Atomic Structure And Theory Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
is a positively charged subatomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom
answer
proton
question
is a negatively charged subatomic particle that is found in the space outside the nucleus
answer
electron
question
is a neutral subatomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom.
answer
neutron
question
equals the number of protons in an atom of that element.
answer
atomic number
question
The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. We get this number by rounding the atomic mass. It must be a whole number with no decimals because we cannot have less than one subatomic particle. (for example we cannot have 1/2 or 3/10 of a proton!)
answer
mass number
question
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass numbers. Because they are the same element they will have the same atomic number. The difference in the number of neutrons is related to the difference in the mass number!
answer
isotope
question
The weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of an element. (will typically be a decimal number and does not generally represent the mass of a particular atom of an element but will be closest to the isotope which is more commonly found)
answer
atomic mass
question
a region of an atom in which electrons of the same energy are likely to be found
answer
energy level
question
a visual model of the most likely locations for electrons in an atom (we cannot identify a specific location but use probability to determine roughly where the electrons will most likely be)
answer
electron cloud
question
a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons (we have used this term interchangeably with electron cloud and energy level)
answer
orbital
question
The arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom. The most stable of these is the one in which the electrons are in orbitals with the lowest possible energies. (in other words if we were filling a Bohr model we would place the electrons in the first energy level and would not go to the second until the first level was full, then electrons in the second level and fill this before going to the third...). This arrangement is also responsible for the chemical properties of the element.
answer
electron configuration
question
When all the electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energies, the atom is said to be in its ground state. Electrons can be excited and removed from this state by going to a higher energy level but they won't stay there indefinitely.
answer
ground state
question
the positively charged dense center of an atom where the protons and neutrons are found
answer
nucleus
question
Having no net electric charge. An atom with the same number of protons and electrons.
answer
neutral
question
the force between electrically charged objects (like charges repel and opposite charges attract each other)
answer
electrostatic force
question
a particle smaller than an atom, such as a proton, neutron, or electron
answer
subatomic particle
question
a tiny particle or packet of light energy (this is emitted when an electron returns from an excited state to its ground state)
answer
photon
question
an electron that is found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom's chemical properties
answer
valence electron
question
the average when the numbers have different weights. We use this to find the atomic mass for the periodic table. However, you can use this to calculate your grades also since each category tests, quizzes, labs, and homework make up a different portion of your grade. For example Homework is only 12% of your final grade but you have several homework assignments so you take the average of all of your homework assignments and then multiply by .12. This will tell you the amount that this type of assignment contributes to your weighted grade.
answer
weighted average
question
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table.
answer
period
question
Vertical columns of the periodic table. The elements within a group have similar properties. This is because the elements have the same number of valence electrons.
answer
group
question
The pattern of repeating properties on the periodic table. Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when atomic numbers are used to arrange elements into groups. The elements in a group have similar electron configurations. An element's electron configuration determines its chemical properties. Therefore, members of a group in the periodic table have similar chemical properties.
answer
periodic law
question
A table that shows all of the known elements, their atomic number, symbol, and weighted average atomic mass. Elements with similar properties are grouped together. Dimitri Mendellev first grouped and organized the elements into what is now known as the periodic table. He used the atomic mass as the primary characteristic to decide where each element belonged in his table. He even left spaces for elements to be discovered because of the pattern he saw once he started organizing those elements known at that that time. Henry Moseley organized the modern periodic table according to atomic number, rather than atomic mass.
answer
periodic table
question
Groups 3-12 of the periodic table. Many of the elements in this group have more than one possible charge.
answer
transition metals
question
This category of elements are usually gases at room temperature. However, they can be found in other states and will be dull in appearance, poor conductors of heat and electricity (poor conductivity). All of these are found above and to the right of the metalloids on the periodic table except Hydrogen.
answer
nonmetals
question
This category of elements are generally solids at room temperature, are shinny (or have metallic luster), are good conductors of heat and electricity (good conductivity). All of these can be found below and to the left of the metalloids on the periodic table. (note that Hydrogen does not fall into this category despite that it is located on the same side of the periodic table)
answer
metals
question
This category of elements have characteristics of metals and nonmetals. They form a sort of staircase of elements, including B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te.
answer
metalloids
question
The ease and speed with which an element combines, or reacts, with other elements and compounds. This is determined by the electron configuration of the element.
answer
reactivity
question
First to theorize the concept of the atom in 5th century BC. The word atom is derived from the Greek word "atomos", meaning indivisible.
answer
Democritus
question
1. All matter is made up of individual indivisible particles called atoms (this is the solid sphere model). 2. All atoms of a given element are identical in properties. Atoms of different elements have different properties. 3. Compounds are formed by a combination of 2 or more atoms 4. Atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or converted into other kinds of atoms during chemical reaction
answer
Dalton's model of atom
question
This model gave evidence that the atom was made up of smaller particles. Called the plum pudding model, this model has negatively charged particles mixed throughout a positive "soup". We have also called it the chocolate chip cookie dough or muffin with chunks model.
answer
Thomson Model of atom
question
This scientist conducted an experiment with gold foil and discovered that the atom was made up of mostly empty space with a dense positively charged nucleus. His model shows this positive nucleus with negatively charged particles somewhere outside the nucleus but not in specific locations.
answer
Rutherford model of atom
question
This model of the atom is also called the planetary model of the atom because it shows electrons orbiting the nucleus in distinct energy levels. This model is great for showing how the electrons are placed outside of the nucleus but is not the most recent model of the atom. The light specra of atoms is evidence of Bohr's atomic model-because light gets emitted from an atom in quantized (fixed) amounts.
answer
Bohr model of atom
question
An atom model wherein electrons are no longer depicted as particles moving around the nucleus in a fixed orbit. Instead, as a quantum mechanically-influenced model, we shouldn't know exactly where they are, and hence describe their probable location around the nucleus only as an arbitrary 'cloud'.
answer
Wave Mechanical/ Quantum, Electron cloud model of atom
question
2
answer
max # of electrons in first energy level of Bohr model
question
8
answer
max # of electrons in second energy level of Bohr model
question
For all elements but Hydrogen and Helium 8 is the max number of valence electrons to be stable or non-reactive Hydrogen and helium only need 2 since this is the maximum in the first energy level.
answer
# of valence electrons to be stable
question
farthest right in the periodic table. Group 18 all of these have a full valence shell with 8 electrons except Helium which has a full valence shell with 2 electrons.
answer
noble gasses
question
farthest left in the periodic table in Group 1 all of these have 1 valence electron and are metals except Hydrogen which is a non-metal but is located above this group because it has 1 valence electron. They are the most reactive of the metals
answer
alkali metals
question
group 2 elements
answer
alkaline earth metals
question
group 17 elements - most reactive of the non-metals
answer
halogens
question
the number of valence electrons
answer
Looking at the group number of the element will tell us what?
question
the number of energy levels the element has.
answer
The period of an element gives us what information?
question
reactivity of the element (how it will bond with other elements to form molecules and compounds).
answer
the number of valence electrons gives us a clue about what?
question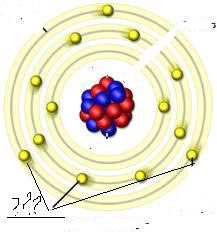
These are all electrons being placed in the Bohr model of an atom. They are found orbiting the nucleus in distinct energy levels.

answer
Where are electrons on the Bohr model of the atom?
question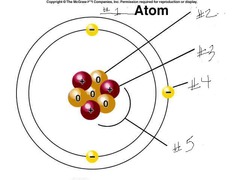
The protons and neutrons are in the nucleus and it is represented by #5 in the diagram.

answer
What subatomic particles are in the nucleus of an atom? And where is the nucleus of an atom located?
question
This image represents Dalton's model of the atom. According to Dalton, the atom was a hard sphere.

answer
Dalton model (Image)
question
They are located in the outermost shell.
answer
Where are valence electrons of an atom located?
question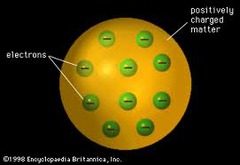
This image represents JJ Thompson's "plum pudding" model of the atom.

answer
Thomson model of atom (picture)
question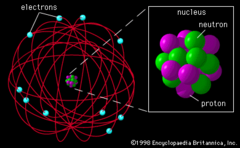
This image represents Rutherford's "nuclear" model of the atom. Small dense positively charged nucleus surrounded by negative electrons.

answer
Rutherford model (picture)
question
Bohr's model built on the Rutherford model, because Bohr theorized that the locations of the electrons outside the nucleus weren't random, but that they were located in well-defined orbits. Don't get orbits confused with orbitals.
answer
Bohr model (picture)
question
Our currently accepted theory of the atom. Electrons exist in orbitals, which are mathematically predicted, most probable regions of finding electrons. Heisenberg and schrodinger are credited most with this theory.
answer
Wave mechanical/ quantum/ electron cloud model of the atom (picture)
question
The bright line spectrum of an element can be explained with the Bohr model of the atom, which shows that electrons in an atom are in discrete energy states and emit distinct amounts of light when going from higher energy states to lower ones. Since the emission spectrum is different for every element, it acts as an atomic fingerprint by which elements can be identified. Some elements were discovered by the analysis of their atomic spectrum. Helium, for example, was discovered while scientists were analyzing the absorption spectrum of the sun.
answer
Bright Line Spectra (Picture)



