Chapter 12- Inventory Management – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Objective of inventory management
answer
Strike a balance between inventory investment and customer service
question
Four functions of inventory
answer
1. To provide a selection of goods for anticipated customer demand and to separate the firm from fluctuations in that demand 2. Decouple various parts of the production process 3. Take advantage of quantity discounts 4. Hedge against inflation
question
Types of inventory
answer
Raw material inventory; work-in-process inventory; maintenance/repair/operating supply (MRO) inventory, and finished-goods inventory
question
Raw material inventory
answer
Materials that are usually purchased but have yet to enter the manufacturing process
question
Work-in-process (WIP) inventory
answer
Products or components that are no longer raw materials but have yet to become finished products
question
Maintenance/repair/operating (MRO) inventory
answer
Maintenance, repair, and operating materials
question
Finished-goods inventory
answer
end item ready to be sold, but still an asset on the company's books
question
ABC analysis
answer
Method for dividing on-hand inventory into three classifications based on annual dollar volume A = high dollar volume B = medium " " C = low " "
question
Cycle counting
answer
Continuing reconciliation of inventory with inventory records
question
advantages of cycle counting
answer
- eliminates shutdown and interruption of production necessary for annual physical inventories - eliminates annual inventory adjustments - trained personnel audit the accuracy of inventory - allows cause of errors to be identified and remedial action to be taken - maintains accurate inventory records
question
Shrinkage
answer
Retail inventory that is unaccounted for between receipt and sale
question
Pilferage
answer
Small amount of theft
question
Independent demand
answer
demand for item is independent of the demand for any other item in inventory
question
Holding costs
answer
Costs associated with holding or "carrying" inventory over time
question
Ordering cost
answer
Cost of ordering process; includes costs of supplies, forms, order processing, purchasing, clerical support, etc.
question
setup cost
answer
cost to prepare a machine or process for manufacturing an order
question
setup time
answer
time required to prepare a machine or process for production
question
Three independent demand models
answer
basic economic order quantity (EOQ) model; production order quantity model; quantity discount model
question
Economic order quantity (EOQ) model
answer
inventory-control technique that minimizes the total of ordering and holding costs
question
EOQ model assumptions
answer
- demand for an item is known, reasonably constant, and independent of decisions for other items - lead time is known and consistent - receipt of inventory is instantaneous and complete - quantity discounts are not possible - only variable costs are the cost of setting up or placing an order and the cost of holding or storing inventory over time - stockouts (shortages) can be completely avoided if orders are placed at the right time
question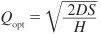
Optimal order quantity
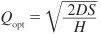
answer
Point where the ordering-cost curve and the carrying-cost curve intersect
question
Annual setup cost
answer
number of orders placed per year x setup or order cost per order ((D/Q)) (S)
question
Annual holding cost
answer
average inventory level x holding cost per unit per year ((Q/2)) (H)
question
expected number of orders
answer
N = (D / Q)
question
Expected time between orders
answer
T = (number of working days per year / N)
question
total annual cost

answer
Setup (order) cost + holding cost
question
Robust
answer
giving satisfactory answers even with substantial variation in the parameters; EOQ is a robust model
question
lead time
answer
In purchasing system, the time between placing an order and receiving it; in production system, the wait, move, queue, setup, and run times for each component produced
question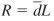
Reorder point (ROP)
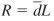
answer
inventory level (point) at which action is taken to replenish the stocked item ROP = d x L
question
Safety stock (ss)
answer
Extra stock to allow for uneven demand; a buffer
question
Production order quantity model
answer
economic order quantity technique applied to production orders
question
probabilistic model
answer
Statistical model applicable when product demand or any other variable is not known but can be specified by means of a probability distribution annual stockout costs = (sum of the units short for each demand level) x (probability of that demand level) x (the stockout cost/unit) x (the number of orders per year)
question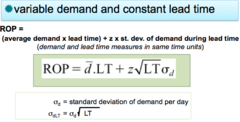
demand is variable and lead time is constant

answer
ROP = (average daily demand x lead time in days) + Z(standard deviation of demand per day x standard deviation lead time in days)
question
demand is constant and lead time is variable
answer
ROP = (daily demand x average lead time in days) + Z x daily demand x standard deviation of lead time in days
question
both demand and lead time are variable
answer
ROP = (average daily demand x average lead time in days) + Z(standard deviation of demand per day x standard deviation lead time in days)
question
single-period inventory model
answer
System for ordering items that have little or no value at the end of a sales period (perishables) -underestimated: Cs = Sales price per unit - cost per unit - overestimated: Co = cost per unit - salvage value per unit
question
Service level
answer
Probability of not stocking out Cs / (Cs + Co)
question
Fixed-period (P) system
answer
System in which inventory orders are made at regular time intervals



