Cell Cycle – Cancer and Mitosis – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
cell cycle
answer
The regular sequence of growth & division that cells undergo.
question
mitosis

answer
Cell's division (PMAT) of the nucleus. Final product is 2 cells that are exactly like the parent cell.
question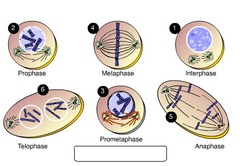
the four phases of mitosis

answer
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
question
prophase
answer
first and longest phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes become visible and the centrioles separate and take up positions on the opposite sides of the nucleus
question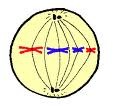
metaphase

answer
the second stage in mitosis in which the duplicated chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
question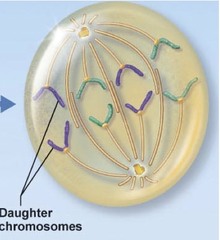
anaphase

answer
the third phase of mitosis , the chromatids of each chromosome separate/ split at the centromere and move in opposite
question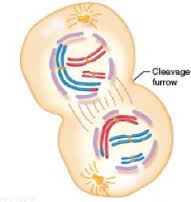
telophase

answer
The fourth and final stage of mitosis, in which daughter nuclei are forming and cytokinesis has typically begun.
question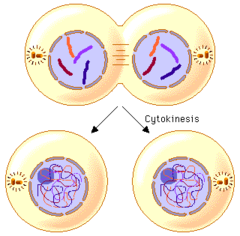
cytokinesis

answer
division of cytoplasm after mitosis & meosis
question
chromosomes
answer
A cellular structure carrying genetic material, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
question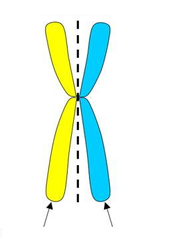
sister chromatids

answer
Duplicate copies of DNA, attached at a centromere; distributed to daughter cells
question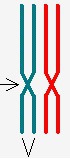
centromere

answer
Area where the two copies of a chromosome are attached.
question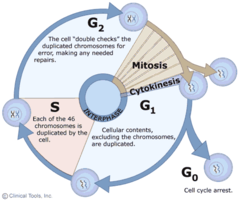
interphase

answer
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
question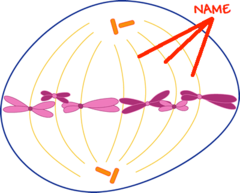
spindle fibers

answer
Special microtubules made of proteins which connect to centromeres and pull apart chromosomes.
question
G1 Phase

answer
Growth Phase: stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions, performs protein synthesis
question
S Phase

answer
Synthesis Phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
question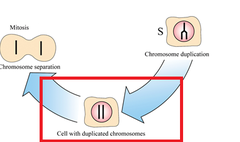
G2 Phase

answer
Growth Phase: The second growth phase, of the cell cycle, Cells prepare to divide
question
DNA
answer
The cell's blueprint. A double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule that determines the inherited traits of an organism.
question
cancer
answer
A disease in which some body cells grow and divide uncontrollably, damaging the parts of the body around them.
question
tumor suppressor genes
answer
A gene whose protein products inhibit cell division, thereby preventing uncontrolled cell growth (cancer).
question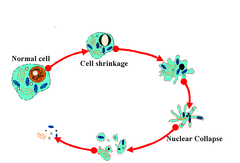
apoptosis

answer
Programmed cell death
question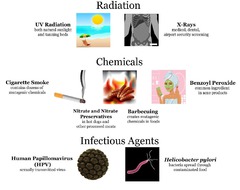
mutagen

answer
A chemical or physical agent that interacts with DNA and causes a mutation.
question
Nucleus
answer
Contains DNA
question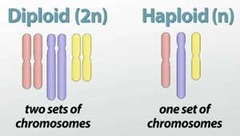
Diploid

answer
2 sets of chromosomes
question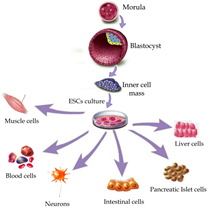
Differentiation

answer
Process in which cells become specialized in structure and function
question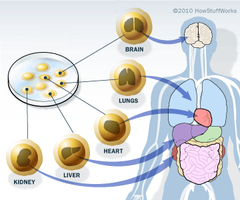
Stem cell

answer
unspecialized cells that retain the ability to become a wide variety of specialized cells
question
onco-
answer
cancer



