Byzantine Empire, Kievan Russia, Early Middle Ages Study Guide – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The Byzantine Empire (c. 400-1453)
answer
Origin: Surviving eastern half of Roman Empire. Byzantine rulers saw themselves as roman emperors. Constantinople founded by Constantine on site of greek colony of Byzantium.
question
Constantinople
answer
Forfeitable peninsula-good for safety. Natural Harbor, crossroads of trade. City between Europe and Asia. Located on the Bosporus Strait, away from Germanic invaders.
question
Protection
answer
Walls and Moat. 14 mile stone wall(25 feet thick). Towers 7 ft tall. Use of secret weapons, such as greek fire-to defend Constantinople.
question
Trade
answer
Mese or "the middle way"-main street running through city. Merchants lined the street, open air market. Products from Asia, Africa and Europe: -Mediterranean -Silk Road -Black Sea -Russian Trade
question
Entertainment
answer
Free to all at hippodrome. Chariot races, circus acts
question
(Early Byzantine Period)
answer
"New Caesar", ruled with absolute power(autocrat), his army under general Belisarius gained almost as much land as had been in the old roman epire
question
Justinian Code
answer
Codification of Roman Law(called the Corpus Juris Civilis) -The code: 5000 roman laws -"The Digest": Legal Opinions -"The Institutes": Law student textbook -"The Novellae": New laws passed after 534 CE ***Justinian serves as the basis of law for 900 years
question
Theodora
answer
Came from poverty. Actress. Passed laws, built churches, met with officials.
question
Byzantine Empire Map
answer
Map
question
Nika Rebellion
answer
-In 532 AD, fights broke out between supporters of different chariot teams(demes). -Ultimately, those fighting turned their, hostility toward the emperor. -They were angry about the highs taxes he had charged for territorial expansion. -They chanted "Nika" which means win of victory.
question
Belisarius
answer
Byzantine general who recaptured much of the Roman Empire.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Hagia Sophia

answer
Built by Justinian, it contains one of most glorious interior spaces ever made by man.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Colossal statue of Constantine

answer
-Head/foot -(Marble) Head: 8 1/2 H
question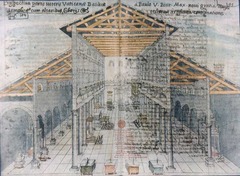
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Church of St. Peter's

answer
The 1st church. Based on Roman Basilica. Not truly Byzantine, but the roman basilica as a form would have a large influence on Byzantine churches.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: The Church of San Vitale
answer
Ravenna, Italy; 528-547 -Roman Elements: the dome, shape of the doorways, and stepped towers. -Byzantine Elements: polygonal apse, narrow bricks, and mosaics. ***The church is of extreme importance in Byzantine art, as it is the ONLY MAJOR CHURCH FROM THE PERIOD TO STILL BE INTACT TO THE PRESENT DAY.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Mosaic of Justinian

answer
Justinian with Bishop Maximan, clergy, courtiers, and soldiers. Designed to look like Christ and his disciples. Mosaic. S. Vitale, Ravenna.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Mosaic of Theodora
answer
Theodora with Courtiers. Designed to look like virgin Mary. Mosaic. S. Vitale, Ravenna
question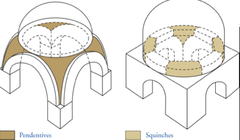
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Dome on Pendentives

answer
The dome on pendentives was a major innovation and produced the largest dome in the world at the time.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Icons
answer
Religious figures painted for veneration. This one is a bust of the savior, 6th century AD. This icon painting(before iconoclasm) shows the influence of classical art.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: The Virgin Eleousa of Vladimir
answer
(12th c.) One of the best examples of the Byzantine Iconography.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: Double-Faced Enkolpion
answer
A devotional pendant or medallion meant to be worn around the neck. One face of this pendant bears an image of Christ and the other that of the Virgin.
question
Byzantine Art/Architecture: St. Basil's Cathedral
answer
Red Square- Moscow, Russia Demonstrates Byzantine Influence mixed with native Russian.
question
The Iconoclastic controversy and Leo
answer
-Initiated by Emperor Leo in 8th c. A.D. -Worship of icons seen as idolatry -Appropriation of Church wealth by emperor -Destruction of Byzantine art form -Back to status quo in ninth century
question
Effects of Iconoclasm on the West
answer
-Iconoclasm damaged relations between Byzantines and Christian West - Pope against iconoclastic movement -Western Christianity turned away from Byzantines and to the Franks for support
question
4th Crusade sacks Constantinople
answer
-1081-1204 CE -Call to West for help versus Seljuk Turks -Constantinople base for operations -Sack of Constantinople 1204 - Fourth Crusade
question
The 1054 Schism
answer
Roman Catholic v. Eastern Orthodox Leaders: Pope(West) and Patriarch(east) Language: West: Latin and East: Greek Authority: Pope's interpretation of the Bible(West) and The Bible(East). Pope was above all government and local laws(West) and Political Leaders above all(East) Divorce: Western pope forbid divorce and Eastern Patriarch began to allow divorces Priests right to marry: West: Restricted and East: Allowed Filioque: West believed that the Holy Spirit was begotten of the Father and the Son while the east believed that the Holy Spirit was begotten of the Father alone Use of Unleavened bread: the West used unleavened bread for communion while the East used leavened bread. ***EFFECT: Christianity was permanently divided between Roman Catholic (in West) and the Orthodox Church (in East).
question
Attacked by Arab armies
answer
empire loses much land but Constantinople never falls (Greek fire), acts as buffer between Islam and Europe
question
Byzantine Empire Falls
answer
-1261-1453 -Territories lost to Ottoman Turks -Commerce dominated by Italian city-states of Venice -and Genoa -The Black Death in 1300's ***1453 - Constantinople fell to Ottoman Turks
question
Kievan Russia(860-c.1450)
answer
:
question
Geography of Russia
answer
-West of Ural Mountains -Black to Baltic Sea -Grasslands in the South, dense forests and swamps in the north. -3 Great Rivers: Dnieper, Don, and Volga.
question
Birth of Russia
answer
-Before 800 AD, the forests and grasslands were inhabited by farmers and traders without any political unity ***Slavic people influenced by Vikings, Byzantine Empire, and the Mongols
question
Influence of the Vikings
answer
-The Vikings influence these groups to begin to build forts along the rivers and the Vikings settled among the Slavic peoples
question
Influence of the Byzantine Empire
answer
Alphabet (Cyrillic-St. Cyril and Methodius), Art and architecture (icons and domes), Religion (Russian Orthodox, Vladimir's conversion)
question
Yaroslav and his influences
answer
In 1019, Yaroslav (Vladimir's son) came to power Increased trade with Europe -Built many churches -Created a legal code -Married his daughters & sisters to kings of surrounding nations ***Ties to Constantinople = wealthy and powerful Kiev
question
The Weakening of Kiev
answer
-In 1054 Yaroslav dies -Divides the empire amongst his sons which weakens the empire -Trade disrupted by the Crusades further weakens the empire
question
Influence of Mongols
answer
Forces Russia to turn Eastward, Centralized autocratic leadership -Allowed religious freedom as long as they were paid large amounts of tribute (taxes) -Increased trade - part of a large empire -Isolated women into separate quarters -Absolute Power - model for later Russian governments -Cut Russia off from the Western advancements
question
Rise of Moscow and the Czars (Tsars): Ivan III and Ivan IV
answer
Ivan III: 1. Defeated Mongols in a bloodless battle 2. Removed Boyars (landed classes) from power and began using the title Czar (Caesar) 3. Declared the Russian Empire to be the Third Rome Ivan IV(The terrible): 1. Early Reign - peaceful and progressive. 2. Focused on trade, law, church, & government 3. Later Reign: became crazy and organized the Oprichniki "agents of terror"
question
Michael Romanov
answer
-The Romanov dynasty is established. -The only Russian royal family lasted for 304 years!
question
The Dark Ages(400-750)
answer
:
question
Germanic tribes settled throughout the Western Roman Empire (especially the Franks)
answer
1. German invasions destroy the Roman Empire 2. Most people remained in the village of their birth
question
Clovis and his conversion to Christianity
answer
1.Clovis - Frankish leader -Becomes a Christian -Leads to increased ties to Church -Gains more power for his tribe -Frankish kingdom grows -ruler of the Merovingian dynasty
question
Isolation, decline of trade, loss of learning, and horrible conditions
answer
1. Money no longer used -Decline in Trade 2.Most people remained in the village of their birth -No more cities -Decline of learning -Loss of common language -No central government
question
World of Charlemagne(750-850)
answer
:
question
Charles Martel aka "the hammer"
answer
1.Becomes Frankish king after Clovis - given title "mayor of the palace" in 714 2.He begins the Carolingian dynasty which replaces the Merovingian family's rule. 3. ***Defeats the Muslims at the Battle of Tours in 732 A.D.*** -Europe will be Christian, not Muslim
question
Pepin the Short
answer
1. He became Mayor of the Palace in 741. 2. In 751, he had himself appointed king with papal consent (consent of the Pope). 3. He started an era of very good relations between the Franks and the Church. 4. He gave the pope land he controlled in Italy, the area around Rome to become the papal states.
question
Charlemagne
answer
***"Char le magna" = Charles the Great 1. Becomes king upon his father's death in 768. 2. Early reign was spent at war with the Lombards, the Saxons and the Muslims. 3. Greatly expanded his territory into what is now Italy, Germany and Spain. 4. Most of western Europe was included in the new empire.
question
Charlemagne cont.
answer
***In the year 800, on Christmas, the Pope crowns him*** 1. "Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire." -This increases tensions between the West and the Eastern Orthodox Christianity of the Byzantine Empire and ESTABLISHES THE POWER OF THE CHURCH IN POLITICS. 2. Charlemagne works closely with the church to set up a Christian Empire. -He helps convert, often by force, many barbarians to Christianity. 3. Divides his empire into regions, each ruled by a noble called a count. -***To keep control of the counts and watch over the empire, he sends out his officials called missi dominici.***
question
Charlemagne cont.
answer
1. Stressed education -Set up many schools. The largest was at his palace at Aix-la-Chapelle aka Aachen 2. Tried to bring back a classical education for the upper class. 3. Had scholars work on copying the Bible and other great Christian and Roman works. 4. Public works included roads and churches as well as schools which helped to unite the empire. 5. Charlemagne died in 814 leaving his empire to his incompetent son. 6. ***Within 30 years, his empire would be split into 3parts by his grandsons at the Treaty of Verdun. 7. Europe regresses backwards again*** 8. However, Charlemagne sets an example for all future kings and emperors of the Middle Ages.
question
A time of Invasions(800-1000)
answer
:
question
Magyar invasions
answer
Invasions from central Europe (Hungary), and continued Muslim invasions from the south. 1. In 1240, the Mongols attacked Kiev. 2. Led by Batu Khan (Genghis' grandson) 3. Mongols would rule Russia for 200 years. 4. This was called the Khanate of the Golden Horde
question
Viking invasions
answer
Invasions from Scandinavia ravage coastlines and cities along rivers throughout Europe. 1. The fierce and destructive Vikings destroy any European unity and force further isolation, however they do help stimulate trade and exploration as well as setting up colonies. Viking longships
question
Viking colonization and exploration
answer
1. Legend says that a Viking chief named Rurik was invited to be king. 2. He founded the city of Novgorod, Russia's first important city.
question
Feudalism and Manor System(800-1100)
answer
:
question
The relationship between a lord, vassal, and a fief, and the social and political hierarchy of feudalism
answer
1. King gives lord (vassal) a fief (land). 2. In exchange, the lord (vassal) gives the king his loyalty and protection (military service) when needed.
question
The establishment of feudal estates and manors, and how the lords took power away from the king.
answer
Lords gradually became more powerful than kings as they acquired more land
question
The manor-system
answer
an economic system where land, not money, is the basis of wealth
question
Manor
answer
1. The lord's estate including the town, peasant houses, church, and fields 2. It was self-sufficient, which led to a decline in trade 3. Three-field system -two fields planted, one left fallow (empty) to regain fertility
question
The Roman Catholic Church(c.400-c.1100)
answer
:
question
The hierarchy of the church from Pope to Priest
answer
1. Pope 2. Cardinals 3. Archbishops 4. Bishops 5. Priests
question
Sacraments, tithe, canon law, excommunication, and interdict.
answer
-7 Sacraments: Baptism, Confirmation, Eucharist, Penance, Anointing of the Sick, Matrimony, and Holy Orders. The purpose of the sacraments is to make people holy, to build up the body of Christ, and finally, to give worship to God. -Tithe: 1/10 of annual produce or earnings, taken as a tax for the support of the church and clergy. - Canon law: law, especially (in the Roman Catholic Church) that laid down by papal pronouncements. -Excommunication: an institutional act of religious censure used to limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular receiving of the sacraments -Interdict: an authoritative prohibition
question
The life of monks under Benedictine rule and monasteries, and importance to preservation of classical learning
answer
1. Monasteries -Christian religious communities for men -Cut off from outside contact -Spend time praying and copying Roman and Greek books and the Bible -***The Catholic Church is the only place where reading/ writing and centralized order continues during the Dark Ages
question
Growth of papal state
answer
1. Church becomes involved in politics. 2. Pope's palace is the center of government in parts of old Roman Empire. -The Vatican 3. Church raises armies, repairs roads, helps poor, and negotiates peace treaties 4. *The idea of a churchly kingdom, ruled by the pope, would become a central theme of the Middle Ages.



