Connective Tissue – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Connective Tissue. CT
answer
Can vary in appearance and function. It is all throughout the body but it is never exposed to anything from the outside like food or anything. It is underneath the epithelium, many have blood vessels and sensory receptors.
question
Sarcoma
answer
Cancer of connective tissue origin. Makes up 10% of cancers because there is a relatively high cell turnover rate.
question
functions of CT
answer
establishing a structural framework for the body transporting fluids and dissolved materials protecting delicate organs supporting, surrounding, and interconnecting other types of tissue storing energy reserves, especially in the form of triglycerides defends the body from invading microorganisms
question
features of CT
answer
they all contain specialized cells, fibers, and fluids (ground substance) They have a matrix
question
ground substance
answer
fluids in CT
question
matrix
answer
fibers plus the ground substance in CT. The matrix is everything except the specialized cells. The matrix surrounds the specialized cells.
question
Types of CT
answer
three main types: Connective Tissue Proper Fluid Connective Tissue Supportive Connective Tissue
question
Connective Tissue Proper
answer
May be loose of dense. There are many types of cells and fibers with a syrupy ground substance. Includes fibroblasts
question
Loose Connective Tissue Proper
answer
The fibers are not tightly bound. They create a loose, open framework that you can see through. example- adipose tissue
question
Dense Connective Tissue Proper
answer
The fibers are densely packed, strong, and tough to see through. These are in tendons and ligaments.
question
Fibroblast
answer
a specialized cell that lays down fibers in CT proper, it produces collagen and elastic fibers
question
collagen fibers
answer
give the bulk of connective tissues
question
elastic fibers
answer
give fibers elasticity.
question
Fluid Connective Tissue
answer
This is a watery matrix, it is blood which is in the cardiovascular system and lymph which is in the lymphatic system
question
Supporting Connective Tissue
answer
Less diverse cells, but the matrix is packed with dense fibers. Mainly cartilage (solid, rubbery matrix) and bone (solid, crystalline matrix)
question
Mesenchyme
answer
The original stem cell that all connective tissues come from, it will make all of the connective tissue.
question
Bone marrow transplant and importance of stem cells
answer
Leukemia comes from white blood cells being cancerous and continually producing cancer cells. So this person has bone marrow producing bad cells, so we destroy all the stem cells in this person and take good stem cells from a donor so they will hopefully produce good cells.
question
Loose areolar CT
answer
collagenous and elastic fibers produced by fibroblasts are embedded in a gel like matrix. Binds organs together beneath the skin and found between the muscles
question
Adipose CT
answer
cells filled with fat droplets nucleus and cytoplasm are pushed to the sides cushions, insulates, and stores energy found beneath the skin, around the kidneys, heart, and eyeballs
question
Dense CT
answer
matrix filled with parallel bundles of collagenous fibers Binds structures together found in tendons and ligaments
question
Elastic CT
answer
matrix filled with yellow elastic fibers important for elasticity found in vocal cords and ligaments between adjacent vertebrae.
question
Hyaline cartilage
answer
solid matrix with fibers and scattered cells supports, protects, and provides framework. found in the ends of long bones, connects ribs to the sternum
question
fibrocartilage CT
answer
numerous cartilage fibers in the matrix cushions and protects found in intervertebral disks, pads in the knee joint
question
elastic cartilage
answer
numerous elastic fibers in the matrix supports and provides framework found in the external ear, auditory tubes
question
osseous
answer
bone tissue. Hard matrix with mineral salts protects, supports, provides a framework. found in bones of the skeleton
question
blood CT
answer
liquid matrix called plasma transports oxygen, protects against disease found in blood vessels and heart
question
Cartilage characteristics
answer
has cells- chondrocytes in lacunae has ground substance- chondroitin sulfate and water has fibers- collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers no vascularity has covering- two layers of perichondrium strength is limited, bends easily but it hard to break
question
characteristics of bone
answer
has cells- osteocytes in lacunae has ground substance- liquid surrounds insoluble crystals of calcium salts has mainly collagen fibers has extensive vascularity has covering- two layers or periosteum it is strong, resists distortion until breaking point
question
collagen fibers color
answer
thick and pink
question
elastic fibers color
answer
thin and black
question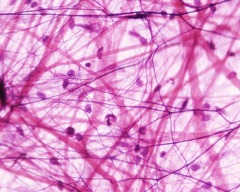
areolar connective tissue

answer
loose CT. Has all three fiber types Wraps and cushions organs Found under epithelia of the body. Keeps everything compact and cushions organs.
question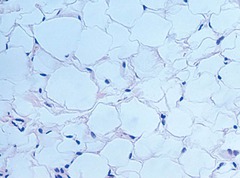
adipose connective tissue

answer
Loose CT provides reserve food fuel, insulates against heat loss found under skin, around kidneys
question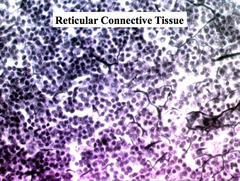
reticular connective tissue

answer
loose CT forms a soft internal skeleton that supports other cells. found in organs of the immune system- spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow.
question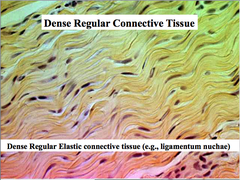
dense regular connective tissue

answer
mainly collagen fibers that are moving in a regular, parallel way. So dense that you cannot see through. Attaches muscles to bones or muscles. Attaches bones to bones. Withstands stress. Found in tendons, most ligaments.
question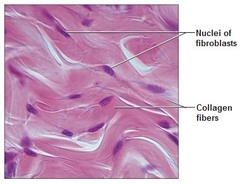
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue

answer
mainly collagen fibers that are moving everywhere. Able to withstand tension exerted in many directions. Provides structural strength. Found in dermis of the skin and certain areas of the digestive system
question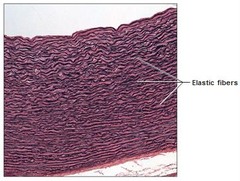
Dense elastic connective tissue

answer
Dense, regular connective tissue that contains a high amount of elastic (black) fibers allows tissues to recoil after stretching, maintains flow of blood through arteries found in the aorta
question
Fluid connective tissues
answer
Blood and lymph. we will focus on blood
question
Blood
answer
the bodys fluid tissue. composed of plasma and formed elements not attached to anything it transports respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes contained within blood vessels
question
plasma
answer
the fluid matrix of blood
question
formed elements
answer
erythrocytes (red blood cells) leukocytes (white blood cells) thrombocytes (platelets for clotting your cells)
question
hematocrit
answer
the percentage of red blood cells in the total blood volume
question
red blood cells
answer
carries oxygen and carbon dioxide
question
white blood cells
answer
fights infections
question
platelets
answer
clots blood
question
Polycythemia
answer
increase of red blood cells
question
Anemia
answer
decrease of red blood cells
question
Infection, Inflammation, Malignancy
answer
Increase of white blood cells
question
Immunodeficiency
answer
decrease of white blood cells
question
Hypercoagulable state
answer
increase of platelets
question
Hypocoagulable state
answer
decrease of platelets
question
supporting connective tissues
answer
hyaline cartilage elastic cartilage fibrous cartilage compact bone
question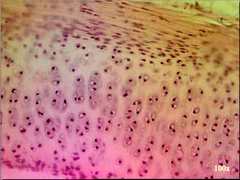
hyaline cartilage

answer
firm, smooth matrix with collagen fibers, has little cubby holes called lacuna. supports and reinforces, resists compressive stress covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities.
question
lacuna
answer
little cubby holes that are in all cartilage. have Chondrocytes in them.
question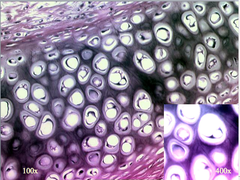
Elastic cartilage

answer
unsmooth matrix, more elastic fibers are in the matrix maintains the shape of a structure while allowing flexibility. hard but flexible. supports the external ear
question
fibrous cartilage

answer
a matrix of mainly thick collagen fibers. Distinctive blue matrix. Gives strength and can absorb compressive shock Found in intervertebral discs.
question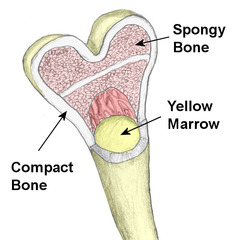
Compact bone

answer
looks like tree stumps. It is a hard, calcified matrix containing many collagen fibers Supports and protects, provides levels for muscles to work on, stores calcium, marrow is the site of blood cell formation found in bones
question
Medullary cavity
answer
the hollow middle of compact bone. This contains the bone marrow.
question
Endosteum
answer
The lining of the medullary cavity.
question
Periosteum
answer
Similar to the endosteum, but this lines the outside of the compact bone
question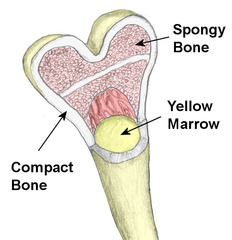
spongey bone

answer
spongey looking material on the inside of the bone
question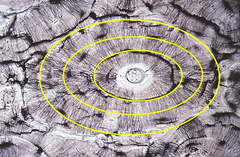
Lamellae

answer
Rings of the compact bone
question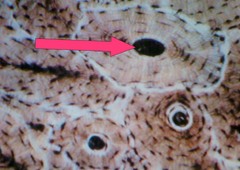
Haversian canal

answer
AKA osteonic canal the center, dark circle of the compact bone section. Contains blood vessels.
question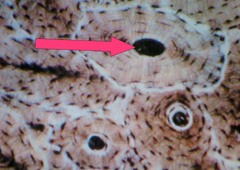
Haversian system

answer
AKA osteon. The whole system, the circle. This is the functional unit of compact bone.
question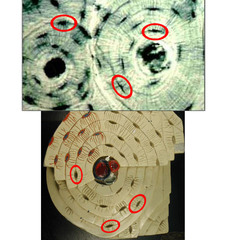
lacunae

answer
They have canaliculi to connect one lacuna to another so nutrients can get passed throughout. Inside lacunae are osteocytes.
question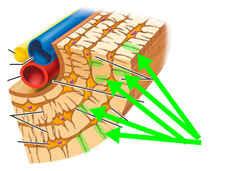
Canaliculi

answer
connects one lacuna to another to pass nutrients.
question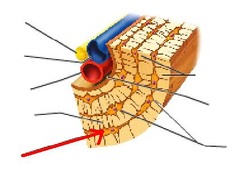
Osteocyte

answer
give nutrients to the bone. found in the lacuna. this is a mature bone cell that delivers nutrients to the bones.
question
osteoblast
answer
build the bulk of the bone. Its like a kid painting the floor of a room, he just spills the paint all over to create a huge base coat, but he backed himself into a little corner that has no paint. this secretes a ground substance (the bone matrix)
question
osteoclasts
answer
now we need to clean up the mess the kid made. These will break down and resorb the bone matrix and chisel away at all the excess. They shape the bone material by resorbing calcium from the bone and putting it back into the blood stream. If calcium is low in the blood, these become active to bring it from the bone to blood. Estrogen keeps them from being too active, during menstruation estrogen dips, makes them overactive. Women are prone to osteoporosis because it keeps taking from the bone.



