Astronomy Definitions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Astronomy
answer
The branch of science that deals with celestial objects, space, and the physical universe as a whole
question
Celestial Object
answer
Any object that exists in space, such as a planet, the star, or the moon.
question
Universe
answer
All existing matter and space considered as a whole.
question
Star/Sun
answer
A celestial body made up of hot gases, mainly hydrogen, and some helium.
question
Planet
answer
An object that orbits one or more stars (and is not a star itself), is spherical, and does not share its orbit with another object.
question
Satellite

answer
An artificial object or vehicle that orbits the earth, the moon, or other celestial bodies; also, a celestial body that orbits another body of larger size (for example, the moon is earth's natural satellite.
question
Moon
answer
The natural satellite of the earth.
question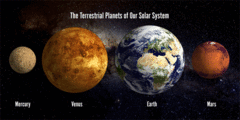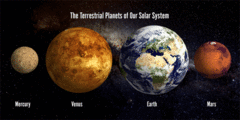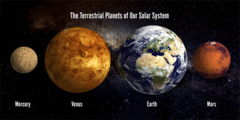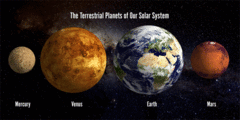
Terrestrial Planet

answer
A planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. The terrestrial planets are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.
question
Gas Giant Planet
answer
Gas giants have a mostly gaseous composition, such as hydrogen and helium. The four gas giants are (in order of distance from the Sun): Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. They're larger than the 'inner' planets.
question
Astronomical Unit (AU)
answer
The average distance between earth and the sun, about 150 x 10^6 km.
question
Dwarf Planet
answer
A round, celestial object tat orbits around the sun; it may share its orbit with another celestial body, but it is not a satellite.
question
Asteroid
answer
An object in space that ranges in size from a tiny speck, like a grain of sand, to 500km wide; most asteroids originate in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
question
Meteoroid
answer
A piece of rock moving through space.
question
Meteor

answer
A meteoroid that hits Earth's atmosphere and burns up.
question
Meteorite

answer
A meteoroid that is large enough to pass though Earth's atmosphere and reach the ground, without being totally burned up.
question
Comet
answer
An object composed of rocky material, ice, and gas; comes from the Kuiper Belt or Oort Cloud.
question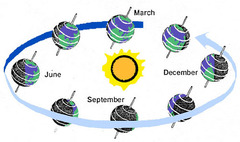
Revolution

answer
The time it takes for an object to orbit around another object; Earth's revolution around the sun is 365.24 days.
question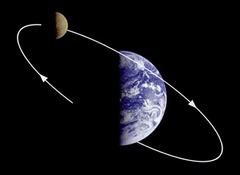
Orbit

answer
The gravitationally curved path of an object about a point in space.
question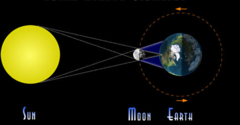
Solar Eclipse

answer
The phenomenon in which the shadow of the Moon falls on Earth's surface.
question
Lunar Eclipse
answer
The phenomenon in which the full Moon passes into Earth's shadow.
question
Constellation
answer
A group of stars that seem to form a distinctive pattern in the sky.
question
Nebula
answer
Giant cloud of gas and dust that is compressed to form a star.
question
Neutron Star
answer
A star so dense that only neutrons can exist in its core.
question
Supernova
answer
A massive explosion in which the entire outer portion of a star is blown off.
question
Black Hole
answer
The remnant of a supernova explosion with a gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape its pull.
question
Galaxy
answer
A huge collection of stars, planets, gas, and dust that is held together by gravity. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way.
question
Rotation
answer
The turning of an object around an imaginary axis running through it; Earth's rotation around its axis is 24 hours.
question
Similarities between inner and outer planets.
answer
They all follow an elliptical orbit, share the same orbital plane, and are spherical.
question
Explain the Moon's relationship with the Earth.
answer
The Moon's gravity pulls on Earth's oceans and distorts them, causing tides.
question
Phases of a lunar eclipse
answer
1. New Moon 2. Waxing Crescent 3. First Quarter 4. Waxing Gibbous 5. Full Moon 6. Waning Gibbous 7. Last Quarter 8. Waning Crescent 9. New Moon
question
What causes seasons?
answer
The seasons are caused by the tilt of the Earth's rotational axis away or toward the sun as it travels through its year-long path around the sun
question
Spiral Galaxies
answer
- Band of stars that make up a 'swirl'. - Usually have a 'bulge' in the middle. - There can be a bar of stars in the middle. - Have organization and structure, look 'flat'.
question
Elliptical Galaxies
answer
- Can range in shape from a sphere to an oval, to oblong. - Houses some of the oldest stars in the universe.



