Chapter 13 cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Cancer
answer
is the uncontrollable growth of cells. Growth Division Differentiation
question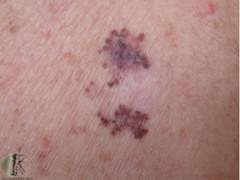
metastasize

answer
spread from where they develop to another part of the body
question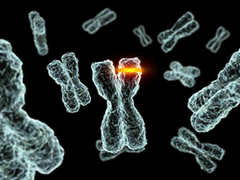
mutations

answer
can be inherited or caused by exposure to: Low-dose radiation Drugs Toxic chemicals Infection with certain viruses
question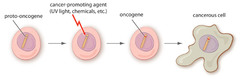
Oncogenes

answer
"on" switches that speed cell growth.
question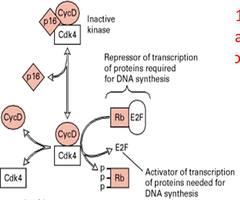
Tumor-suppressor genes

answer
"off" switches that slow cell growth. If tumor-suppressor genes mutate, they will no longer restrict cell growth
question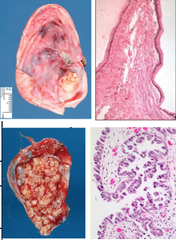
Benign tumors

answer
are surrounded by a capsule, and they do not spread or invade surrounding tissues.
question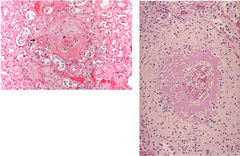
malignant

answer
Cells that metastasize
question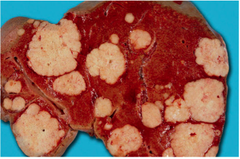
Metastasis

answer
Cancers are named according to the type of tissue from which they develop
question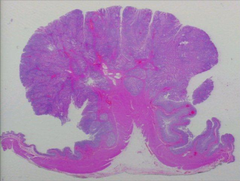
Carcinomas

answer
arise from epithelial tissue. Tissues that line & cover internal & external body surfaces (such as skin, lung, oral, stomach, breast, ovarian)
question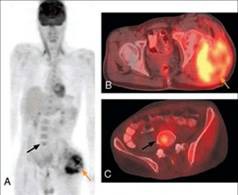
Sarcomas

answer
arise from connective or muscle tissue.
question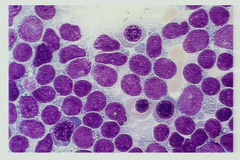
Leukemias

answer
cancers of the blood
question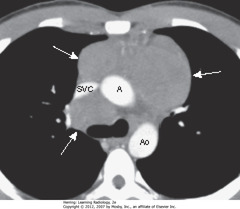
Lymphomas

answer
are cancers of the lymphatic
question
Cancer screening
answer
is an examination to detect cancer before a person has symptoms. Cancer screening and detection methods depends on the location of the possible cancer. Visual examination: skin, oral cavity Self-examination: breast, testicullar Clinical examination (physician) Laboratory testing: micro cells, blood spl Scans: MRI, CAT, x-ray, fiberscope
question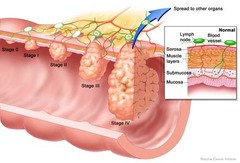
Staging

answer
Cancer staging describes the extent of growth and metastasis of cancer
question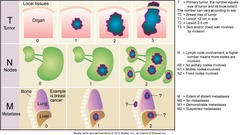
TNM system

answer
T describes the original tumor N describes if cancer has reached lymph nodes M describes if cancer has metastasized
question
Cancer Treatment

answer
Surgery Radiation Chemotherapy Laser therapy Photodynamic therapy Targeted therapies Stem Cell Transplants
question
Cure

answer
means that all traces of a localized tumor have been removed from the body and the former cancer patient has the same life expectancy as a person who never had cancer.
question
Surgery

answer
physician removes localized cancers by cutting it away. Usually physician removes tissue beyond the obvious cancer to increase the probability that all cancerous tissue is removed.
question
Radiation
answer
is energy which interferes with the molecular structures of cells, killing them
question
Chemotherapy
answer
is the use of anti-cancer drugs It is used most often when cancer has metastasized. Chemotherapy does not always destroy cancers completely because: Dosages are not high enough. Some tumors are drug resistant or develop resistance during therapy.
question
Laser
answer
is high intensity lights that can be focused with great precision. Shrink and destroy tumors Remove superficial cancers (skin) and in interior body locations (uterus, esophagus, and colon).
question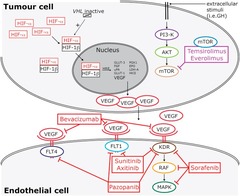
Targeted Therapies

answer
are substances that target specific molecules in specific cancers, they harm only the cancer, not the surrounding tissues. Limitation: cancer cells may develop changes that no longer allow the therapy to work
question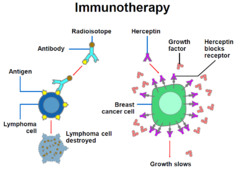
Immunotherapy

answer
biomodulation
question
Stem Cell Transplant

answer
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells whose daughter cells can develop into a variety of cell types.
question
Prevalent Cancers in the US
answer
Tobacco Diet Hormone Function Viral Infection Ultraviolet Radiation Unknown Causes
question
Cancers Related to Tobacco
answer
30% of all cancer deaths 87% of lung cancer deaths
question
Lung Cancer
answer
In the early stages, may be hard to detect because smokers often show the signs. chronic cough, excess sputum, wheezing, chest pain, and lung infection.
question
Lung Cancer RF & Prevention
answer
The number of cigarettes smoked/day, years smoked, how deeply inhaled Quitting smoking reduces the risk of developing lung cancer (after 10 years, the risk of lung cancer will be half that of a person who continued to smoke) Regular/high consumption of alcoholic beverages and obesity Passive smoking (secondhand smoke) is associated with a 20-30% increase in lung cancer risk for the nonsmoker. Asbestos particle inhalation Radon Gas exposure multiplies the carcinogenic effects of tobacco smoke
question
Larynx
answer
Hoarse voice, difficulty swallowing, and a sore throat
question
Oral cavity
answer
Visible, but they metastasize quickly
question
Esophagus
answer
Recurrent heartburn
question
Kidneys & bladder
answer
come in contact with inhaled carcinogens after the substances enter the bloodstream. Kidneys filter the carcinogens into the urine; thus exposing the kidney and bladder.
question
Pancreas
answer
Pancreas functions to secrete digestive enzymes & hormones Called "a silent cancer", are vague & nonspecific (nausea, vomiting, weakness and discomfort in the abdomen) causing the disease to go undetected as it progresses
question
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
answer
Affects blood-producing cells in bone marrow, primarily neutrophils (WBC which combat bacterial infections). Primary known causes are exposure to benzene and ionizing radiation contained in cigarette smoke.
question
Cancers Related to Diet
answer
Studies show that 1/3 of all annual cancer death in the US result from poor nutrition & lack of physical activity. Type of cancer related to diet: Stomach Colon & Rectum
question
Stomach Cancer
answer
Categorized as a "silent cancer" because in its early stages are attributed to minor intestinal upsets. Risk increases with age; doubling with each decade after 55. Primary RF are diets high in salt-cured, nitrate-cured, & smoked. Other RF are alcohol & cigarette smoking
question
Colon and Rectum
answer
Colorectal cancer is the third most deadly cancer in the United States. depend on location of the tumor. General signs are abdominal pain, change in bowel habits, and blood in the stools. Diet RF: red or processed meat, meat cooked in high temp. Inadequate fruits and vegetables intake
question
Fecal occult blood test
answer
home test that detects hidden blood in the stool.
question
Digital rectal exam
answer
a test in which a physician uses a gloved finger to feel the rectum or the prostate for abnormal growths
question
Sigmoidoscopy
answer
a procedure in which a physician views the lower portion of the colon via a flexible fiber-optic tube.
question
Colonoscopy
answer
a procedure in which a physician views the entire length of the colon using a flexible fiber-optic tube.
question
Cancers Related to Hormones
answer
Breast & Endometrial Cancers
question
Breast Cancer
answer
The 2nd leading cancer killer of women in the US Breast cancer in men accounts for 1% of cases in the US
question
Breast Cancer RF
answer
Inheritance (genes BRCA1/BRCA2) Age (incidence rises after 20 and drops in mid 70s) High cumulative exposure to ovarian hormones (specially estrogen). Early menarche (younger than age 12) Late menopause (older than age 55) Not bearing children Currently taking oral contraceptives or HRT Overweight & obesity(fat tissue produce estrogen)
question
Lumpectomy
answer
surgical removal of a breast tumor, including a layer of surrounding tissue.
question
Total mastectomy
answer
surgical removal of a breast & involved lymph nodes
question
Radical mastectomy
answer
surgical removal of a breast, underlying muscle, underarm fat, & lymph nodes
question
Endometrial Cancer
answer
The endometrium is the lining of the uterus. Endometrial cancer is most common in postmenopausal women. Primary symptom is abnormal uterine bleeding. Pap tests do not reveal endometrial cancer; a biopsy is needed. Associated with high cumulative exposure to estrogen similar to breast cancer RF (early menarche, late menopause, not bearing children & delaying pregnancy)
question
Cancers Related to Viral Infection
answer
Scientist believe the interaction between the virus and another agent result in the development of the cancer. Virus, alone, does not = cancer. In the US, the most prevalent is
question
Cervical Cancer
answer
Most women who are diagnosed with cervical cancer have no symptoms; their cancers are discovered early through a pap test.
question
Human papillomavirus
answer
is sexually transmitted; risk of infection increases with an increased number of sexual partners. There are many types of HPV *HPV 16 & 18 cause 70% of cervical cancers *HPV 6 & 11 cause 90% of genital warts *Vaccine is available for males and females before becoming sexually active. Vaccines do not prevent infection with all types of HPV, so vaccinated women still need periodic Pap tests.
question
Skin cancer
answer
Three types of UV radiation: UVA UVB UVC Exposure to UV radiation from the sun & tanning beds.
question
Melanin
answer
pigment, produced by melanocytes on the skin, which protect the skin from UV damage.
question
Skin Cancer
answer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Squamous Cell Carcinoma Malignant Melanoma
question
Basal Cell Carcinoma
answer
The most common cancer of the skin usually affects the head & neck. May look like moles or pimples with pearl-like borders Often crust, scale, and bleed Grows slowly and rarely metastasizes Treatment: Removed by surgery & cryotherapy
question
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
answer
The 2nd most common skin cancer. Caused mainly by UV exposure, but it can appear on skin which has been damaged by chemicals, burned, or exposed to x-ray. Other susceptible sites: skin that lines the mouth, nose, anus, & vagina. At risk people: construction workers, farmers, people who regularly sunbathe & use tanning beds.
question
Malignant Melanoma
answer
Melanoma starts at the melanocytes, which are located at the deepest layer of the epidermis. Deadly skin cancer because it grows deep into the skin and often metastasize. Primarily affects whites at a rate of 50% more men than women. The incidence of melanoma has been rising over the last 30 years. Most often seen on men's back & women's legs. Other body sites head, neck, skin under finger/toe nails, genitals, sole of feet, palms of hands, eye, anus, or vagina.
question
Typical Characteristics: "ABCDE
answer
Asymmetry (one side does not match other) Border (irregular, blurred, uneven) Color (blue, black, red or gray), Diameter (larger than a pencil eraser) Evolving (change in size, shape, color or appearance)
question
Atypical characteristics
answer
(rapidly growing melanomas do not show the typical "ABCDE"): Red and raised with regular border; often itch and bleed or It may have no color or be only slightly red.
question
Prostate Cancer
answer
Prostate is located beneath the bladder, surrounding the urethra, & it secretes part of the seminal fluid. The most prevalent cancer in men; most are slow-growing type of cancer. Because treating prostate cancer can be serious, many men consider the "watchful waiting" as their treatment choice.
question
Testicular Cancer
answer
The testicles are the organs in which sperm develop and are located in the scrotal sac beneath the penis. Testicular cancer is rare & curable Signs and symptoms Painless, swollen testis Sensation of heaviness or aching in the testis Small lump in one testis
question
Ovarian Cancer
answer
The ovaries are female organs in which eggs mature & are ovulated each month. The ovaries also produce estrogen & progesterone No S&S in early stage. As cancer progresses: Frequent urination or bloating Pressure in the abdomen Vaginal bleeding in postmenopausal women Irregular or heavy menses in premenopausal women
question
Reducing Your Risk for Cancer
answer
Change in bowel or bladder habits A sore that does not heal Unusual bleeding or discharge Thickening or lump in breast or elsewhere Indigestion or difficulty in swallowing Obvious change in a wart or mole Nagging cough or hoarseness



