Biological catalyst
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
macromolecule
answer
There are Four major types of biological macromolecules that make up the human body: nucleic acids (DNA & RNA), Carbohydrates, Proteins and Fats
question
polymer
answer
a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together by covalent bonds
question
monomer
answer
the subunit that serves as the building block of a polymer
question
enzyme
answer
a macromolecule serving as a catalyst, a chemical agent that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Most are proteins.
question
dehydration reaction
answer
a chemical reaction in which 2 molecules become covalently bonded to each other with the removal of a water molecule
question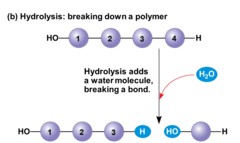
hydrolysis

answer
a chemical reaction that breaks bonds between 2 molecules by the addition of water; functions in disassembly of polymers to monomers
question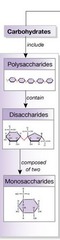
carbohydrates

answer
a sugar (monosaccharide) or one of its dimers (disaccharide) or polymers (polysaccharide)
question
monosaccharide
answer
the simplest carbohydrate, active alone or serving as a monomer for disaccharides and polysaccharides. Also known as simple sugars, that are generally some multiple of CH2O
question
disaccharide
answer
a double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic linkage formed by a dehydration reaction
question
glycosidic linkage
answer
a covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction
question
polysaccharide
answer
Polymers of simple sugars covalently linked by glycosidic bonds
question
starch
answer
a storage polysaccharide in plants, consisting entirely of glucose monomers joined by alpha glycosidic linkages
question
glycogen
answer
an extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch
question
cellulose
answer
a structural polysaccharide of plant cell walls, consisting of glucose monomers joined by beta glycosidic linkages
question
chitin

answer
a structural polysaccharide, consisting of amino sugar monomers, found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthopods
question
lipid
answer
Hydrophobic. Considered monomers. Any of a group of large biological molecules, including fats, phospholipids, and steroids, that mix poorly, if at all, with water. Provide an efficient form of energy storage.
question
fat
answer
a lipid consisting of 3 fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule; also called a triacylglycerol or a triglyceride.
question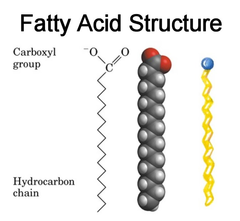
fatty acid

answer
a carboxylic acid with a long carbon chain; vary in length and in the number and location of double bonds; 3 fatty acids linked to a glycerol molecule form a fat molecule, also known as a triacyglycerol or a triglyceride
question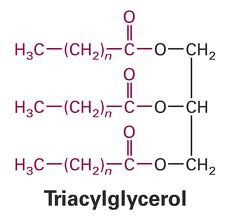
triacylglycerol

answer
a lipid consisting of 3 fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule; also called a fat or triglyceride
question
saturated fatty acid

answer
a fatty acid in which all carbons in the hydrocarbon tail are connected by single bonds, thus maximizing the number of hydrogen atoms that are attached to the carbon skeleton
question
unsaturated fatty acid

answer
a fatty acid that has one or more double bonds between carbons in the hydrocarbon tail. Such bonding reduces the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton
question
trans fat
answer
an unsaturated fat, formed artificially during hydrogenation of oils, containing one or more trans double bonds
question
phospholipid
answer
a lipid made up of glycerol joined to 2 fatty acids and a phosphate group. The hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids act as nonpolar, hydrophobic tails, while the rest of the molecule acts as a polar, hydrophilic head.; form bilayers that function as biological membranes
question
steroids
answer
a type of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of 4 fused rings with various chemical groups attached
question
cholesterol
answer
a steroid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids, such as many hormones
question
catalyst
answer
a chemical agent that selectively increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
question
Polypeptide
answer
A chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds or dehydration reactions
question
protein
answer
a biologically functional molecule consisting of one or more polypeptides folded and coiled into a specific 3D structure
question
amino acid
answer
An organic molecule possessing both a carboxyl and an amino group; serve as monomers of polypeptides
question
peptide bond
answer
the covalent bond between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on another, formed by dehydration reaction
question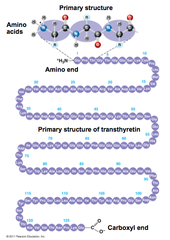
primary structure

answer
the level of protein structure referring to the specific linear sequence of amino acids
question
secondary structure
answer
regions of repetitive coiling or folding of the polypeptide backbone of a protein due to hydrogen bonding between constituents of the backbone (not the side chains).
question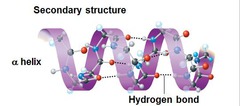
alpha helix

answer
a coiled region constituting one form of the secondary structure of proteins, arising from a specific pattern of hydrogen bonding between the atoms of the polypeptide backbone (not the side chains)
question
beta pleated sheet
answer
one of the secondary structure of proteins in which the polypeptide chain fold back and forth. 2 regions of the chain lie parallel to each other and are held together by hydrogen bonds between atoms of the polypeptide backbone (not the side chains).
question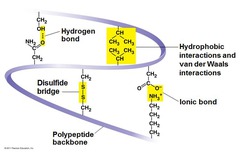
tertiary structure

answer
The overall shape of a protein molecule due to interactions of amino acid side chains, including hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and disulfide bridges
question
hydrophobic interaction
answer
a type of weak chemical interaction caused when molecules that do not mix with water coalesce to exclude water
question
disulfide bridge
answer
a strong covalent bond formed when the sulfur of one cysteine monomer bonds to the sulfur of another cysteine monomer
question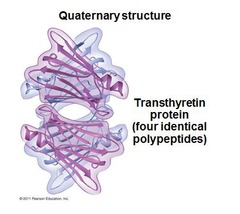
quaternary structure

answer
the particular shape of a complex, aggregate protein, defined by the characteristic 3D arrangement of its constituent subunits, each a polypeptide
question
sickle-cell disease
answer
a recessively inherited human blood disorder in which a single nucleotide change in the beta globin gene causes hemoglobin to aggregate, changing red blood cell shape and causing multiple symptoms in afflicted individuals
question
denaturation
answer
in proteins, a process in which a protein loses its native shape due to the disruption of weak chemical bonds and interactions, thereby becoming Biologically inactive; in DNA, the separation of the two strands of the double helix. Occurs under extreme (noncellular) conditions of pH, salt concentration or temperature
question
chaperonin
answer
a protein complex that assists in the proper folding of other proteins
question
gene
answer
a discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses)
question
nucleic acid
answer
a polymer (polynucleotide) consisting of many nucleotide monomers; serves as a blueprint for proteins and, through the actions of proteins, for all cellular activities. the 2 types of nucleic acid are DNA and RNA
question
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
answer
a double-stranded, helical nucleic acid molecule, consisting of nucleotide monomers with a deoxyribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T); capable of being replicated and determining the inherited structure of a cell's proteins
question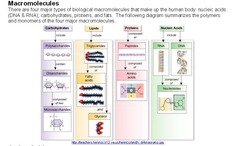
ribonucleic acid (RNA)

answer
a type of nucleic acid consisting of a polynucleotide made up of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis, gene regulation, and as the genome of some viruses
question
polynucelotide
answer
a polymer consisting of many nucleotide monomers in a chain. The nucelotides can be those of DNA or RNA.
question
nucleotide
answer
the building block of a nucleic acid, consisting of a 5 carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and one or more phosphate groups
question
pyrimidine
answer
1 of 2 types of nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides, characterized by a 6-membered ring. Cytosine (C), thymine (T) and uracil (U) are examples of these.
question
purines
answer
1 of 2 types of nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides, characterized by a 6-membered ring fused with a 5-membered ring. Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are examples of these.
question
deoxyribose
answer
the sugar component of DNA nucleotides, having 1 of fewer hydroxyl group than ribose, the sugar component of the RNA nucleotide
question
ribose
answer
the sugar component of RNA nucleotides
question
double helix
answer
the form of native DNA, referring to its 2 adjacent antiparallel polynucleotide strands wound around an imaginary axis into a spiral shape
question
antiparallel
answer
referring to the arrangement of the sugar-phophate backbones in a DNA double helix (they run in opposite 5' -> 3' directions)
question
Saturated fat
answer
All carbons in the hydrocarbon tail are connected by single bonds
question
Unsaturated fat
answer
A fatty acid that has one or more double bonds between carbons in the hydrocarbon tail.
question
What are 6 functions of Proteins?
answer
Structural support Storage Transport Cellular Communications Movement Defense against substaces
question
Primary Protein Structure
answer
Primary structure - the sequence of amino acids in a protein Primary structure is determined by inherited genetic information
question
Ester bond
answer
...
question
Phosphodiester bond
answer
...
question
ATP
answer
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
question
nitrogenous base
answer
...
question
What are the three types of Polymers?
answer
C - P - N Carbohydrates Proteins Nucleic Acids
question
In which two ways do we classify monosaccharides?
answer
The location of the carbonyl group The number of carbons in the carbon skeleton
question
Give two examples of 3 Carbon Sugars
answer
Aldose and Ketose
question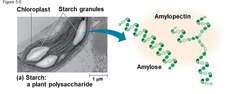
What is the simplest form of starch?

answer
Amylose
question
What are the three main types of Lipids?
answer
Triglycerides Phospholipids Steroids
question
Enzymes
answer
Proteins that act as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions
question
What are the Four Levels of Protein Structure?
answer
Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary
question
What determines Tertiary Structure?

answer
Interactions between R Groups rather than interactions between backbone constituents
question
What are the R groups that determine Tertiary Structure?
answer
Hydrogen Bonds Ionic Bods Hydrophobic Interactions van der Waals interactions
question
What is Collagen?

answer
A fibrous protein consisting of three polypeptide coiled like a rope
question
What determines the quaternary structure of a protein?
answer
When two or more poplypeptide chains form one macromolecule
question
How many essential amino acids are there and what are they used for?
answer
There are 20 essential amino acids used to form a protein.
question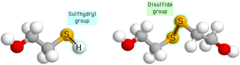
Sulfhydryl Group

answer
...
question
Phosphate Group

answer
...
question
What area the FOUR categories of organic molecules that make up all living things
answer
Nucleic Acids (DNA ; RNA) Carbohydrates Lipids or Fats hyc Proteins
question
Monosaccharide
answer
The simplest carbohydrate, active alone or serving as a monomer for disaccharides and polysaccharides. Also known as simple sugars, the molecular formulas of monosaccharides are generally some multiple of CH2O.
question
dissaccharide

answer
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
question
polysaccharide (Cellulose)
answer
A structural polysaccharide of cell walls, consisting of glucose monomers joined by ?-1, 4-glycosidic linkages. A major component of pant cell walls
question
polysaccharide (glycogen)
answer
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
question
Which monosaccharide is the energy storing molecule produced by photosynthesis. Two of these molecules combine to make glucose
answer
Glyceraldehyde
question
Which monosaccharide is a major nutrient, central to cellular metobolism. It is broken down for energy in the process of cellular respiration. The carbon skeleton of this sugar can also be used to build many other organic molecules, including amino acids and fatty acids.
answer
Glucose
question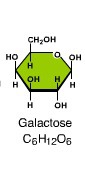
Which monosaccharide combines with glucose to form lactose, the disaccharide in milk

answer
Galactose
question
Which monosaccharide is sometimes called fruit sugar-- the one that makes apples and berries sweet. This monosaccharide is also used to make the disaccharide sucrose, or table sugar.
answer
Fructose
question
Which monosaccharide is an important component of RNA and ATP. A modified form is used in building DNA.
answer
Ribose
question
List the 4 categories of organic macromolecules that make up all living things and the main functions of each
answer
...
question
Explain how organic macromolecules are polymers made up of monomer subunits.
answer
...
question
Describe the hydrolysis process of breaking down organic macromolecules to monomer subunits.
answer
...
question
Relating to carbohydrates, distinguish between and give examples of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
answer
...
question
Relating to carbohydrates, Know which types of organism make the following polysachharides as well as the function of each: Cellulose, glycogen, chitin, starch
answer
...
question
Relating to carbohydrates, state the monomer subunits that make up carbohydrates.
answer
...
question
Relating to carbohydrates, State the name given to the bond between monosaccharides.
answer
...
question
Relating to lipids, Describe a major difference between carbohydrates and lipids
answer
...
question
Relating to lipids, Give examples of lipids and the function of eachTriglycerides (fats/oils), phospholipids, steroids, waxes
answer
...
question
Relating to lipids, State the subunits that make up fats.
answer
...
question
Relating to lipids, Describe a triglyceride molecule and state the name given to the bond between glycerol and a fatty acid
answer
...
question
Relating to lipids, distinguish between the structure of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, and between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
answer
...
question
Relating to nucleic acids, state the 2 kinds of nucleic acids
answer
...
question
Relating to nucleic acids, state the monomer subunits that make up nucleic acids
answer
...
question
Relating to nucleic acids, describe the molecular structure of a nucleotide
answer
...
question
Relating to nucleic acids, state the name given to the bond between nucleotides
answer
...
question
Relating to nucleic acids, explain the function of DNA
answer
...
question
Relating to nucleic acids, explain the function of RNA
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, give examples of protein functions
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, state the monomer subunits that make up proteins
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, show the structural formula of an amino acid, including the amino group, the carboxyl group, and the R group.
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, describe the hydrophilic/hydrophobic nature of each of the following types of amino acids: nonpolar, polar, and electrically charged
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, state the name given to the bond between amino acids
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, distinguish between a polypeptide and a protein
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, specifically describe the four levels of protein structure that give proteins their specific shape: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, describe what is meant by denaturation and renaturation of a protein.
answer
...
question
Relating to proteins, explain why proteins function best under optimum pH and optimum temperature conditions.
answer
...



