Ap Human Geography Vocab Unit 5 Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
agriculture
answer
the deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for subsistence or economic grain
question
aquaculture
answer
the farming of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and aquatic plants
question
sustainability
answer
a method of harvesting or using a resource so that the resource is not depleted or permanently damaged
question
animal domestication
answer
altering the behaviors, size and genetics of animals to benefit humans
question
second agricultural revolution
answer
Began in W. Europe in 1600s; intensified agriculture by promoting higher yields per acre/ perfarmer
question
crop rotation
answer
the practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year to avoid exhausting the soil
question
truck farm
answer
farms that produce high consumer demand products and either trucks them to market or to processing plants
question
Third Agricultural Revolution
answer
began in mid 1950'2; modern farming that refers to the industrialized production of livestock and crops
question
biotechnology
answer
the use of genetically altered crops and DNA manipulation in order to increase production
question
agribusiness
answer
the system of agriculture found in developed countries
question
organic agriculture
answer
crops that are grown without fertilizers and pesticides
question
vegetative planting
answer
the reproduction of plants by direct cloning from existing plants, such as cutting stems and dividing roots
question
seed agriculture
answer
the reproduction of plants through annual planting of seeds ; practiced by most farmers
question
subsistence agriculture
answer
the production of food primarily for consumption by the farmer's family; found in LDC's
question
commercial agriculture
answer
farmers and ranchers sell all of their output for money and buy their families' food at stores
question
intensive agriculture
answer
yields a large amount of output per acre through concentrated farming (uses a small amount of land)
question
extensive agriculture
answer
yields a large amount of output per acre through less intensive farming (uses a large amount of land)
question
intensive subsistence agriculture
answer
a form of subsistence agriculture where farmers expend a relatively large amount of effort to produce the maximum crop yield
question
extensive subsistence agriculture
answer
a form of subsistnece agriculture that involves large areas of land with minimal labor
question
plant domestication
answer
altering the behaviors, size and genetics of plants to benefit humans
question
slash-and- burn
answer
farmers clear land for planting by slashing vegetation and burning the debris
question
swidden
answer
an area cleared for farming using the slash and burn technique
question
shifting cultivation
answer
a form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift crop activity from one field to another
question
Neolithic Revolution/First agricultural revolution
answer
time period when society went from hunters and gathers to farming and domestication of animals, 10,000 BCE
question
pastoral nomadism
answer
a form of subsistence agriculture based on the herding of domesticated animals (sheep, goats, cows, etc)
question
wet rice
answer
the practice pf planting rice on dry land in a nursery and then moving it to a flooded field to promote growth
question
double cropping
answer
a type of intensive agriculture where two crops are harvested in the same field a year
question
hunting and gathering
answer
the capturing and killing of animals and the knowledge and collection of edible plants and food of early humans
question
Carl Sauer
answer
Carl O. (the geographer), believed that the hearth of vegetative planting was Southeast Asia, believed vegetative planting came before seed agriculture
question
plantation
answer
a form of commercial agriculture, it is a large farm that specializes in one or two crops
question
cereal grains
answer
a grass such a oats, wheat, rye or barkey used as food
question
milkshed
answer
the ring around a city from which fresh milk can be supplied without spoiling
question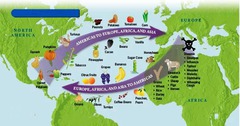
Columbian Exchange

answer
it began in late 15 and 16 century ,where products were carried both ways across the Atlantic and Pacific oceans during colonization
question
The Enclosure Movement
answer
England 1700s; the fencing or hedging of large blocks of land for farming
question
erosion
answer
the natural process by which material is worn away from the earth's surface; usually by wind, water, or ice
question
mixed crop and livestock farming
answer
farmers grow crops and raise livestock on the same land with most of the crops fed to the animals rather than people
question
patriarchal system
answer
a society in which men controlled the holding power in the family, the economy, and the government
question
horticulture
answer
the growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers for human consumption
question
Johann von Thunen
answer
a german farmer who created a model for rural land use
question
ridge tillage (intertillage)
answer
a system of planting crops on ridge tops in order to reduce farm production costs and promote soil conservation
question
desertification
answer
degradation of land because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting in semi arid land. excessive water is in south america and asia
question
seed drill
answer
a machine that more effectively planed seeds
question
Green Revolution
answer
began in 1970's; the use of higher yield seeds and expanded use of fertilizers primary- raw materials ( agriculture) secondary- take the raw materials and produce something ( manufacture) teritary- to provide a service
question
norman Bourlaug
answer
He created the green revolution, he saved Mexico in 1960 from lack wheat He saved india and pakistan in 1960 from lack of rice
question
market gardening
answer
a farm where people grow products that will be sold in a market
question
adaptive strategies
answer
the idea that humans can adapt their agricultural practices to the needs of the society or the environment
question
collective farm
answer
farm or group of farms organized as a unit and managed and worker by a group of laborers under state supervision; communist countries
question
dairying
answer
branch of agriculture that deals with the breeding, raising, and utilization of dairy animals and the selling of their products
question
staple grains
answer
a principal raw material or commodity grown or produced in a region
question
forestry
answer
the art and science of cultivating, maintaining, and developing forest
question
ranching
answer
the commercial grazing of livestock over an extensive area
question
specialization
answer
the growth of specialized crops
question
suitcase farm
answer
when someone owns and operates a farm, but lives somewhere else; usually a crops only farm
question
Ester Boserup
answer
based on the observation that population increases, necessitate increased inputs of labor and technology to compensate for reduction in the natural yeilds of swidden farming. population growth forces an increased use of technology in farming, switches from extensive to intensive agriculture.
question
Intensive Subsistence (Rice)
answer
Humid low and warm latitude, flat lands, terracing, flooding, double cropping. Subsistence, intensive, labor intensive, sedentary, communal, nucleated settlements, irrigated.
question
Mixed Crop ; Livestock Farming
answer
Warm mid latitude, rotation of corn and soybeans. Commercial, intensive, irrigated, large corporate owned tracts of land, capital intensive, sedentary.
question
Mediterranean Agriculture
answer
Warm mid latitude, west coasts of continent, dry summer, wet winter, fruits, veggies, grapes, olives, wine, chick peas, live stock production less.
question
plantation farming
answer
Humid low latitude, colonization, cotton, sugarcane, coffee, rubber, tobacco, coca, jute, bananas, tea, coconuts. Commercial intensive, capital intensive, sedentary, irrigated, large tracks of corporation land.
question
Commercial Gardening and Fruit Farming
answer
Warm and mid latitude, human climate. Truck farming, fruits, vegetables, fresh or frozen, specialty farming, salmon, saffron. Commercial, intensive, human intensive, sedentary, irrigated.
question
Pastoral Nomadism
answer
Dry climates, animals, milk, meat, hides, hair, camels, goats, sheep, horse. Subsistence, extensive, labor intensive, nomadic, no irrigation, tribe family groups
question
Dairy Farming
answer
cold climate, close to urban centers, various types of dairy products. Commercial, intensive, capital intensive, sedentary, irrigated, landholding by corporations.
question
grain farming
answer
Dry climates, clustered in regions, wheat belts. Commercial, intensive, sedentary, irrigated, large tracts of corporate owned land.
question
livestock ranching
answer
Semi arid and arid, open range vs. fixed location. Breeding, Dust Bowl, lack of fertile soil, commercial, extensive, capital intensive, sedentary, irrigated, large tracts of corporate owned land.
question
Intensive Subsistence (non Rice)
answer
Wheat, bailey, oats, milet, corn, soybeans, crop rotation. Subsistence, intensive, labor intensive, sedentary, irrigated, nucleated settlements.
question
Shifting Cultivation
answer
Tropics. Cycles of planting (swidden, slash ; burn), hand tools, rice, maize, millet, Intertillage + multicropping. Subsistence, extensive, labor intensive, nomadic sedentary, non irrigated, communal.
question
interillage
answer
the growing of various types of crops
question
metes and bounds
answer
physical landmarks like trees and rivers to show boundaries. problem; boundaries move over time found east of the Appalachians
question
French long lots
answer
-pre dated PLSS -divides land into narrow parcels that extends from rivers, roads or canals. - commonly found in quebec , texas and Lousiana
question
spanish land grants
answer
- uses physical features - land that is issued by goverment that is no longer in control of that land
question
township and range
answer
- based on longitude and latitude - used in all the USA staes except the 13 colonies and the southwest( spanish land grants) -it is 640 acres in 1862 the homestead law passed (- earn a land title without paying for the land. - live on land for 5 years -build a home on land' - engage in agricultural enterprise)
question
GMOS
answer
Genetically modified food (or GM food) is food produced from plants or animals whose DNA has been altered through genetic engineering. . Genetically modified foods have been on the U.S. market since 1994, ever since the introduction of "Flavr Savr" tomatoes that had been engineered to ripen more slowly. 75% in USA is GMO 50% in the world is GMO Africa; adv.: higher yeilds, increased nutrients, more reistance to pestiscides, better tasting dis.; health problems, export problems in europe, increased dependence on USA
question
origins and diffusion of of vegetative planting
answer
The first vegetative planting diffused from the Southeast Asian hearth: northward and eastward to China and Japan. westward through India, Southwest Asia, tropical Africa, and the area around the Mediterranean Sea. West Africa: palm trees and yams Northwestern South America: manioc, sweet potatoes, and arrowroot
question
origins of seed agriculture
answer
Three hearths: western India, northern China, and Ethiopia Origin of crops in W hemisphere Southern Mexico: squash and maize (corn) Peru: beans, cotton, squash Southwest Asia domesticated cereal crops such as wheat, barley & oats-10,000 years ago MesoAmerica-maize (corn), squash & beans Africa-millet, sorghum, watermelons
question
strategies to increase the worlds food supply and challenges
answer
strategies: -increasing exports from countries with surpluses - expanding the land area used for agriculture - expanding the fishing -increasing the productivity of land now used for agriculture challenges: - not enough land to expand -dependence on other countries - overfishing
question
subsistence crops
answer
The principal subsistence crops are the staple crops like rice, corn, root and tuber crops and sometimes rice.
question
biofuels pro and cons
answer
pro: the cost is less easily renewable less dependence on foreign aid con: require greater quantities to be consumed in order to produce the same energy level. uses up valuable crop land to grow fuel crops
question
grain production in USA
answer
the us corn belt is from ohio to dakota and mainly in Iowa. They also have alot of soybeans. The cattle and beef is mainly in the south and texas. USA produces half of the worlds corn. The USA bread basket for wheat is north and south dakota, kansas, nebraska, iowa, missouri.
question
agricultural consumption
answer
cocaine: columbia , peru, bolivia heroin(opium): Afghanistan marijuana(mexico)



