Bio 7-10 – Flashcard
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
DNA
answer
deoxyribonucleic acid, hereditary molecule that is passed from parents to offspring, serves as manual for how to build an individual
question
all
answer
why type of organism has DNA?
question
Discovery of DNA
answer
known to be a chemical by end of nineteenth century, stores genetic info, can be passed from generations
question
molecular biology
answer
study of heredity at the molecular level
question
nucleus
answer
where is DNA located in Eukaryotes?
question
nucleosome
answer
where is DNA located in Prokaryotes?
question
chromosome
answer
single DNA molecule wrapped around proteins called histones
question
human DNA
answer
23 pairs of chromosomes, one from each set is from each parent
question
nucleotides
answer
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that consist of..
question
polynucleotide
answer
a nucleotide polymer is a ...
question
4 nucleotides
answer
thymine, cytosine, adenine, guanine
question
RNA has _______ instead of thymine
answer
uracil
question
Crick and Watson, Rosalind Franklin used X-ray crystallography
answer
who discovered DNA?
question
saves space, protein interactions
answer
Why use a double helix?
question
prokaryotic nucleoid
answer
bacteria pack their DNA into a series of loops or domains, collectively called the nucleoid
question
topoisomerases
answer
regulate widing of DNA, induce super coiling or unwind DNA
question
genome
answer
haploid set of chromosomes in a gamete or microorganism, in each cell.
question
conserved regions
answer
tend to be more G-C rich in many organisms. Stronger binding affinity
question
need to be able to pull strands apart to replicate
answer
why do we want weaker bonds in between strands?
question
dna replication
answer
how does info from dna pass to offspring and new cells?
question
dna replication
answer
when a cell produces a complete copy of the dna must pass frm one generation the the next
question
dna helicases
answer
separate double stranded DNA into two single strands
question
dna polymerases
answer
enzymes make the covalent bond between the nucleotides of a new dna strand
question
semi-conservative mechanism
answer
produces two copies of the original dna molecule, each molecule consists of one of the strands
question
origin of replication
answer
where replication starts
question
genotype
answer
genetic makeup, sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA
question
phenotype
answer
physical traits, arise from actions of a wide variety of proteins coded by DNA
question
G-C
answer
which base pair is strongest?
question
half
answer
DNA replications ic called semi conservative because ____ of the original helix appears in the newly formed helix after replication
question
DNA directionally
answer
5 - upstream, 3 - downstream
question
primers- short segments of dna that guide dna polymerase to the section of dna to copy
answer
how does dna know where to attach on a single stranded DNA?
question
exonuclease activity
answer
removal or rna primer, and replaced by dna polymerase with new polymerase
question
DNA ligase
answer
seals off fragments in DNA in DNA replication
question
50 base pairs per second
answer
how fast is DNA polymerase?
question
about 3 million base pairs
answer
how big is the human genome?
question
dna profile
answer
visual representation of a persons unique dna
question
genomic library
answer
collection of dna fragments that included an organisms entire genome
question
repetitive DNA
answer
makes up much of the DNA that lies between genes in humans and consists of nucleotide sequences
question
STR analysis
answer
method of DNA profiling, compares lengths
question
genome science
answer
DNA based technologies of tomorrow and today
question
Helicase
answer
in PCR heat takes the place of which enzyme?
question
1
answer
how many cells does it take to get enough DNA for fingerprinting?
question
gel electrophoresis
answer
separates fragments of DNA by size, concentration determines how well DNA filters through gel
question
dna profiling
answer
look at multiple STRs, pattern of STR repeats at multiple sites is unique to a person
question
innocence project
answer
uses DNA to free wrongly convicted people
question
CSI effect
answer
DNA can take weeks, machinery is expensive generates scientific awareness
question
DNA technology
answer
creation of genetically modified crops, identify and treat disease, criminal justice system
question
introns
answer
repetitive dna sequences, gene control sequences all do not code for specific proteins
question
plants largest: amoeba dubia
answer
what organism has the largest genome?
question
myriad genomics
answer
claimed a patent on the BRCA1/2 genes in humans with breast cancer
question
amino acids
answer
building blocks of proteins all have same basic core structure unique chemical side group
question
found on chromosomes, carries a unique set of genes
answer
where do proteins come from?
question
gene expression
answer
synthesis of a protein from a gene
question
alleles
answer
alternative versions of the same gene, have different nucleotide sequences, different alleles influence protein function
question
central dogma of biology
answer
dna > rna> protein
question
transcription
answer
dna > rna, tranfer of genetic information from dna to rna molecule
question
translation
answer
transfer of information from rna to a protein
question
mRNA
answer
messenger RNA - carries information from genes to ribosome for protein
question
rRNA
answer
ribosomal RNA - structural makes up ribosome subunits for a functioning ribosome
question
tRNA
answer
transfer RNA - pairs up with matching mRNA at the ribosome and attached amino acids to make amino acid chains, which then go on to making functional proteins
question
RNA polymerase
answer
binds to the regulatroy of the genes coding region, DNA strands unwind, copies a strand of DNA intro a complementary strand of mRNA
question
codon
answer
triplet of bases, which codes for one amino acid
question
genetic code
answer
set of rules that convert a nucleotide sequence in rNA to an amino acid sequence
question
mRNA, enzymes, ribosomes, ATP, tRNA
answer
what do we need to make translation happen?
question
anticodons
answer
special triplet of bases that is complementary to a codon triplet on mRNA
question
rna
answer
transcription creates?
question
a site
answer
holds newest tRNA carrying the next amino acid to be added to a growing chain
question
p site
answer
holds tRNA carrying growing polypeptide chain
question
e site (exit site)
answer
empty tRNA leaves the ribosome
question
translation 3 steps
answer
initiation, elongation, and termination
question
initiation
answer
brings together mRNA, amino acid, subunits of ribosome
question
elongation
answer
subsequent amino acids are brought to mRNA by tRNA and adds to a growing polypeptide chain
question
termination
answer
a stop codon reaches ribosomes a site, polypeptide is freed ribosome splits back into subunits
question
genomic trunk
answer
about 98% of human DNA was identified as noncoding
question
regulatory sequence
answer
determine when and how much protien a gene makes
question
coding sequence
answer
determine the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein
question
eukaryotic transcription
answer
RNA transcribed from a gene functions as mRNA, euk cell modifies RNA
question
eukaryotic rna processing
answer
adding a cap and tail of extra nucleotides, removes introns, join exons
question
alternative RNA splicing
answer
exons may be spliced together in different combinations producing more than one type of polypeptide from a single gene
question
DNA
answer
reverse transciptase converts RNA to ....?
question
yes
answer
do virgin births happen in nature?
question
heal wounds, growth, cell replacement
answer
what does cell reproduction accomplish?
question
reproduction
answer
asexual (mitosis) sexual (meiosis)
question
asexual (mitosis)
answer
single-celled organisms reproduce by simple cell division, no fertilization of an egg by sperm
question
diploid cells, growth and development
answer
what types of cells are produced by mitosis?
question
sexual
answer
requires fertilization of an egg by a sperm, used for reproduction
question
46
answer
how many chromosomes do humans have?
question
chromosomes
answer
made of chromatin, fibers composed of roughly equal amounts of DNA and protein molecules
question
histones
answer
proteins used to package DNA in eukaryotes
question
nucleosomes
answer
consist of DNA wound around histone molecules
question
chromosomes are evenly divided, sister chromatids are separated, centromere
answer
how do mitosis cells divide?
question
cell cycle
answer
ordered sequence of evens that extrend from time of cell is formed to its own division
question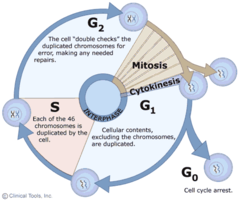
interphase

answer
metabolism and growth (90% of time), G1 G2 & S phases
question
mitotic phase
answer
cell division (10% of time)
question
2%
answer
what percent of microbes can we grow in the lab (are culturable)?
question
DNA primase
answer
adds RNA primer
question
DNA helicase
answer
unwinds DNA
question
exonuclease
answer
removes RNA primers
question
ligase
answer
repairs breaks that may occur
question
primers
answer
short segments of DNA that guide DNA polymerase to the section of DNA to copy
question
polymerase chain reaction
answer
allows dna replication to occur many times, can make billions of copies from a starting same of just a few molecules of DNA
question
sister chromatids
answer
before a cell divides, it duplicates chromosomes, resulting in two copies called ________ containing identical genes
question
preparatory phase
answer
copy cellular content, duplicate organelles, DNA, and cytoplasm, interphase
question
G1 phase
answer
cell grows, makes extra cytoplasm
question
S phase
answer
DNA replication identical sister chromatids
question
division phase
answer
mitosis cytokinsesis
question
4 states of mitosis
answer
P(rophase) M(etaphase) A(naphase) T(elophase&cytokinsesis)
question
prophase

answer
replicated chromosomes begin to coil up, nuclear membrane begins to disassemble, microtubule fibers form mitotic spindle
question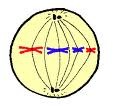
metaphase

answer
microtubules attach to the sister chromatids, replicated chromosomes become aligned along the middle of cell
question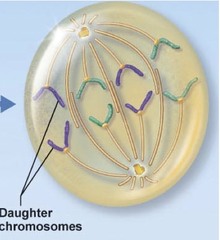
anaphase

answer
microtubules shorten, pulling the sister chrimatids to the opposite ends of the cell
question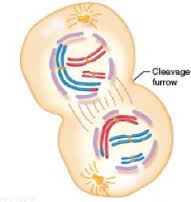
telophase

answer
identical sets reach each pole, spindle fibers disassemble, nuclear membrane forms
question
mitotic spindle
answer
made of microtubules, hollow protein fibers, key components of cytoskeleton, attach to centromere on chromosome via kinetochore proteins
question
cytokinesis
answer
the cell membrane pinches in to separate daughter cells
question
prokaryotes
answer
mitosis prokaryotes vs eukaryotes, who wins in terms of numbers over 30 hours?
question
meiosis
answer
sexual reproduction, produces offspring that contain a unique combination of genes from the parents
question
how unique are you?
answer
1:70 trillion chance of offspring
question
sex chromosomes
answer
XX - female, XY- males
question
autosomes
answer
22 pairs of matching chromosomes
question
down syndrome
answer
also called trisomy 21, individual has an extra chromosome, 1 in 700 children
question
gametes
answer
reproductive cells that carry one copy of each chromosome
question
meiosis 1
answer
separates homologous chromosomes, daughter cell is haploid, each chromosomes still has 2 sister chromatids
question
meiosis 2
answer
separate sister chromatids, four haploid daughter cells, develop into egg or sperm
question
recombination
answer
when maternal and paternal chromosomes pair and physically exchange DNA segments
question
independent assortment
answer
alleles of different genes are distributed independently of one another
question
heterozygote
answer
two different alleles (Aa)
question
homozygote
answer
two identical alleles (AA) (aa)
question
mutation
answer
why has nature designed only 1 start and 3 stops?
question
nucleotide substitutions
answer
replacement of one base by another
question
nucleotide deletion
answer
loss or addition of a nucleotide
question
missense mutation
answer
single nucleotide causes an amino acid change that results in a non-functional protein
question
nonsense mutation
answer
a SNP causes incomplete translation and thus a non functional protein
question
silent mutation
answer
a SNP causes no change in amino acid, however the codon has changed functions
question
change in blueprint, makes mistakes, environmental factors, DNA polymerase adds wrong nucleotide
answer
how do mutations arise?
question
mutation
answer
change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA, affects structure and function of protein.
question
photo-oncogenes
answer
promote cell division can be mutated to become permanently activated, encode for growth factors
question
tumor suppressor genes
answer
pause cell division, repair dna or initiate cell death, can be mutated to become inactivated
question
cell cycle checkpoints
answer
either repair damage or direct cell to commit suicide (apoptosis)
question
benign tumor, then tumor may develop and spread, malignant tumor
answer
tumor stages
question
somatic mutation
answer
occurs in a body cell and is not passed on to offspring
question
germ-line mutation
answer
occurs in gametes and is passed on to offspring, heritable mutations
question
born with mutation, develops into malignant quicker
answer
why do people with "inherited" cancer often develop cancer at a relatively young age?
question
telomere
answer
prevent chromosomes from losing base pair sequences, stop chromosomes from fusing to each other



