Econ160: Practice Questions Chapters 7, 9 10 & 11
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Marginal utility can be:
answer
positive, negative, or zero.
question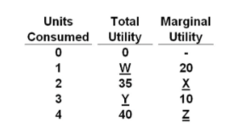
Refer to the data. The value for W is:

answer
20.
question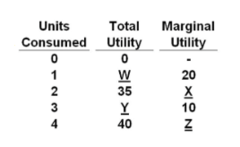
The data illustrate the:

answer
law of diminishing marginal utility.
question
If the price of product X rises, then the resulting decline in the amount purchased will:
answer
increase the marginal utility of the last unit consumed of this good.
question
Marginal utility is the:
answer
change in total utility obtained by consuming one more unit of a good.
question
Utility refers to the:
answer
satisfaction that a consumer derives from a good or service.
question
The law of diminishing marginal utility explains why:
answer
demand curves slope downward.
question
The theory of consumer behavior assumes that:
answer
consumers behave rationally, attempting to maximize their satisfaction.
question
To maximize utility, a consumer should allocate money income so that the:
answer
marginal utility obtained from the last dollar spent on each product is the same.
question
The marginal utility of the last unit of apples consumed is 12 and the marginal utility of the last unit of bananas consumed is 8. What set of prices for apples and bananas, respectively, would be consistent with consumer equilibrium?
answer
$6 and $4
question
Suppose you have a limited money income and you are purchasing products A and B, whose prices happen to be the same. To maximize your utility, you should purchase A and B in such amounts that:
answer
their marginal utilities are the same.
question
A consumer is maximizing her utility with a particular money income when:
answer
MUa/Pa = MUb/Pb = MUc/Pc = . . . = MUn/Pn.
question
If a rational consumer is in equilibrium, which of the following conditions will hold true?
answer
The marginal utility of the last dollar spent on each good purchased will be the same.
question
A consumer who has a limited budget will maximize utility or satisfaction when the:
answer
ratios of the marginal utility of each product purchased divided by its price are equal.
question
Prashanth decides to buy a $75 ticket to a particular New York professional hockey game rather than a $50 ticket for a particular Broadway play. We can conclude that Prashanth:
answer
has a higher "marginal utility-to-price ratio" for the hockey game than for the play.
question
Why do people tend to eat more at all-you-can-eat buffet restaurants than at restaurants where each item is purchased separately?
answer
Once the all-you-can-eat meal is purchased, consumers view additional trips back to the buffet as having a price of zero.
question
Which of the following statements is correct?
answer
Noncash gift-giving creates a value loss, but cash gifts do not.
question
(Last Word) All of the following would reduce property crime by increasing its "price," except:
answer
cutting out the middlemen ("fences") by selling stolen goods via Internet auction sites.
question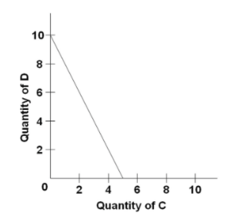
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $20, the:

answer
price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2.
question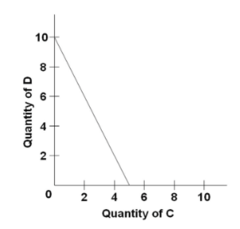
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. The absolute value of the slope of the budget line is:

answer
PC/PD.
question
Increases in product prices shift the consumer's:
answer
budget line to the left.
question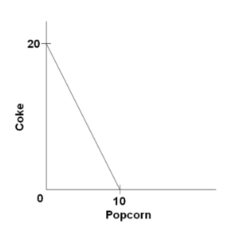
Suppose you have money income of $10, all of which you spend on Coke and popcorn. In the diagram, the prices of Coke and popcorn respectively are:

answer
$.50 and $1.00.
question
The slope of a budget line reflects the:
answer
price ratio of the two products.
question
Edith is buying products X and Y with her money income. Suppose her budget line shifts rightward (outward). This might be the result of:
answer
her money income increasing more than proportionately to increases in the prices of X and Y.
question
Which of the following is correct?
answer
Budget lines are linear and downsloping; indifference curves are downsloping and convex to the origin.
question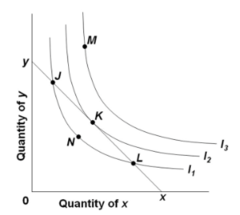
Refer to the diagram where xy is the relevant budget line and I1, I2, and I3 are indifference curves. If the consumer is initially at point L, he or she should:

answer
purchase more of Y and less of X.
question
Refer to the diagram in which the downsloping lines are budget lines and I1, I2, and I3 comprise an indifference map. The combinations of products M and N indicated by points 1, 2, and 5 are such that:
answer
points 1, 2, and 5 yield equal amounts of utility.
question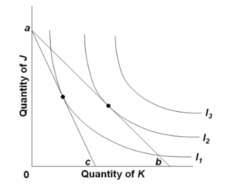
Refer to the diagram. If the budget line shifts from ab to ac, the:

answer
price of K has increased.
question
Refer to the diagram. If the budget line shifts from ab to ac, the:

answer
consumer will purchase more of J and less of K.
question
A rational consumer will try to achieve the highest indifference curve that his or her income will allow.
answer
True
question
Which of the following constitutes an implicit cost to the Johnston Manufacturing Company?
answer
Use of savings to pay operating expenses instead of generating interest income.
question
Which of the following is most likely to be an implicit cost for Company X?
answer
Forgone rent from the building owned and used by Company X.
question
An explicit cost is:
answer
a money payment made for resources not owned by the firm itself.
question
Economic profits are calculated by subtracting:
answer
explicit and implicit costs from total revenue.
question
Normal profit is:
answer
the return to the entrepreneur when economic profits are zero.
question
The following is cost information for the Creamy Crisp Donut Company: Entrepreneur's potential earnings as a salaried worker = $50,000 Annual lease on building = $22,000 Annual revenue from operations = $380,000 Payments to workers = $120,000 Utilities (electricity, water, disposal) costs = $8,000 Value of entrepreneur's talent in the next best entrepreneurial activity = $80,000 Entrepreneur's forgone interest on personal funds used to finance the business = $6,000 Refer to the data. Creamy Crisp's total economic costs are:
answer
$286,000.
question
The following is cost information for the Creamy Crisp Donut Company: Entrepreneur's potential earnings as a salaried worker = $50,000 Annual lease on building = $22,000 Annual revenue from operations = $380,000 Payments to workers = $120,000 Utilities (electricity, water, disposal) costs = $8,000 Value of entrepreneur's talent in the next best entrepreneurial activity = $80,000 Entrepreneur's forgone interest on personal funds used to finance the business = $6,000 Refer to the data. If, other things equal, Creamy Crisp's revenue fell to $286,000:
answer
it would earn a normal profit but not an economic profit.
question
To economists, the main difference between the short run and the long run is that:
answer
in the long run all resources are variable, while in the short run at least one resource is fixed.
question
The long run is characterized by:
answer
the ability of the firm to change its plant size.
question
Which of the following best expresses the law of diminishing returns?
answer
As successive amounts of one resource (labor) are added to fixed amounts of other resources (capital), beyond some point the resulting extra or marginal output will decline.
question
The law of diminishing returns results in:
answer
a total product curve that eventually increases at a decreasing rate.
question
Which of the following is not correct?
answer
Where total product is at a maximum, average product is also at a maximum.
question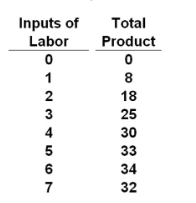
Use the following data to answer the question: Refer to the data. Marginal product becomes negative with the hiring of the __________ unit of labor.

answer
seventh
question
If you owned a small farm, which of the following would most likely be a fixed cost?
answer
Hail insurance.
question
Which of the following is most likely to be a variable cost?
answer
Fuel and power payments.
question
For most producing firms:
answer
average total costs decline as output is carried to a certain level, and then begin to rise.
question
Average fixed cost:
answer
declines continually as output increases.
question
Which of the following is correct as it relates to cost curves?
answer
Marginal cost intersects average total cost at the latter's minimum point.
question
Other things equal, if the prices of a firm's variable inputs were to fall:
answer
marginal cost, average variable cost, and average total cost would all fall.
question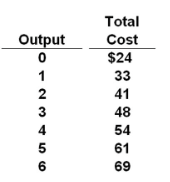
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data: Refer to the data. The profit-maximizing output for this firm:

answer
cannot be determined from the information given.
question
Answer the question on the basis of the following information: Refer to the information. Average fixed cost is:

answer
MC/Q
question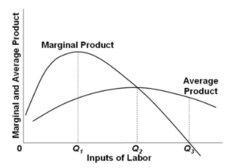
Refer to the diagram, where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. The total output of this firm will cease to expand:

answer
if a labor force in excess of Q3 is employed.
question
In the short run, which of the following statements is correct?
answer
Total cost will exceed variable cost.
question
Which of the following holds true?
answer
When AP is rising AVC is falling, and when AP is falling AVC is rising.
question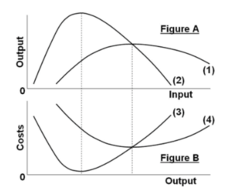
Refer to the short-run production and cost data. In Figure A curve (1) is:

answer
average product and curve (2) is marginal product.
question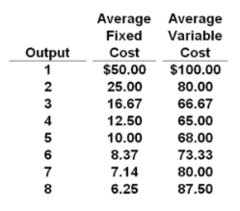
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data: Refer to the data. If the firm closed down in the short run and produced zero units of output, its total cost would be:

answer
$50.
question
If a technological advance increases a firm's labor productivity, we would expect its:
answer
average total cost curve to fall.
question
The Sunshine Corporation finds that its costs are $40 when it produces no output. Its total variable costs (TVC) change with output as shown in the accompanying table. Use this information to answer the following question. Refer to the information. The average fixed cost of 3 units of output is:
answer
$13.33.
question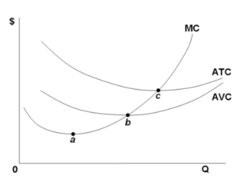
Refer to the diagram. The profit-maximizing level of output for this firm:

answer
cannot be determined from the information given.
question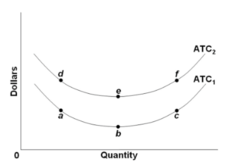
Refer to the graph. Which one of the following would cause a move from point b to point c along short-run average total cost curve ATC1?

answer
Diminishing marginal returns.
question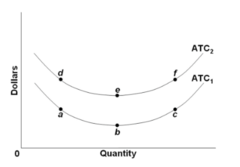
Refer to the graph. Which one of the following would cause a move from point d to point e along short-run average total cost curve ATC2?

answer
Increasing marginal returns.
question
When diseconomies of scale occur:
answer
the long-run average total cost curve rises.
question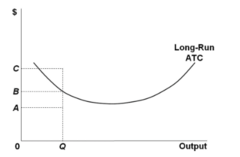
Refer to the diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are:

answer
attainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources.
question
A natural monopoly exists when:
answer
unit costs are minimized by having one firm produce an industry's entire output.
question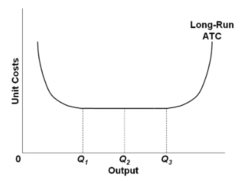
In the diagram it is assumed that:

answer
all costs are variable.
question
(Consider This) If the law of diminishing returns applies to study time:
answer
the tenth hour of study will likely be less productive than the third.
question
(Last Word) Which of the following is predicted to deliver a Third Industrial Revolution characterized by low production and transportation costs?
answer
New technology in additive manufacturing.
question
Diseconomies of scale stem primarily from the difficulties in managing and coordinating a large-scale business enterprise.
answer
True
question
Average fixed costs diminish continuously as output increases.
answer
True
question
A firm's economic profit is usually higher than its accounting profit.
answer
False
question
In which of the following market structures is there clear-cut mutual interdependence with respect to price-output policies?
answer
Oligopoly.
question
A purely competitive seller is:
answer
a "price taker."
question
In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis. Refer to the information. For a purely competitive firm, total revenue graphs as a:
answer
straight, upsloping line.
question
In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis. Refer to the information. For a purely competitive firm:
answer
the demand and marginal revenue curves will coincide.
question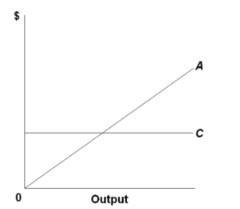
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents:

answer
total revenue only.
question
Marginal revenue is the:
answer
change in total revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output.
question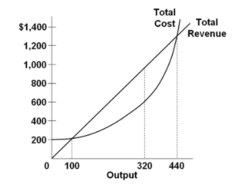
Refer to the short-run data. The profit-maximizing output for this firm is:

answer
320 units.
question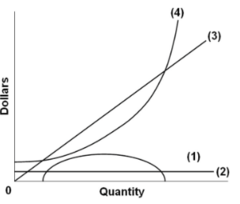
Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's:

answer
total economic profit curve.
question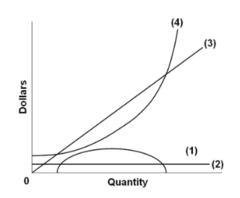
Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's:

answer
total revenue curve.
question
When a firm is maximizing profit, it will necessarily be:
answer
maximizing the difference between total revenue and total cost.
question
Assume the XYZ Corporation is producing 20 units of output. It is selling this output in a purely competitive market at $10 per unit. Its total fixed costs are $100 and its average variable cost is $3 at 20 units of output. This corporation:
answer
is realizing an economic profit of $40.
question
A purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve is:
answer
upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve.
question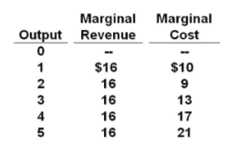
Answer the question on the basis of the following data confronting a firm: Refer to the data. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm's total revenue is:

answer
$48.
question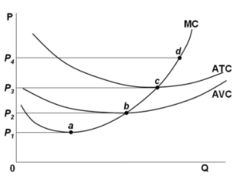
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce at a loss at all prices:

answer
between P2 and P3.
question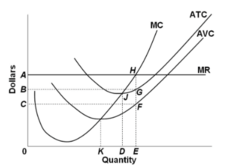
Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total variable cost is equal to:

answer
0CFE
question
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market: Refer to the data. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce:
answer
8 units at an economic profit of $16.
question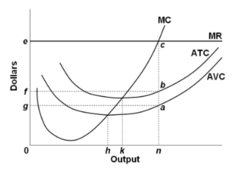
Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total profit is:

answer
efbc
question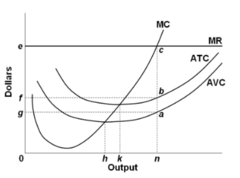
Refer to the diagram. The short-run supply curve for this firm is the:

answer
segment of the MC curve lying to the right of output level h.
question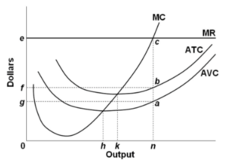
Refer to the diagram. This firm is selling its product in a(n):

answer
purely competitive market.
question
In the short run, a purely competitive seller will shut down if product price:
answer
is less than AVC.
question
The short-run supply curve for a purely competitive industry can be found by:
answer
summing horizontally the segments of the MC curves lying above the AVC curve for all firms.
question
In contrast to American firms, Japanese firms frequently make lifetime employment commitments to their workers and agree not to lay them off when product demand is weak. Other things being equal, we would expect Japanese firms to:
answer
continue to produce in the short run at lower prices than would American firms.
question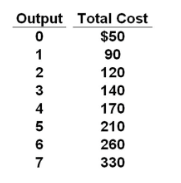
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a purely competitive seller: Refer to the data. If product price is $25, the firm will:

answer
shut down and incur a $50 loss.
question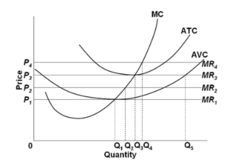
Refer to the diagram. The firm will realize an economic profit if price is:

answer
P4
question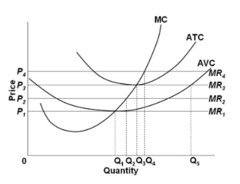
Refer to the diagram. The firm will shut down at any price less than:

answer
P1.
question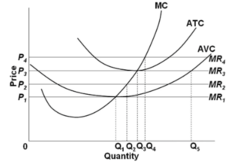
Refer to the diagram. The firm's supply curve is the segment of the:

answer
MC curve above its intersection with the AVC curve.
question
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. Refer to the data. At 3 units of output, total variable cost is ____ and total cost is ____.
answer
$60; $210
question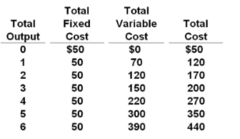
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a purely competitive seller: The data are for:

answer
the short run.
question
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a purely competitive seller: Refer to the data. At 5 units of output, average fixed cost, average variable cost, and average total cost are:
answer
$10, $60, and $70 respectively.
question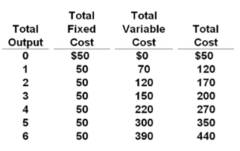
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a purely competitive seller: Refer to the data. The marginal cost of the fifth unit of output is:

answer
$80.
question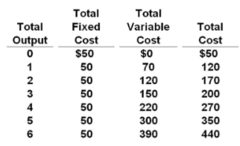
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a purely competitive seller: Refer to the data. If product price is $75, the firm will produce:

answer
4 units of output.
question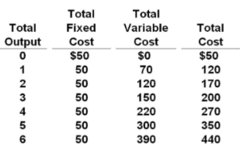
Answer the question on the basis of the following cost data for a purely competitive seller: Refer to the data. Given the $75 product price, at its optimal output the firm will:

answer
realize a $30 economic profit.
question
(Last Word) Temporary shutdowns of firms are most widespread when:
answer
the economy experiences recession.
question
The term imperfect competition refers to every market structure besides pure competition.
answer
True
question
In a purely competitive industry competition centers more on advertising and sales promotion than on price.
answer
False
question
Price and marginal revenue are identical for an individual purely competitive seller.
answer
True
question
In maximizing profit, a firm will always produce that output where total revenues are at a maximum.
answer
False
question
A competitive firm will produce in the short run so long as its price exceeds its average fixed cost.
answer
False
question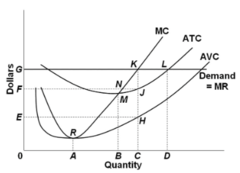
Refer to the diagram. If demand fell to the level of FNJ, there would be no output at which the firm could realize an economic profit.

answer
False
question
The ability of a good or service to satisfy wants is called:
answer
utility
question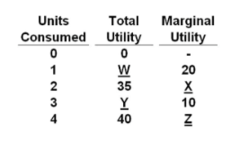
Refer to the data. The value for Z is:

answer
-5
question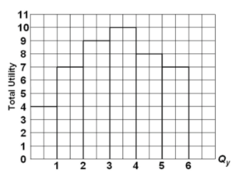
Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility:

answer
becomes negative after consuming 4 units of output.
question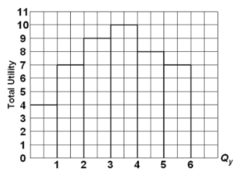
If total utility is increasing, marginal utility:

answer
is positive but may be either increasing or decreasing.
question
The law of diminishing marginal utility explains why:
answer
demand curves slope downward.
question
Why do people tend to eat more at all-you-can-eat buffet restaurants than at restaurants where each item is purchased separately?
answer
Once the all-you-can-eat meal is purchased, consumers view additional trips back to the buffet as having a price of zero.
question
A rational consumer will cease purchasing a product at that quantity where marginal utility begins to diminish.
answer
False
question
If the price of A is $12 and the price of B is $3, the budget line tells us that a consumer in effect can trade:
answer
1 unit of A for 4 of B.
question
Assume initially that the price of X (measured on the horizontal axis) is $9 and the price of Y (measured on the vertical axis) is $4. If the price of X now declines to $6, the budget line will:
answer
shift outward on the horizontal axis.
question
Refer to the diagram where xy is the relevant budget line and I1, I2, and I3 are indifference curves. If the consumer is initially at point L, he or she should:

answer
purchase more of Y and less of X.
question
Which of the following is true concerning purely competitive industries?
answer
In the short run, firms may incur economic losses or earn economic profits, but in the long run they earn normal profits.
question
If a purely competitive firm is producing at the MR = MC output level and earning an economic profit, then:
answer
new firms will enter this market.
question
Assume a purely competitive increasing-cost industry is initially in long-run equilibrium and that an increase in consumer demand occurs. After all economic adjustments have been completed, product price will be:
answer
higher and total output will be larger than originally.
question
Assume a purely competitive, increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium. If a decline in demand occurs, firms will:
answer
leave the industry and price and output will both decline.
question
A purely competitive firm:
answer
cannot earn economic profit in the long run.
question
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. The predicted long-run adjustments in this industry might be offset by:
answer
a technological improvement in production methods.
question
A purely competitive firm is precluded from making economic profits in the long run because:
answer
of unimpeded entry to the industry.
question
Under what conditions would an increase in demand lead to a lower long-run equilibrium price?
answer
The firms in the market are part of a decreasing-cost industry.
question
A decreasing-cost industry is one in which:
answer
input prices fall or technology improves as the industry expands.
question
Suppose that an industry's long-run supply curve is downsloping. This suggests that:
answer
it is a decreasing-cost industry.
question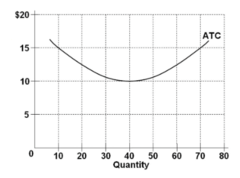
Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue:

answer
is $400.
question
Refer to the diagram. Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for:
answer
an increasing-cost industry.
question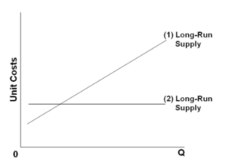
Refer to the diagram. Line (1) reflects a situation where resource prices:

answer
increase as industry output expands.
question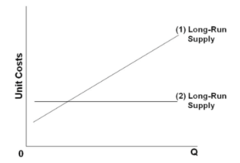
Refer to the diagram. Line (2) reflects a situation where resource prices:

answer
remain constant as industry output expands.
question
Resources are efficiently allocated when production occurs where:
answer
price is equal to marginal cost.
question
The term productive efficiency refers to:
answer
the production of a good at the lowest average total cost.
question
The term allocative efficiency refers to:
answer
the production of the product mix most desired by consumers.
question
Under pure competition in the long run:
answer
both allocative efficiency and productive efficiency are achieved.
question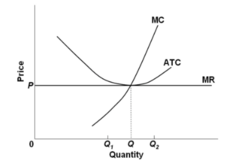
Refer to the diagram. By producing at output level Q:

answer
both productive and allocative efficiency are achieved.
question
If production is occurring where marginal cost exceeds price, the purely competitive firm will:
answer
fail to maximize profit and resources will be overallocated to the product.
question
In long-run equilibrium, purely competitive markets:
answer
maximize the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
question
Which of the following would not be expected to occur in a purely competitive market in long-run equilibrium?
answer
Consumer and producer surplus will be minimized.
question
Creative destruction is least beneficial to:
answer
workers in the "destroyed" industries.
question
(Consider This) Which of the following statements is true about U.S. firms?
answer
Over half are bankrupt within the first five years after starting up.
question
(Last Word) Patents are most likely to infringe on innovation:
answer
for products that incorporate many different technologies into a single product.
question
(Last Word) "Patent trolls:"
answer
buy up patents in order to collect royalties and sue other companies.
question
The long-run supply curve for a decreasing-cost industry is downsloping.
answer
True
question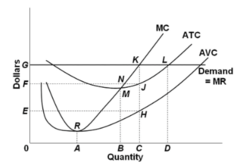
Refer to the diagram. If this firm is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then it is achieving productive and allocative efficiency.

answer
False
question
When entrepreneurs in competitive industries successfully innovate to lower production costs, it usually results in long-run economic profits for the firm.
answer
False
question
The process by which new firms and new products destroy existing dominant firms and their products is called creative destruction.
answer
True



