Chapter 5 – Function of Skin, Sweat Glands, Cancer, & Burns – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Sudoriferous Glands
answer
Another name for Sweat Glands; all skin surfaces except nipples and parts of external genitalia contain sweat these (about 3 million per person)
question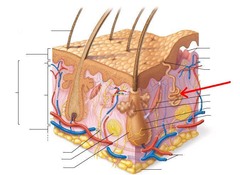
Eccrine Sweat Glands

answer
Type of Sweat Gland; most numerous type, abundent on palms, soles, and forehead, their secretion is sweat - regulation the body temperature
question
Apocrine Sweat Glands
answer
Type of Sweat Gland; confined to axillary and anogenital areas, secrete viscous milky or yellowish sweat that contains fatty substances and proteins
question
Ceruminous Gland
answer
Modified Apocrine Gland; lining of external ear canal, secretes earwax
question
Mammary Gland
answer
Modified Apocrine Gland; secretes milk out of tits
question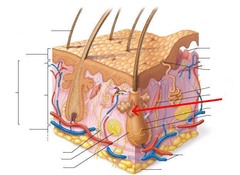
Sebaceous Gland

answer
Widely distributed gland, except for thick skin of palm and soles; relatively inactive until puberty and then stimulated by hormones
question
Secrete Sebum
answer
Oily holocrine secretion
question
Protection
answer
Function of Skin; protect body from outside sources
question
Body Temperature Regulation
answer
Function of Skin; homestasis, achieved by sweating or goosebumps
question
Cutaneous Sensation
answer
Function of Skin; Exteroreceptors respond to stimuli outside body, such as temperature and touch, free nerve endings sense painful stimuli
question
Metabolic Functions
answer
Function of Skin; Skin can synthesize vitamin D needed for calcium absorption in intestine, chemicals from keratinocytes can disarm some caracinogens
question
Blood Reservoir
answer
Function of Skin; skin can hold up to 5% of the body's total blood volume, skin vessels can be constricted to shunt blood to other organs, such as an exercising muscle
question
Excretion of wastes
answer
Function of Skin; skin can secrete limited amounts of nitrogenous wastes, such as ammonia, urea, and uric acid, sweating can cause salt and water loss
question
Chemical, Physical, and Biological Barriers
answer
Skin barriers of Protection
question
Chemical Barrier
answer
Skin Protection Barrier; skin secretes many chemicals, such as sweat, sebum, defensins, and melanin
question
Physical Barrier
answer
Skin Protection Barrier; flat, dead, deratinized cells of stratum corneum, surrounded by glycolipids, block most water and water-soluble substances
question
Biological Barrier
answer
Skin Protection Barrier; Epidermis contains phagocytic cells (dentritic cells of epidermis engulf foreign antigens and present to white blood cells, activating the immune response) and dermis contains macrophages (macrophages also activate immune system by presenting foreign antigens to white blood cells)
question
Insensible Perspiration
answer
Under normal, resting body temperature, sweat glands produce about 500 ml/day of unnoticeable sweat
question
Sensible Perspiration
answer
If body temperature rises, dilation of dermal vessels can increase sweat gland activity to produce 12L of noticeable sweat
question
Basal Cell Carcinoma
answer
Major type of Skin Cancer; least malignant and most common type, stratum basale cells proliferate and slowly invade dermis and hypodermis, cured by surgical excision in 99% of cases
question
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
answer
Major type of Skin Cancer; second most common type, involves keratinocytes of stratum spinosum, usually is a scaley redded papule on scalp, ears, lower lip, or hands, good prognosis if treated by radiation therapy or removed surgically
question
Melanoma
answer
Major type of Skin Cancer; cancer of melanocytes, is most dangerous type because it is highly metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy, treated by wide surgical excision accompanied by immunotherapy
question
Burn
answer
Tissue damage caused by heat, electricity, radiation, or certain chemicals
question
First-Degree Burn
answer
Degree of burn; epidermal damage only, localized redness, edema (swelling), and pain
question
Second-Degree Burn
answer
Degree of burn; epidermal and upper dermal damage, blisters appear
question
Third-Degree Burn
answer
Degree of Burn; entire thickness of skin invovled (full thickness burns), skin turns gray-white, cherry red, or black, no edema is seen and area is not painful because nerve endings are destroyed, skin grafting usually necessary
question
Asymmetry
answer
ABCD Rule for diagnosing Melanoma; What does A stand for?
question
Border Irregularity
answer
ABCD Rule for diagnosing Melanoma; What does B stand for?
question
Color
answer
ABCD Rule for diagnosing Melanoma; What does C stand for?
question
Diameter
answer
ABCD Rule for diagnosing Melanoma; What does D stand for?
question
6mm
answer
ABCD Rule of diagnosing Melanoma; What diameter length does the growth have to be?
question
Black, brown, tan, red, or blue
answer
ABCD Rule of diagnosing Melanoma; What colors does the growth contain?



