Biochemistry DNA and RNA – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What are the components of nucleotides?
answer
3 components: 1. Nitrogenous base 2. pentose sugar (5 carbon atoms) 3. Phosphate group
question
What are the differences between purine and pyrimidine structures?
answer
Purine: Adenine (A), Guanine (G)> 2 ring bases Pyrimidine: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U)> 1 ring bases CUT PY and PUR As AG
question
Describe the hydorgen bonds between A, T, C, G
answer
A double hydrogen bonds T G triple hydrogen bonds C
question
Define phosphodiester bonds
answer
Nucleotide unitls aer connected via 3' carbon and 5' carbon atoms (3' to 5' and 5' to 3')=phospodiester bonds
question
What are the differences between DNA and RNA with regards to replication?
answer
DNA: replicates itself once before cell division RNA: made continuously
question
What is helicase?
answer
Enzyme that separates DNA molecule to form a replication bubble. Replication fork: Y-shaped region
question
Define ORC binding to DNA
answer
Origin recognition complex and has 6 proteins. Requires presence of single stranded binding protein (SSBP) or Minichromosomal maintenance proteins (MCMs) to coat DNA and permit ORC binding.
question
How are MCMs removed in DNA replication?
answer
They are destroyed by ubiquitinylation.
question
Classes of RNA molecules
answer
3 classes: 1. rRNA: ribosomal RNA; were proteins are made 2. tRNA: transfer RNA; hold amino acids 3. mRNA: messenger RNA; DNA template
question
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
answer
-Interact with each other and with proteins to form ribosomes -Ribosomes provide basic machinery where protein synthesis takes place -Synthesized on single strand RNA transcript -60s subunit: 28s, 5.8s and 5s: associate to form larger subunit -40s subunit: 18s rRNA associates with proteins -80s: large and small subunits combine to form ribosome
question
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
answer
1. 65-110 nucleotides long 2. Functions: a) carries amino acids b) recognize mRNA nucleotide sequence c) translate sequence into amino acid sequence of proteins 3. Cloverleaf structure with 4 loops: a) D loop: contains methyicted cytosine and dihydrouridine b) Anticodon loop: responsible for recognition of the complementary codon of an mRNA c) T psi C loop: contains pseudoruidine d) Acceptor stem: i) last 3 bases found at 3' end remain unpaired ii) always have 5'CCA3' iii) amino acid is attached via ester bond: 3'-hydroxyl group of adenosine and carboxyl group of an amino acid
question
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
answer
-500-6000 nucleotides long -Carriers of genetic information (working copy of genome) -Transcription: pre-mRNA processing> 5' cap addition> splicing> editing> polyadenylation> transport> translation -Triplets: found on DNA -Codons: found on mRNA -Anticodons: found on tRNA
question
RNA polymerases
answer
RNA Polymerases: responsible for synthesis of RNA; need a primer and is synthesized in 5' to 3' direction; 3 types 1. RNA polymerase 1: makes rRNA 2. RNA polymerase 2: transcribes mRNA a) sensitive to alpha-amanitin in poisonous mushrooms: transcription inhibitor; prevents mRNA formation 3. RNA polymerase 3: transcribes tRNA Initiation phase: 1. interaction of RNA Polymerase and DNA 2. Promoters: recruit RNA polymerase to transcription start site 3. Located upstream/in front of gene needing to be transcribed; 2 regions: a) TATA box b) CAAT box 4. Transcription factors must bind to promoter region to begin transcription; 4 promoters: a) Leucine zipper b) Zinc finger c) Winged helix d) helix-loop-helix (HLH): protein dimerization Elongation phase: 1. phosphodiester bond 2. RNA polymerase translocates to the template strand and new nucleotide is added a) protein factors stabilize RNA polymerase: viral infections b) pre-RNA: once RNA is synthesized it must go through editing 3. Initially synthesized RNA contains: introns and exons but INTRONS need to be removed a) mutations: can arise at splice sites> abnormal protein formation 4. 5' cap: 7-methylquanidine residue added to mRNA 5' end
question
Initiation phase of RNA transcription
answer
Initiation phase: 1. interaction of RNA Polymerase and DNA 2. Promoters: recruit RNA polymerase to transcription start site 3. Located upstream/in front of gene needing to be transcribed; 2 regions: a) TATA box b) CAAT box 4. Transcription factors must bind to promoter region to begin transcription; 4 promoters: a) Leucine zipper b) Zinc finger c) Winged helix d) helix-loop-helix (HLH): protein dimerization
question
Elongation phase of RNA transcription
answer
Elongation phase: 1. formation of phosphodiester bridges between each nucleotide in an RNA molecule 2. RNA polymerase translocates to the template strand and new nucleotide is added
question
Termination phase of RNA transcription
answer
Termination phase: 1. dislocation of RNA polymerase from the DNA template done via: a) RNA secondary structure b) specific protein factors: stabilize RNA polymerase 2. Editing a) snRNAs: need these 5-proteins (U1, U2, U3, U4, U5) to form SPLICEOSOME> machine that edits mRNA b) pre-RNA: once RNA is synthesized it must go through editing c) Initially synthesized RNA contains: introns and exons but INTRONS need to be removed at splice sites i) mutations: can arise at splice sites> abnormal protein formation ii). 5' CAP: 7-methylquanidine residue added to mRNA 5' end iii). Poly A tail: >250 adenosine residues added (AAA...) at 3' end> prevents destruction
question
Translation (protein synthesis )
answer
Culmination of the transfer of genetic information stored as nucleotide bases in DNA to protein molecules which function in living cells. Protein folds into 3-D structure depending on its amino acid sequence once formed. -begins at 5' end of mRNA to 3' end -amino terminal end of protein: 5' end -carboxyl-terminal end: 3' end -3 nucleotides (codons) in MRNA: required to specify each amino acid
question
What are the 3 main RNA components necessary to translate RNA?
answer
1. tRNA: amino acids that are to be incorporated into the protein are attached to tRNA 2. Ribosomes: have rRNA and interact with mRNA so correct amino acid is incorporated into protein 3. mRNA: ribosome interacts mRNA
question
How many nucleotides are used for translation from mRNA?
answer
Only 4 nucleotides: A,C,G,U -these encode a protein containing up to 20 amino acids: not 1:1 ratio
question
Stop codons
answer
64 possible codons, but only 3 are used as stop codons: 1. UAA 2. UAG 3. UGA
question
Can more than one codon specify a specific amino acid?
answer
Yes, more than one codon can specify a specific amino acid 1. GUU, GUS, GUA, GUG: all code for valine 2. all amino acids except METHIONINE (AUG) and TRYPTOPHAN (UGG) have more than one codon
question
What marks the starting point for protein synthesis?
answer
All proteins create METHIONINE first
question
Mutations
answer
Cause different protein to be synthesized via: 1. insertions 2. deletions: cause FRAME SHIFT mutation
question
Machinery of protein synthesis
answer
1. Ribosomes have 3 sites where tRNA binds: a) A site: acceptor site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) b) P site: tRNA + newly synthesized protein c) E site: AMINOACYL-tRNA SYNTHETASE adds amino acids to tRNA and then exits ribosome i) Carboxyl group of amino acid is activated with ATP ii) tRNA + amino acid-AMP release
question
Define the Wobble Hypothesis
answer
1. Base pairing rules are the same as DNA except at 3rd position 3' base of codon a) Non-classic base pairing i) forms between this nucleotide and 5' base of anticodon ii) allows tRNA to incorporate DIHYDROURIDINE ii) not a perfect match so Wobble allows for non-classic base pairing to occur 2. Guanine residue at 5' position on anticodon can form base pair with either a) cytosine or a uridine residue b) G can bind to Uridine unlike Watson-Crick base pairing
question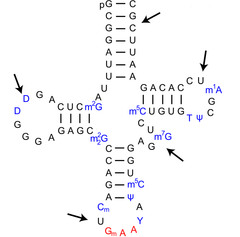
Label the tRNA structure

answer
Label the structure
question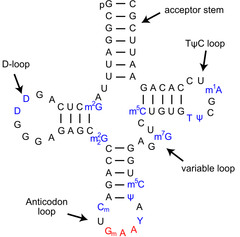
tRNA structure

answer
Labeled tRNA
question
What is the first step in the initiation phase of protein synthesis?
answer
A dissociated small subunit of ribosome (40s) forms a complex with a Eukaryotic Initiation Factor: 1. EIF 1A 2. EIF 2 3. EIF 3 Pre-initiation complex: EIF 2 + Met + tRNA + 40s + EIF 1A + EIF 3
question
What does EIF 4F do?
answer
1. Directs pre-initiation complex to 5' end of mRNA and binds a 5'cap
question
What does EIF 5 do?
answer
Directs Met+tRNA to P site -Large ribosomal unitl binds to small unit with Met -tRNA/mRNA complex -Scans mRNA until AUG (Met) code is found
question
What is the first step of elongation?
answer
Peptidyl transferase: forms peptide bond between amino groups; conveyor belt A site: growing peptide chain P site: end of growing peptide chain; forms bond with AA
question
Termination
answer
Occurs when A site of ribosome reaches mRNA stop codons Releasing factors recognize stop codons> release protein from tRNA
question
Chaperone
answer
Proteins responsible for folding newly synthesized protein into 3D shape 1. bind to expose hydrophobic regions of unfolded proteins 2. Prevent their interaction with each other by shielding interactive surfaces a) prevent from aggregating b) induce folding of molecule c) Heat shock proteins (HSP70): protective protein with cancer tx implications
question
How many histone proteins are there?
answer
8 histone proteins
question
What are the 2 classes of chromatin?
answer
1. Non-histone proteins: polymerases, hormone receptors, nuclear enzymes 2. Histones: Hi, H2A, H2B, H3, H4
question
Describe nucleosomes
answer
Octameric protein with 2 subunits each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4
question
Describe the roles of telomeres
answer
1. Ends of each chromosome: telomeres 2. Consist of repeated DNA sequences: TTA, GGG a) long repeating unitls b) repair enzymes leave this alone c) TELOMERASE: catylic ribonucleoprotein that makes telomeres> adds repeats to 3' end using RNA template i) it is a REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE: RNA to DNA
question
Describe telomerase
answer
Composed of 2 subunits that bring their own RNA template 1. Telomerase reversetranscriptase (hTERT) 2. HTR: telomerase RNA Protects terminal ends of chromosomes from fraying 1. protects ends of chromosomes from being processed as DNA strand breaks Telomerase inhibitors: prevent cancer cell division Telomerase inducers: anti-aging> cells can only divide 50-90 times and then G.O. phase
question
What is a kinetochore? What is a centromere?
answer
1. Spindle fibers bind here 2. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to centromere in a specific protein region 3. Centromeres: binds central constricted parts of chromosomes and divides into 2 arms made of undefined repetitive DNA: location indicator for genes a) P arm: short arm b) Q arm: long arm
question
In what direction is DNA read and synthesized?
answer
DNA is read in a 3' to 5' direction but is synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction, which is called a complimentary strand.
question
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
answer
Catalyzes the formation of hydrogen bonds and makes phosphodiester bonds. It is the enzyme that copies and elongates DNA strand after primase forms a primer.
question
Geminin vs. MCM
answer
Geminin binds to newly formed DNA strands and prevents them from being replicated. MCMs coat DNA that need to be copied and prevents them from snapping back together.



