Biochemistry: Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
when the amino and carboxyl group are on the same carbon
answer
alpha amino acid
question
only amino acid that is not chiral
answer
Glycine
question
all chiral amino acids in eukaryotes, amino group on left side of the fisher projection, S configuration
answer
L-amino acids
question
L- amino acid, R configuration
answer
Cysteine Configuration
question
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Proline
answer
Nonpolar nonaromatic amino acids
question
1 of 2 with sulfur atom on side chain, nonpolar/nonaromatic
answer
Methionine
question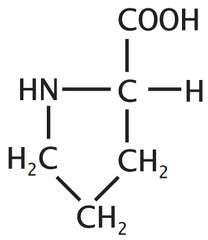
forms a cyclic amino acid, contrains on flexibility, non polar

answer
Proline
question
alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, proline
answer
Amino acids with alkyl side chains
question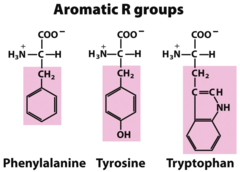
Tryptophan, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine

answer
Aromatic Amino Acids
question
largest aromatic amino acid side chain
answer
Tryptophan
question
smallest aromatic amino acid side chain, non polar
answer
Phenylalanine
question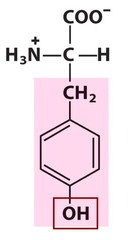
relatively polar, aromatic amino acid

answer
Tyrosine
question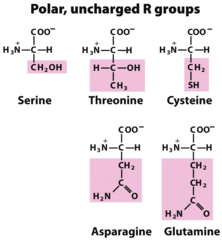
Serine, threonine, Asparagine, Glutamine, Cysteine

answer
Polar amino acids
question
OH makes them highly polar and able to participate in H-bonding
answer
Serine and Threonine
question
amide N's do NOT gain or lose protons with change in pH
answer
Asparagine and Glutamine
question
thiol group, S is larger than O making the S-H bond weaker than OH Thiol group more prone to oxidation
answer
Cysteine
question
basic, arginine, lysine, histidine
answer
Positively Charged Amino Acids
question
positive charge delocalized over 3 nitrogens
answer
Arginine
question
imidazole, at pH 1 atom is protenated at highly acidic pH, 2nd N becomes protenated-->R positive charge
answer
Histidine
question
amino acids with long alkyl chains -alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine -found at interior of protein
answer
Hydrophobic Amino Acids
question
glutamate, aspartate, histidine, lysine, arginine, glutamine, asparagine

answer
Hydrophilic Amino Acids
question
Aspartic Acid-aspartate, Glutamic Acid-Glutamate
answer
Negatively Charged Amino Acids
question
Protenated
answer
At a low pH, ionizable groups of aa tend to be _____
question
deprotenated
answer
At a high pH, ionizable groups of aa tend to be _____
question
majority of species is protenated
answer
pH;pKa
question
majority of species is deprotenated
answer
pH;pKa
question
the pH at which, on average, half of the molecules of a species are deprotenated
answer
pKa
question
Carboxyl group (~2)
answer
pKa 1 of an amino acid
question
Amino group (~9-10)
answer
pKa 2 of glycine
question
-many protons - pH;pKa2=amino group is protenated (+1) -pH;pKa1=carboxy group is protenated (0) -aa is positively charged
answer
Glycine at pH 1
question
zwitterion -pH;pKa1= carboxy group deprotenated (-1) -pH;pKa2=amino group protenated (+1) -neutral molecule
answer
Glycine at Intermediate pH
question
-pH;pKa1= carboxy group deprotenated (-1) -pH;pKa2= amino group deprotenated (0) - -1 charge
answer
Glycine under Basic Conditions
question
When pH of solution is almost equal to pKa of solute
answer
When does the solution during a titration act as a buffer?
question
when the molecule is neutral, very sensitive to pH change
answer
Isoelectric Point
question
pKa2+pKa1/2
answer
Equation of isoelectric Point
question
lower than neutral amino acids -pKa of R group substitutes amino pKa
answer
The pI for acidic amino acids is
question
higher than neutral amino acids -pKa of R group substitutes carboxy pKa
answer
The pI for basic amino acids is
question
COO- --- NH3+
answer
peptide bond
question
condensation/dehydration removes H20 acyl substitution
answer
Peptide Bond Formation
question
chymotrypsin, trypsin specific and cleave at specific points on peptide chain
answer
hydrolytic enzymes
question
Hydrolysis add H to amide N and OH group to carbonyl C
answer
Peptide destruction
question
linear arrangement of amino acids encodes all info needed for folding determined by sequencing
answer
Primary structure of Protein
question
local structure of neighboring amino acids result of H-bonding (alpha helices, Beta Pleated Sheets)
answer
Secondary Structure of Protein
question
rod like structure -side chains of aa point away from helix core
answer
alpha helices
question
parallel or anti-parallel peptide chains forming rows -rippled and pleated -aa point above or below sheet
answer
Beta-pleated sheets
question
rigid structure -kink in a-helix -turns between chains of B sheets
answer
Secondary Structure and Proline
question
structures that resemble long strands and sheets collagen
answer
Fibrous Proteins
question
spherical globin
answer
Globular Proteins
question
3D shape determine by hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions between R groups of amino acids -determined by H bonding -determined by acid base interactions between aa with charged R groups
answer
Tertiary Structure
question
when R groups of different aa interact with one another
answer
Salt Bridges in amino acids
question
2 cysteine molecules oxidized-->cystine
answer
Disulfide Bond
question
protein loses tertiary structure
answer
denaturation
question
causes hydrophobic regions to move inward, philic to move outward
answer
Entropy in Tertiary Structures of Proteins
question
H20 cannot bind to R so it must rearrange to maximize H bonding - -S (entropy) -less disorder -non spontaneous
answer
Hydrophobic R groups Dissolve Process
question
H20 binds to R-->increase entropy-->increase disorder -spontaneous
answer
Hydrophilic R groups in Dissolve Process
question
only exist for proteins with 1+ polypeptide chains -functional form of the protein
answer
Quarternary Structure
question
1. increase stability, decrease surface area 2. lower amount of DNA needed to encode protein complex 3. bring catalytic sites together 4. induce cooperativity and allosteric effects
answer
Roles of Quarternary Structure
question
derive part of their function from covalently attached molecules called prosthetic groups
answer
Conjugated Proteins



