Ch. 5 A & P: The Integumentary System – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Explain the basis of hair color
answer
• Melanins made by melanocytes at base of hair follicle, transferred to cortical cells • Various proportions of 4 colors of melanin (yellow, rust, brown, black) make distinct hair shades; red hair also has pheomelanin • When melanin production slows, air bubbles replace melanin in hair shaft, turning the hair gray or white.
question
What are the 2 component layers of the skin?
answer
1. Epidermis 2. Dermis
question
The Epidermis is composed of what kind of tissue?
answer
Stratified Squamous Epithelial
question
The Dermis is composed of what kind of tissue?
answer
- Bottom layer (reticular layer) is composed of Dense Irregular Connective tissue - The rest is of the Dermis is the Papillary layer (top layer) & is composed of Areolar Connective tissue
question
What are the 5 layers or strata in the Epidermis?
answer
1. Stratum Basale (Basal Layer) 2. Stratum Spinosum (Prickly Layer) 3. Stratum Granulosum (Granular Layer) 4. Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer) 5. Stratum Corneum (Horny Layer)
question
What is a burn?
answer
Tissue damage inflicted by intense heat, electricity, radiation, or certain chemicals, all of which denature cell proteins and kill cells in the affected areas.
question
What is 1 immediate threat to life resulting from severe burns?
answer
Dehydration due to loss of body fluid through uncovered subcutaneous layers
question
How do you evaluate burns?
answer
Use "rule of nines" to estimate surface area affected and thus total fluid loss
question
What is the "rule of nines"?
answer
- Divides the body into 11 areas, each accounting for 9% of total body area, plus an additional area surrounding the genitals accounting for 1% of body surface area.
question
What is the total body % area of the head & neck
answer
- Anterior and posterior= 9% - Just Anterior is 4 1/2%
question
What is the total body % area of the upper limbs?
answer
- Anterior and posterior= 18% - Just anterior is 4 1/2% for each arm
question
What is the total body % area of the trunk?
answer
-Anterior and posterior= 36% - Just anterior is 18%
question
What is the total body % are of the lower limbs?
answer
-Anterior and posterior= 36% - Just anterior is 9% for each leg
question
What accounts for 1% of the total body area?
answer
Perineum (groin)
question
How are burns classified?
answer
• Based on depth of damage as first, second, or third degree burn
question
What happens in 1st degree burns?
answer
- Only the epidermis is damaged.
question
What is an example of 1st degree burn?
answer
Sunburn
question
What happens with 2nd degree burns?
answer
- Injure the epidermis and the upper region of the dermis.
question
What are symptoms of a 1st degree burn?
answer
Symptoms include localized redness, swelling, and pain
question
What is the treatment for 1st degree burns?
answer
Tend to heal in 2 to 3 days without special attention
question
What are symptoms for 2nd degree burns?
answer
Symptoms are same as 1st degree burns but blisters will form also.
question
What is the treatment for 2nd degree burns?
answer
Skin regeneration occurs with little or no scarring within 3 to 4 weeks if care is taken to prevent infection.
question
What are 1st and 2nd degree burns referred to?
answer
Partial-tickness burns
question
What happens with 3rd degree burns?
answer
- Full thickness burns, involving the entire thickness of the skin - Affects entire epidermis and dermis
question
What are symptoms of 3rd degree burns?
answer
- The burned area appears gay-white, cheery red, or blackened - Since the nerve endings have been destroyed, the burned area is not painful
question
What is the treatment for 3rd degree burns?
answer
- Although skin might eventually regenerate by proliferating epithelial cells at the edges of the burn or stem cells in hair follicles, it is usually impossible to wait tat long because of fluid loss and infection - Skin grating is advised
question
When is a burn considered critical?
answer
1 Over 25% of the body has second-degree burns 2. Over 10% of the body has third-degree burns 3. There are third-degree burns of the face, hands, or feet
question
What do facial burns introduce?
answer
The possibility of burned respiratory passageways, which can swell and cause suffocation
question
What do burns at the joints introduce?
answer
Scar tissue can severely limit joint mobility
question
What are the 3 major forms of skin cancer?
answer
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma 2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma 3. Melanoma
question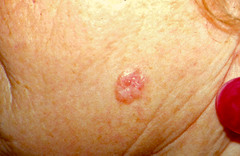
What is Basal Cell Carcinoma?

answer
- Cancer of stratum basal - Least malignant and most common, accounts for nearly 80% of cases. - Slowing growing
question
What causes Basal Cell Carcinoma?
answer
- Stratum basale cells overproliferate, invade dermis and hypodermis
question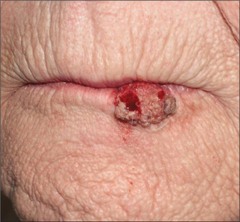
What is Squamous Cell Carcinoma?

answer
- Cancer of keratinocytes of stratum spinosum. - Second most common skin cancer. - Tends to grow rapidly and metastasize if not removed.
question
How does Squamous Cell Carcinoma usually appear?
answer
- Scaly reddened papule (small, rounded elevation) that arises most often on the head (scalp,ears, and lower lip), and hands.
question
Treatment for Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
answer
- If it is caught early and removed surgically or by radiation therapy, the chance of complete cure is good.
question
How does Basal Cell Carcinoma usually appear?
answer
- Occur most often on sun-exposed areas of the face and appear as shiny, dome-shaped nodules that later develop a central ulcer with a pearly, beaded edge.
question
Treatment for Basal Cell Carcinoma:
answer
- Full cure by surgical excision is the rule in 99% of cases.
question
How many Americans develop skin cancer at some point in their life?
answer
1 in 5 Americans
question
What is Melanoma?
answer
- Cancer of Melanocytes - Most dangerous skin cancer because it is highly metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy. - It accounts for only 2-3% of skin cancers, but its incidence is increasing rapidly (by 3-8% per year in the US)
question
How does Melanoma usually appear?
answer
- Can begin wherever there is pigment - Most appear spontaneously, and about one-third develop from preexisting moles. - Spreading brown to black patch that metastasizes rapidly to surrounding lymph and blood vessels.
question
Treatment for Melanoma:
answer
- Key is early detection - Chance of survival is poor if the lesion is over 4mm thick - Wide surgical excision accompanied by immunotherapy (immunizing the body against its cancer cells)
question
What is the ABCD rule?
answer
A: Asymmetry B: Border Irregularity C: Color D: Diameter
question
What does Asymmetry mean in the ABCD rule?
answer
The two sides of the pigmented spot or mole do not match
question
What does Border irregularity mean in the ABCD rule?
answer
The borders of the lesion exhibit indentations
question
What does color mean in the ABCD rule?
answer
The pigmented spot contains several colors (blacks, browns, tans, and sometimes blues and reds)
question
What does diameter mean in the ABCD rule?
answer
The spot is larger than 6mm in diameter (the size of a pencil eraser)
question
Which of the following is a metabolic function of skin? A.) cutaneous sensation B.) synthesis of a vitamin D precursor C.) body temperature regulation D.) elimination of nitrogenous wastes
answer
B.) synthesis of a vitamin D precursor -Yes, this is a function of the skin carried out by chemical reactions in the skin. When sunlight bombards the skin, modified cholesterol molecules are converted to a vitamin D precursor (called cholecalciferol), which is transported via the blood to the liver and kidneys, where it is converted into a hormone called calcitriol, or active vitamin D.
question
Which skin function is NOT correctly matched with the structure that accounts for that function? A.) keratinocytes: physical barrier B.) tactile corpuscles: cutaneous sensation C.) eccrine glands: excretion D.) apocrine gland: thermoregulation
answer
D.) apocrine gland: thermoregulation -While the function of the apocrine cells is not well understood, they do not provide much assistance in thermoregulation because of their location.
question
The most dangerous type of skin cancer is __________. A.) basal cell carcinoma B.) squamous cell carcinoma C.) melanoma D.) All of these skin cancers are equally dangerous.
answer
C.) melanoma -Melanoma, cancer of melanocytes, is the most dangerous skin cancer because it is highly metastatic and resistant to chemotherapy. These cancers appear spontaneously, and about one-third develop from preexisting moles.
question
The biggest risk factor for the development of skin cancer is excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight. Exposure to UV light in a tanning booth is safer. Is this statement true or false? A.) True B.) False
answer
B.) False -The single most important risk factor for skin cancer is overexposure to the UV radiation in sunlight. UV radiation damages DNA bases and appears to disable tumor suppressor genes, leading to the formation of cancerous cells. There is no such thing as a "healthy tan." Tanning booths use the same UV mechanism to stimulate melanin production; the UV exposure is the primary mechanism that leads to skin cancer.
question
Which of the following would be a sign of a melanoma? A.) asymmetry B.) uniform coloration C.) a size smaller than 6 mm D.) regular borders
answer
A.) asymmetry -Cancerous growths exhibit asymmetry. Benign growths exhibit symmetry, regular borders, uniform coloration, and they are usually less than 6 mm in diameter.
question
Which of the following is NOT an immediate threat to the system as a result of burns? A.) bacterial infection B.) renal failure C.) dehydration D.) electrolyte imbalance
answer
A.) bacterial infection -While it is true that infection is a long term threat, the fluid balance must be restored first in order to stabilize the burn trauma.
question
Susan sat out in the sun watching a baseball game. She developed small blisters on her unprotected shoulders and neck. What type of burn is represented by the formation of the blisters? A.) first-degree burn B.) second-degree burn C.) third-degree burn D.) full-thickness burn
answer
B.) second-degree burn -Second-degree burns injure the epidermis and the superficial region of the dermis. Symptoms mimic those of first-degree burns, but blisters also appear.
question
How can the rule of nines help indicate whether a burn should be considered critical? A.) The rule of nines can provide a rough estimation of the percentage of body surface affected by a burn. B.) The rule of nines states that for every nine specified locations of the body that are burned, the degree of burn severity increases. C.) The rule of nines helps to indicate the depth of the burn through the different layers of the skin. D.) The rule of nines indicates that for every 9 square centimeters of skin surface that is burned, the severity of the burn increases
answer
A.) The rule of nines can provide a rough estimation of the percentage of body surface affected by a burn. -The rule of nines divides the body into 11 regions of 9%each, plus 1% for the perineal area. For example, one whole arm, front and back, accounts for approximately 9% of the body surface. Critical burns are classified by the degree or depth of the burn and the surface area affected.
question
Which of the following best describes a third-degree burn? A.) a burn that affects at least 25% of the body surface area B.) a burn that affects all of the layers of the epidermis C.) a burn that affects the entire thickness of the integument D.) a burn that presents extremely painful blisters, redness, and swelling
answer
C.) a burn that affects the entire thickness of the integument -Degree refers to the regions of skin affected by the burn. Third-degree burns are full-thickness burns that involve the entire thickness of the skin.
question
Serious burns pose a significant threat to the body because they can __________. A.) lead to kidney failure and circulatory shock B.) lead to liver failure, which, if untreated, can lead to blood toxicity C.) lead to destruction of muscle tissue, resulting in permanent loss of mobility D.) lead to nervous system failure and permanent paralysis
answer
A.) lead to kidney failure and circulatory shock - Burns can destroy the layers of skin that retain fluids in the body. When burns cause a drastic loss of these fluids, including electrolytes and proteins, kidney and circulatory failure can occur. - Burns on the surface of the body do not significantly affect liver function unless many other critical systems are already failing.
question
Critical burn injuries will likely be treated with all of the following EXCEPT __________. A.) providing the patient with thousands of extra nutritional calories B.) significant infection control measures C.) an intravenous supply of fluids D.) pressing an ice-cold washcloth, towel, or pad to the burned area
answer
D.) pressing an ice-cold washcloth, towel, or pad to the burned area -Pressing a cold pad to a mildly burned site, such as a sunburn, may relieve some discomfort. For a critical burn, however, this is not as important as treating other factors.
question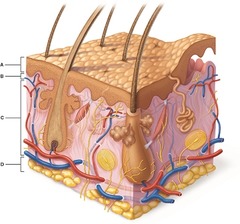
Which layer is composed primarily of dense irregular connective tissue?

answer
- Reticular layer of the Dermis -consists primarily of dense, interwoven fibers of collagen designed to resist tearing from any direction.
question
Which type of cell is NOT found in the epidermis? A.) pain receptors B.) keratinocytes C.) melanocytes D.) dendritic cells
answer
A.) pain receptors -Pain receptors are found deeper in the papillary layer of the dermis.
question
Which skin pigment is made in the skin as a natural defense against UV radiation? A.) carotene B.) keratin C.) melanin D.) hemoglobin
answer
C.) melanin -Melanin is the only one of the three pigments (melanin, carotene, and hemoglobin) that contribute to skin color that is actually produced in the skin itself.
question
Surface skin cells regenerate from stem cells found in which specific region? A.) in the stratum basale B.) in the stratum corneum C.) in the deepest layer of the skin D.) in the papillary layer of the dermis
answer
A.) in the stratum basale -The stratum basale is the deepest layer of the epidermis, and the location of highly mitotic cells.
question
Which of the following layers is found only on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet? A.) stratum basale B.) stratum granulosum C.) stratum lucidum D.) stratum corneum
answer
C.) stratum lucidum -Stratum lucidum is found only in the thick skin on the soles of the feet or palms of the hands. When present, it is located between the stratum corneum and stratum granulosum.
question
The integument's ability to resist tearing when stretched is largely due to the __________. A.) desmosomes that bind together the cells of the stratum basale B.) abundance of dense fibers found in the papillary layer of the dermis C.) network of collagen fibers present in the reticular layer of the dermis D.) dead, flattened layers of keratinized cells that fuse to form the stratum corneum
answer
C.) network of collagen fibers present in the reticular layer of the dermis -The dermis is thick and strong, made up of dense fibrous connective tissue.
question
Which epidermal cells act as sensory touch receptors? A.) melanocytes B.) keratinocytes C.) dendritic cells D.) tactile cells
answer
D.) tactile cells -Tactile means "touch." Tactile cells along the border between the epidermis and dermis are touch receptors.
question
Which dermal layer is responsible for the dermal properties of skin that are evident as cleavage lines? A.) the reticular layer B.) the papillary layer C.) the basal layer D.) the granular layer
answer
A.) the reticular layer -The dermis has a collection of dense regular connective tissues with large amounts of collagen arranged in a regular pattern that creates cleavage lines.
question
In people with lighter skin, respiratory failure can lead to a change in the color of the skin. Which pigmentation factor is affecting this change? A.) hemoglobin B.) folic acid C.) carotene D.) melanin
answer
A.) hemoglobin -As the blood becomes hypoxic, hemoglobin is carrying less oxygen. This deoxygenated state leads to the condition known as cyanosis.
question
A Caucasian patient with pale skin is treated for low blood pressure with medication that elevates the blood pressure; however, the skin's pallor does not change. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the pallor in this patient? A.) respiratory disease that results in the blood being poorly oxygenated B.) the presence of hematomas in the skin C.) hypertension caused by excessive use of the medication D.) Anemia
answer
D.) Anemia - Red blood cells (RBCs) help give blood its color. Anemia is a set of signs and symptoms that appear when a person does not have enough healthy RBCs. Pallor, or paleness, is a sign/symptom of anemia because the blood vessels in the dermal layer lack normal RBCs.
question
Which of the following represents a difference between eccrine sweat glands and apocrine sweat glands? A.) Eccrine sweat glands begin to function at puberty, while apocrine sweat glands function throughout life. B.) Eccrine sweat glands are located deeper in the dermis than apocrine sweat glands. C.) The secretions of apocrine sweat glands contain more fat and protein than do the secretions of eccrine sweat glands. D.) Eccrine sweat glands use exocytosis to make secretions, while apocrine sweat glands do not.
answer
C.) The secretions of apocrine sweat glands contain more fat and protein than do the secretions of eccrine sweat glands - Compared to the watery secretions of eccrine glands, apocrine sweat glands have secretions that are enriched with fats and proteins.
question
You discover a new type of gland associated with the skin. Chemical analysis of the product shows a secretion has a pH of 4, consists of 99% water, and contains traces of normal electrolytes including urea, vitamin C, and dermicidin. There are no traces of fats or proteins. How would you classify this new gland? A.) mammary gland B.) sebaceous gland C.) ceruminous gland D.) eccrine gland
answer
D.) eccrine gland - Eccrine glands produce true sweat
question
Which glands secrete an oily product that softens the skin and hair? A.) eccrine sweat glands B.) ceruminous glands C.) sebaceous glands D.) apocrine sweat glands
answer
C.) sebaceous glands - Sebaceous glands secrete an oily substance called sebum. Sebum softens and lubricates the hair and skin, slows water loss from the skin when external humidity is low, and has bactericidal properties.
question
If a person were born without eccrine glands, what skin function would he or she have a hard time completing? A.) thermoregulation B.) metabolic function C.) cutaneous sensation D.) having the skin act as a physical barrier
answer
A.) thermoregulation - Sweat is used for thermoregulation. As sweat is released onto the surface of the epidermis, heat from the body is conducted into the water. Water is a better conductor of heat than air is. As the sweat evaporates, the heat from the body dissipates into the environment.
question
The skin is permeable to organic solvents, such as acetone or turpentine, because they ________. A.) can dissolve the lipid bilayers of epidermal and dermal cell plasma membranes B.) are small molecules that bypass skin cells and therefore directly enter the blood C.) solubilize the skin's keratin filaments D.) solubilize the skin's collagen fibers
answer
A.) can dissolve the lipid bilayers of epidermal and dermal cell plasma membranes. - Organic solvents are carbon-based substances that are capable of dissolving or dispersing one or more other substances like the phospholipids of the plasma membrane.
question
When a baby is born what is its skin covered with?
answer
Vernix caseosa
question
What is Vernix caseosa?
answer
A white, cheesy-looking substance produced by the sebaceous glands that protects the fetus's skin within the water-filled amnion.
question
How is the baby's skin when born?
answer
- Very thin and often has accumulations in the sebaceous glands on the forehead and nose that appear as small white spots called milia. - This normally disappeared by the third week after birth.
question
During infancy and childhood what does the skin do?
answer
- Skin is usually well formed by the 5th gestation - The skin thickens, and more subcutaneous fat is deposited - Although we all have approximately the same number of sweat glands, the number that function increases in the first two years after birth and is determined by climate.
question
Why do some people have more active sweat glands than others?
answer
- People who grow up i hot climates have more active sweat glands than those raised in cooler areas.
question
What happens to the skin during adolescence?
answer
- Skin & hair become oilier as sebaceous glands are activated, and acne may appear. - Acne generally subsides in early adulthood, and skin reaches its optimal appearance when we reach our 20s and 30s - After that the skin starts to show the effects of cumulative environmental assaults (abrasion, wind, sun, chemicals)
question
What happens to the skin when old age approaches?
answer
- The rate of epidermal cell replacement slows - The skin thins, and its susceptibility to bruises and other injuries increases - Elastic fibers clump, and collagen fibers become fewer and stiffer - Subcutaneous fat disappears - Wrinkles form due to loss of tissue - Activity of hair follicles slows - Hair loses pigment



