has long contractions and few mitochondria?
answer
Smooth muscle
question
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
answer
Smooth, Skeletal, Cardiac
question
True or false: striations in muscle tissue result from parallel orientation of myosin and actin
answer
true
question
True or false: you become stronger because your body creates more muscle fibers
answer
false
question
True or false: force comes from the number of myofibers recruited.
answer
true
question
What are the 4 main types of cell-cell connection?
answer
tight junction, desmosome, hemidesmosome, gap junction
question
Which cell-cell connection completely encircles an epithelial cell and joins it tightly to it's neighboring cells by transmembrane cell-adhesion proteins?
answer
Tight junctions
question
Which cell-cell junction can be described as a patch that holds cells together, and is found in the epidermis, cervix, and cardiac muscle?
answer
Desmosome
question
What cell-cell connection connects the deepest layer of cells to the basement membrane?
answer
Hemidesmosome
question
What cell-cell connection is found in cardiac and most smooth muscle,connects the cytoplasm of one cell to another and is formed by a connexon?
answer
Tight junction
question
True or false: the pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine glands.
answer
True
question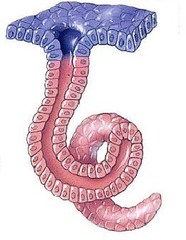
Name an example of a simple coiled tubular exocrine gland

answer
Sweat gland
question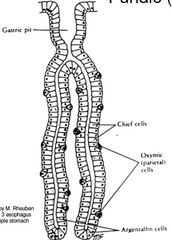
Name an example of a simple branched tubular exocrine gland

answer
Gastric Gland
question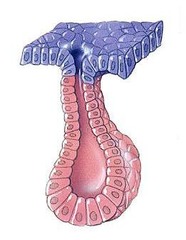
Name an example of a simple acinar exocrine gland

answer
Glands of penile urethra
question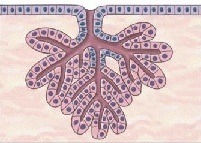
Name an example of a compound tubular exocrine gland

answer
kidney
question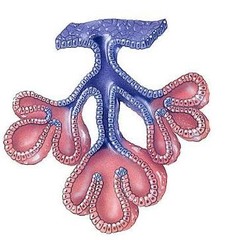
Name an example of a compound acinar exocrine gland

answer
mammary gland
question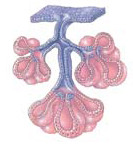
Name an example of a compound tubuloacinar exocrine gland

answer
Pancreas
question
What tissue consists of layers of flat cells that lack keratin?
answer
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Non-keratinized
question
What tissue consists of cells that have cilia and an elongated shape with all cells contact with basement membrane, but irregular nuclei arrangement?
answer
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
question
Name the three primary germ layers.
answer
Ectoderm, Endoderm, Mesoderm
question
Integument consists of what two parts.
answer
Epidermis, dermis
question
What underlying layer supports the epidermis and dermis?
answer
hypodermis
question
What does the hypodermis consist of of?
answer
Adipose CT, subcutaneous fat
question
Another word for skin.
answer
Integument
question
Are blood vessels found in the epidermis?
answer
No
question
What are the layers of the epidermis from deep to superficial?
answer
Stratum basale, Stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum
question
Which layer of the epidermis produces melanocytes?
answer
Stratum basale
question
What does the protein melanin do for us?
answer
protects underlying cells from uv radiation and absorbs light
question
Another word for Pallor
answer
pale
question
another word for blushing
answer
erythema
question
What color does carotene appear as?
answer
orange
question
What color is jaundice associated with?
answer
yellow
question
What is hemangioma?
answer
benign tumor of blood vessel
question
What color is cyanosis associated with?
answer
blue
question
What is Albinism?
answer
Medical condition defined by an absence of melanin pigment
question
Define dermatology.
answer
the study of the skin
question
What is the official term for stretch marks?
answer
Striae
question
Why are the elderly, infants, and anorexics often cold?
answer
Less fat
question
Why do females need more fat than males?
answer
the possibility of pregnancy
question
Name 5 types of glands found in the integument we learned in class.
answer
1. sebaceous, 2. Apocrine, 3. Merocrine(eccrine), 4. Mammary, 5. Ceruminous
question
What type of gland produces the oil in your ear?
answer
Ceruminous
question
What type of gland secretes oils and dead cells into your hair follicle?
answer
Sebaceous
question
What are the two types of sweat glands?
answer
Merocrine(eccrine) ; apocrine
question
Which sweat gland is responsible for scent?
answer
Apocrine
question
Excessive sweating is known as?
answer
Diaphoresis
question
Bromhidrosis
answer
condition of abnormal or offensive body odour, to a large extent determined by apocrine gland secretion
question
Another word for inflamation
answer
rubor
question
Define Vellum hair.
answer
hair that appears on most of your body
question
What are some examples of Vibrissae hair?
answer
big hairs/whiskers/nose hairs
question
What is lanugo hair?
answer
hair that appears on a fetus and a newborn baby's body
question
What is terminal hair?
answer
hair that appears after puberty
question
What are some things the arrector pili muscle does?
answer
moves hair up to insulate skin, goosebumps
question
Eponychium is also known as what?
answer
cuticle
question
What is the hyponychium?
answer
The skin under the free Edge, Attatched to the nail
question
Define hypoxia.
answer
oxygen deficient
question
Name three types of skin cancer.
answer
Basal Cell carcinoma, Squamous cell carcinoma, malignant melanoma
question
Which skin cancer is the most dangerous, but least common?
answer
Malignant Melanoma
question
What does the acronym ABCD stand for when considering skin cancer?
answer
Asymmetry, Border Irregularity, Color, Diameter
question
Which skin cancer arises from the stratum spinosum, and sometimes metastasizes to the lymph nodes?
answer
Squamous cell carcinoma
question
Which skin cancer arises from the stratum basale and rarely metastasize?
answer
Basale Cell Carcinoma
question
What does the A in the ABCD skin cancer acronym stand for?
answer
Asymmetry
question
What does the B in the ABCD skin cancer acronym stand for?
answer
Border Irregularity
question
What does the C in the ABCD skin cancer acronym stand for?
answer
Color
question
What does the D in the ABCD skin cancer acronym stand for?
answer
Diameter
question
What is pus?
answer
Bacteria that the body has killed
question
Define Angiogenesis.
answer
formation of new blood vessels
question
What is the 1st part of a scar?
answer
granulation tissue
question
True or False: The wound is critical if over 10% of the area has 3rd degree burns
answer
True
question
True or False: If the over 25% of the area has second degree wounds it's not critical.
answer
False
question
True or False: If there are any 3rd degree burns on the hands, face or feet a wound is critical.
answer
True
question
True or False: Cells in the Stratum Lucidum and Cornea have no DNA and cannot become cancerous.
answer
True
question
True or False: UV light damages the regions of DNA that make proteins that control cell division rates
answer
true
question
Define Hematopoiesis.
answer
Process of Blood cell formation
question
Where does Hematopoiesis occur?
answer
In the bones
question
What is hydroxyapatite?
answer
Calcium Phosphate ; calcium carbonate
question
What structure consists of Hydroxyapatite and collagen?
answer
bones
question
What are the four classes of bone?
answer
Long, short, irregular, flat
question
Give an example of a long bone.
answer
Ulna, radius, femur
question
Give an example of a short bone.
answer
Talus, capitate
question
Give an example of a flat bone.
answer
Scapula, sternum
question
Give an example of a irregular bone.
answer
Vertebrae, sphenoid bone
question
What bone marrow do flat and spongy bones produce?
answer
Red
question
What are three characteristics of flat and spongy bones?
answer
Red marrow, hematopoiesis, trabeculae
question
What bone characteristic allows compression and supports sheets of bones?
answer
Trabeculae
question
What type of bone contains yellow marrow?
answer
Long and hollow bones
question
Does the location of hematopoiesis change with age?
answer
yes
question
Does bone stress stimulate osteoblast or osteoclast activity?
answer
osteoblast
question
Why do bones have a hollow core?
answer
The hollowness keeps bones light
question
What is a osteocyte?

answer
Bone cell
question
True or false: bone cells can be found in lacunae
answer
true
question
Define lamellae.
answer
Concentric rings around central canal in osteon
question
Define Canaliculi.
answer
Small canals or cracks in the matrix that allow for diffusion on the tissue level of bones. These tiny channels allow osteocytes to communicate with each other.
question
Does flat bone have lamellae?
answer
no
question
What is the epiphyseal plate known for?
answer
Growth plate
question
What is the purpose of a medullary cavity in bones?
answer
Fill with fat and yellow marrow, helps bone flex
question
What part of a long bone allows for articulation?
answer
Epiphyseal ends
question
What is the middle of the long bone called?
answer
Diaphysis
question
Where on the bone are osteoblasts more often found?
answer
lacunae
question
Where on the bone are osteoclasts more often found?
answer
surface of bone
question
Why is it dangerous for the bones to be too hard at birth?
answer
Bones would break during birth
question
What are the three methods of ossification?
answer
Endochondral ossification, intramembranous ossification, ectopic ossification
question
What happens during endochondral ossification?
answer
bone matrix is deposited where the hyalin cartilage was and eventually the growth plate closes
question
What is atherosclerosis?
answer
hardening of arteries because of plaque build up
question
What happens during intramembranous ossification?
answer
bone replacing mesenchyme tissue
question
Which method of ossification is abnormal, unhealthy, may indicate a hormonal imbalance and can lead to infection/irritation?
answer
Ectopic ossification
question
What do you call the place where the epiphysis and diaphysis converge?
answer
Metaphysis
question
Which bones form as a set of trabeculae within fibrous connective tissues?
answer
Flat bones
question
Hypocalcemia
answer
low blood calcium
question
Hypercalcemia
answer
high blood calcium
question
What are some actions of calcium in the body?
answer
Muscle contraction, Nerve cell function, Bone formation
question
Which 3 hormones regulate the levels of calcium in the body?
answer
parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, and Calcitonin
question
How does calcitonin work regulate calcium levels?
answer
Lowers Calcium levels in the body via kidney
question
How does the parathyroid hormone regulate calcium levels?
answer
absorbs it from intestine
question
How does vitamin D regulate calcium levels?
answer
absorbs it from bones
question
Can exocytosis and muscle contraction happen with insufficient Calcium levels in cytosol or plasma?
answer
No
question
What is vitamin D call when it's produced in your body?
answer
calcitriol
question
Name 3 functions of calcitriol.
answer
Increases intestinal Ca++ and Phosphate absorption, Decreases Ca++ loss from kidney, Increases bone osteoclast activity
question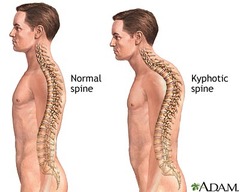
Define kyphosis.

answer
abnormal curvature of thoracic spine (humpback)
question
What is Osteogenesis imperfecta known as?
answer
Brittle Bone disease
question
What is Achondroplastic dwarfism?
answer
Type of dwarfism where epiphyseal plate closes too early and calcified into bone, growth is prohibited
question
What is an osteoma?
answer
Bone tumor
question
What is osteosarcoma?
answer
A malignant tumour of bone
question
What is ricketts?
answer
softening or weakened version of bones *in children resulting in bowlegged appearance.
question
What is osteomalacia?
answer
(adult rickets)...bones become soft calcium and phosphorus imbalance secondary to vitamin D deficiency
question
What is the 1st step of healing a fracture?
answer
Hematoma formation and angiogenesis
question
What is the 2nd step of healing a fracture?
answer
Granulation tissue formation:
question
What is the 3rd step of healing a fracture?
answer
Callus formation: Fibrocartilage then Soft Callus then Bony Callus
question
What is the 4th step of healing a fracture?
answer
Remodeling
question
What is the 1st step of healing the integument?
answer
Inflammatory Phase: Clot unites wound and vasodilation brings warmth, rubor, leukocytes and nutrients
question
What is the 2nd step of healing the integument?
answer
Migratory Phase: Fibroblasts migrate through clot and angiogenesis begins creating granulation tissue
question
What is the 3rd step of healing the integument?
answer
Proliferation Phase: Epithelial cells grow underneath scab and fibroblasts lay down excess collagen
question
What is the 4th step of healing the integument?
answer
Maturation Phase: Scab sloughed off when epithelial cells complete migration/proliferation and fibroblast numbers/activity drop followed by remodeling
question
What are some purposes of cerebral spinal fluids?
answer
shock absorber, prevents bruising of brain
question
What are the 3 layers of the meninges from superficial to deep?
answer
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
question
What tissue does the dura mater consist of?
answer
Dense irregular CT
question
Why do we have sinus in our head?
answer
shock absorber, reduce weight of skull
question
What are the 4 sinuses in our head?
answer
Frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, maxillary
question
Why does snoring happen?
answer
the concha resonate improperly
question
What humidify's and cleans the air before it enters the lung?
answer
The mucus membranes of the concha in the ethmoid bone.
question
How many vertebrae do we have?
answer
33
question
How many cervical vertebrae do we have?
answer
7
question
What do we call our 1st cervical vertebrae?
answer
Atlas
question
What do we call our 2nd cervical vertebrae?
answer
Axis
question
How many thoracic vertebrae do we have?
answer
12
question
How many Lumbar vertebrae do we have?
answer
5
question
How many saccral(fused) vertebrae do we have?
answer
5
question
How many coccygeal vertebrae do we have?
answer
4
question
What part of the vertebrae stops them from sliding off eachother?
answer
Spinous process
question
Define caudal
answer
directed to tail
question
What is a herniated disc?
answer
Rupture to the anulus fibrosus
question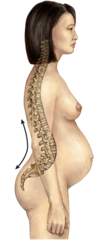
"Swayback" is known as what?

answer
Lordosis
question
How are joints classified?
answer
By structure (how they attach two bones) and function (way they allow two bones to move).
question
What are the three ways bones can be held together in a joint?
answer
Synovial, Fibrous, Cartilaginous
question
What are the three ways bones move across a joint?
answer
Diathroses, amphiarthroses, synarthroses
question
Define a Diathroses joint.
answer
feely moving - knee
question
Define a Amphiathroses joint.
answer
slightly moveable - ribs
question
Define a Synarthroses joint.
answer
little, to no movement
question
Describe a serrate joint
answer
wavy overlap-sagittal suture
question
Describe a lap joint
answer
single overlap-temporal/parietal suture
question
describe a plane joint
answer
flat-two halves of palate
question
Describe a gomphoses joint
answer
tooth and socket peridontal ligament
question
Describe a syndesmoses joint
answer
a simple ligament holds bones together side by side
question
Describe an example of a synchondrosis joint
answer
attachment of ribs to sternum via hyalin cartilage
question
Describe an example of a symphysis joint
answer
pubic symphysis and vertebral discs made of fibrocartilage
question
Describe an example of a synostosis joint
answer
the saccrum where two bones become ossifed together (fused)
question
What is a bursa?
answer
sac of fluid in joint
question
Name 6 types of diarthrotic synovial joints
answer
Ball and socket, hinge joint, saddle joint, pivot joint, gliding joint, condyloid joint
question
Give an example of ball and socket joint
answer
humeroscapular
question
give an example of hinge joint
answer
hemeroulnar
question
give an example of a saddle joint
answer
carpometacarpal 1
question
give an example of a pivot joint
answer
radioulnar
question
give an example of a gliding joint
answer
intercarpal
question
give an example of a condyloid joint
answer
metacarpophalangeal



