Comm 168 – Soc Marketing Exam – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
WWII
answer
Comm starting to get studied more. Grants given to find ways to persuade people to support war.
question
Social Marketing
answer
Marketing principles used for social issues.
question
Invisibility of Privilege
answer
Privilege is invisible to those who have it.
question
Problem with individualizing Racism
answer
- Separates individual from structures that cause it. - Suggests it is anomaly
question
Getting rid of problem like racism
answer
- Educate the youth, ANT THEIR EDUCATORS.
question
Normalization of Privilege
answer
Members of society are judged, and succeed or fail measured against the characteristics that are held by those privileged.
question
Extreme Suffering
answer
Premature and painful illness... as well as torture and rape. More insidious assaults on dignity, such as institutionalized racism and gender inequality, are also acknowledged by most to cause great and unjust injury.
question
Structural Violence
answer
Suffering "structurely" by historically given processes and forces that conspire to constrain you.
question
Axes of Oppression
answer
Gender, Race/Ethnicity, and Socio-economic Status
question
Gender (Axes of Oppression)
answer
Men domniate political, legal, and econ structures. Women suffer from domestic violence, rape, and maternal morality.
question
Race/Ethnicity (Axes of Oppression)
answer
Race used as a sort of class system. Has been used across world to create diff systems of laws and access.
question
Socio-Econ Status
answer
Econ Status crosses every axis in deep ways and sharply shapes life experiences.
question
Intersectionality
answer
Forms of oppression inter-relate. EX: Oppressed through race and gender.
question
"White Savior"
answer
White person helps those who are less privileged with THEIR idea of what is help (not by asking the struggling community what they need). EX: Helping Native Americans by pushing American like structures/norms on them.
question
Audeince Focus
answer
Segment audience and choose particular focus carefully.
question
Social Marketing V. Commercial Marketing
answer
(1) Societal Gain V. Financial Gain. (2) Behavior is Competitor V. Another company as competitor. (3) Financial Resources of Competition. (4) Difficulty of Changing Health Behaviors V. Purchasing Behavior.
question
Levels of Action
answer
Short-term Change & Long-term Change broken into 3 levels. (1) Individual Level [Personal]. (2) Group-Level [Social]. (3) Societal-Level.
question
Short-Term Change: Individual Level [Personal]
answer
Focus on individual behavior change. EX: Don't bully on a particular day.
question
Short-Term Change: Group-Level [Social]
answer
Want to change norms. EX: Make bullying unacceptable at one school.
question
Short-Term Change: Societal-Level
answer
Want to change policy. EX: Stricter policies against bullying.
question
Long-Term Change: Individual Level [Personal]
answer
Want to change a person's lifestyle. EX: Don't ever bully.
question
Long-Term Change: Group-Level [Social]
answer
Want organizational change. Ex: Don't ever bully.
question
Long-Term Change: Societal-Level
answer
Want socio-cultural evolution. EX: healthier climate for children's growth.
question
Transformative Social Marketing
answer
Using Value Space, Scope, and Design to create a marketing campaign.
question
Scope (Transformative Social Marketing)
answer
- CO-CREATION (Working with partners not on them). - Promote CONVERSATIONS. - Value relationships and build COMMUNITIES. - alter MARKETS.
question
Value Space (Transformative Social Marketing)
answer
- Prioritize Communities DIGNITY. - Make HOPE visible. - Build LOVING relationships. - Build TRUST in campaign.
question
Design (Transformative Social Marketing)
answer
- HONOR People (Retarded vs. Handicapped). - Understand their VALUES. - Teach communities how to engage with needed SERVICES. - ENHANCE EXPERIENCES (Persuasive work connects w/audience)
question
Place
answer
Where and when target audience will perform desired behavior, acquire any related goods, and receive any associated services.
question
Implications on Place
answer
Want to understand physical, social, and cultural environment in which that behavior occurs.
question
3 Questions about Audience behavior
answer
1) does audience have OPPORTUNITY to engage in behavior? 2) Does audience have ABILITY to engage in behavior? 3) Does adueince have MOTIVATION to engage in behavior?
question
Example of Local Places
answer
Homes, Schools, Neighborhoods, Places or worship, and Bars.
question
Example of Distant Places
answer
Iowa Politics, Supreme Court, Wall Street, and Middle East.
question
4 Aspects of Place
answer
(1) Availability of Products/services. (2) Physical structure of environment. (3) Social Structure (Laws and policies) and enforcement. (4) Social attitudes (media and cultural messages)
question
Ways to make actions more Convenient (Place)
answer
(1) Make Location closer/more accessible. [EX: flu shots at malls, blood drives on campus.] (2) Extend Hours. [EX: Voting by mail as an option.] (3) Be there at point of decision-making. [EX: Drug testing area at raves.] (4) Make location more likely to produce behavior. [EX: Adding bike lanes to separate bikers and cars.] (5) Be more accessible than competition. [EX: Making nutritious food more accessible than junk food.] (6) Make location less likely to produce negative behavior. [EX: adding tax on cigarettes].
question
Attitudes role in Place
answer
Attitudes are critical in community. Attitudes shape behavior.
question
Emapthy
answer
Feeling with people. Being understanding, recognize emotion, perspective taking, and create connection.
question
Sympathy
answer
Feeling Pity. Often not helpful.
question
Understanding Audience
answer
- Understand what your audience acts the way it does. - Understand their primary values. - Understand their motivations.
question
Understand Audience Current Behavior
answer
What are the benefits and costs of their current behaviors.
question
Understand the audience desired behavior.
answer
- What are the barriers. - What are costs of new behavior. - What are perceived benefits of new behavior.
question
Understanding the Exchange: Intoxication Culture. Perceived benefits of intoxication.
answer
Pleasure Seeking: feels good, makes you happy, feel like part of group. Is seen as rite of passage.
question
Understanding the Exchange: Drug Driving
answer
Lower perception of risk. Perceived benefits to drug driving. Drug as unplanned activity that makes planning difficult.
question
Understanding the exchange: Drug Driving. Barriers
answer
- Buses stop at 11. - Buses dont go to many places. - Taxis too expensive and dangerous. - Costs of sleeping at someone else's house.
question
Exchange
answer
Trade of tangible and/or intangible resources between 2+ parties.
question
Things to know about your campaign.
answer
(1) Product you are offering. (2) What are the cost and benefits. (3) What are the barriers.
question
Diffusion
answer
Process thru which innovation spreads via certain comm channels over time among members of a social system.
question
Types of Innovation
answer
(1) Commencement Innovation. (2) Cessation Innovation. (3) Prevention Innovation.
question
Commencement Innovation
answer
Work to see adoption of behavior.
question
Cessation Innovation
answer
Work to stop adoption of behavior. (People already do behavior)
question
Prevention Innovation
answer
Work to prevent behavioral adoption. (People are starting to adopt behavior)
question
Innovation - Decision Process
answer
(1) KNOWLEDGE of innovation. You have to help people gain knowledge toward innovation. (2) PERSUASION formation of + or - attitudes toward innovation. (3) DECISION to adopt or reject innovation. (4) APPLICATION of innovation. (5) CONFIRMATION of an application of decision.
question
Change Agents
answer
People who try to induce change.
question
Adopters
answer
People that adopt new behaviors
question
Type of Adopters
answer
(1) Innovators. (2) Early Adopters. (3) Early Majority. (4) Late Majority. (5) Laggards.
question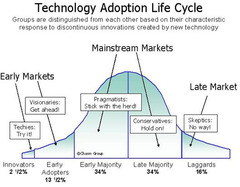
Rate of Adoption

answer
How fast a population adopts a behavior.
question
Innovators (Type of Adopters)
answer
The first to take on/use innovation. Done by risk-takers. Has high uncertainty.
question
Early Adopters (Type of Adopters)
answer
People who are a bit less comfortable with uncertainty. They are the next to accept innovation after innovators.
question
Early Majority
answer
When 1/3 of population adopts innovations.
question
Late Majority
answer
Low risk-taking. Adopt innovation late in campaign. Rely on peer pressure.
question
Laggards
answer
Skeptical of Innovation.
question
Factors that determine rate of Adoption
answer
- Perceived advantage of adopting innovation. - Complexity of innovation (Less complex -> faster adoption). - Triability (how easy people can try it) - Observability of Innovation. - Network strength & connectedness. - Social position of innovators & early adopters. - Exposure to innovators and early adopters.
question
Applying Innovation to campaigns
answer
- Target Innovators. - Be aware of factors affecting rate of adoption. - Don't forget the role of cultural benefits.
question
Transtheoretical Model of Change
answer
Stages people go through when changing behavior.
question
Problem with most Interventions.
answer
Target People as if they are ready to change.
question
Stages of Transtheoretical Model of Change
answer
(1) Precontemplation. (2) Contemplation. (3) Preparation. (4) Action. (5) Maintenance. (6) Termination.
question
Precontemplation (Transtheoretical Model of Change)
answer
Unaware of problem. Strategy: Create awareness; change values and beliefs.
question
Contemplation (Transtheoretical Model of Change)
answer
Aware of problem and want to change. Strategy: Persuade and Motivate.
question
Preparation (Transtheoretical Model of Change)
answer
Intends to take action. Strategy: Educate.
question
Action (Transtheoretical Model of Change)
answer
Practices desired behavior. Strategy: Facilitate Action.
question
Maintenance (Transtheoretical Model of Change)
answer
Already changed behavior and wants to maintain change. Strategy: Reinforce changes.
question
Termination (Transtheoretical Model of Change)
answer
Behavior is no longer temptation. Have complete confidence in control. Some may never reach this.
question
Self-efficacy
answer
Confidence in one's percieved ability to do what she/he wants, needs, or tries to do.
question
Role of Self-efficacy
answer
Self-efficacy beliefs are a mediator between knowledge and action.
question
Mastery Experiences
answer
When you succeed in something. Next time you approach it, you know how to do it.
question
Risk of Failure
answer
When you fail at something, next time you approach it you perceive yourself as less capable of handling it.
question
Vicarious Experiences Through Social Models
answer
learning through the experiences of people like you.
question
Social Persuasion
answer
Persuaded to change behavior by others in society.
question
Emotions and Efficacy
answer
Happiness --> more efficacy. Sadness --> less efficacy.
question
Benefits of Self-efficacy
answer
- Success. - Resilience to failures. - Try multiple times.
question
Costs of Too Much Self-Efficacy
answer
Unrealistic Levels of Efficacy --> Failure. High Coping Efficacy --> Risky Behavior.
question
Fear Appeals
answer
Imply some sort of risk/fear to cause behavior change.
question
Fear Appeals: Threat Component
answer
Must consider severity of threat and susceptibility to threat.
question
Fear Appeals: No Response
answer
When THREAT IS LOW and there is NO RESPONSE then message is not processed and efficacy is not considered.
question
Fear Appeals: Control the Danger
answer
When THREAT IS HIGH and EFFICACY IS HIGH then people control danger and protect selves. THEY ACCEPT MESSAGE. This is what you want.
question
Fear Appeals: Control Fear
answer
When THREAT IS HIGH and EFFICACY IS LOW then people control their fear. THEY IGNORE MESSAGE. Don't want this.
question
Creating high threat message. (Fear Appeals)
answer
It is personal and vivid (noise, language, vision, etc.)
question
Creating high efficacy message. (Fear Appeals)
answer
Explains how to do recommended response. Addresses barriers, gives evidence of behavior's effectiveness, and may role play desired behavior.
question
Social Comparison Theory
answer
People compare self to others who are similar to you. This offers guidance on attitudes and behavior. (Downward & Upward Comparisons)
question
Downward comparison (Social Comparison Theory)
answer
Comparing yourself to someone who is "Below' you. This helps with self esteem.
question
Upward comparison (Social Comparison Theory)
answer
Comparing self to someone who is "better" then you. Hurts self-esteem.
question
Bystander Effect
answer
When you don't act because you are with many people who are also not acting. EX: Woman falls and becomes conscious on street. No one does anything so when you see her you dont do anything either.
question
Causes of Bystander Effect
answer
Uncertainty and assumption that others will act.
question
Dyadic Effects
answer
Being effected by a specific person (EX: spouse).
question
Marriage Effects
answer
when you are influenced directly by the behavior of your spouse.
question
Widower Effect
answer
When someone dies just after their spouse dies.
question
Non-spousal Effects (things that effect others)
answer
Disability among family members, health behavior among friends, and breast cancer & mammography motivation.
question
Social Norms: Primary Premise
answer
We are influenced by our perceptions of others' behavior.
question
Social norms: Primary Suggestion
answer
Focus campaigns on majority healthy behaviors, as opposed to minority unhealthy behaviors.
question
Social Norms: Assumptions of Approach
answer
Behavior is shaped by how we THINK our peers behave. People over-perceive negative behavior of their peers.
question
Types of Misperceptions
answer
Misperception of Majority and Misperception of minority.
question
Pluralistic Ignorance (Misperception of Majority)
answer
Majority who engage in healthy behavior incorrectly believe they are in minority when they are actually in majority.
question
False Cosensus
answer
People incorrectly think that they are in majority when they are in minority.
question
Social Norms Campaigns how to.
answer
(1) Gather Data on Norms. (2) Raise awareness for underestimated positive majority behaviors or overestimated minority behaviors. (3) Help form more accurate perceptions. (4) More people act with positive norms.
question
Social Judgment Theory

answer
Change people's attitudes using Latitude of Rejection (LR), Latitude of Acceptance (LA), and Latitude of Non-commitment (LNC).
question
Elaboration Likelihood model (ELM)
answer
Individuals process info in either central processing or peripheral processing. and this effects how you form a message.
question
Central Processing (ELM)
answer
Used when person has high ability and is highly involved with issue. Focused on argument quality.
question
Peripheral Processing (ELM)
answer
Used when personal involvement is low and/or processing ability is low. Focused on delivery of message more then just message.
question
Sequential Persuasion Strategies
answer
Foot in the Door and Door in the Face.
question
Foot in the Door (Sequential Persuasion Strategies)
answer
Get presence known. Begin with small request most would do, follow with larger request. Focuses on consistency.
question
Door in the Face (Sequential Persuasion Strategies)
answer
Ask for initial requests so large that most reject it. Follow with 2nd moderate requests.



