Antibodies / Gene Therapy Quiz – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Vaccinations have been effective for...
answer
protection
question
Which types of vaccines are being explored?
answer
cancer
question
T or F: The cancer vaccines being explored are therapeutic and not preventive.
answer
True
question
How are cancer vaccines administered?
answer
patients injected with cancer cell antigens to stimulate patient's immune system to attack existing cancer cells.
question
What is the relationship between vaccines and antibodies?
answer
vaccines stimulate antibody production by the immune system antibodies themselves may be used to treat existing conditions.
question
How are antibodies specified?
answer
specified based on molecules or pathogens to which they are produced
question
What are some characteristics and uses of antibodies?
answer
can find and bind to their targets with great affinity many techniques to diagnose and treat use antibodies, including Monoclonal Antibodies & ELISA.
question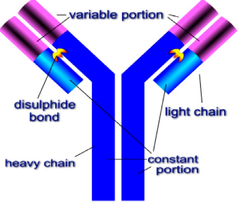
What do antibodies look like?

answer
See picture. (notice locations of variable and constant regions)
question
What does MAbs stand for?
answer
Monoclonal Antibodies
question
What are MAbs
answer
purified antibodies that are very specific for certain molecules
question
What are they also considered? (nickname)
answer
"magic bullets" for disease treatment
question
How are MAbs administered and what do they do?
answer
injected into patients where they seek out and target antigens
question
What antigens do they target?
answer
Those of Cancerous tumors, Arthritis, Alzheimer's disease
question
What are the initial steps in the procedure for making a MAb?
answer
Mouse/rat injected with purified antigen and makes antibodies to antigen (over several weeks)
question
What are the next steps in the procedure for making a MAb?
answer
Animal's spleen removed (rich source of B lymphocytes) In culture dish, B cells mixed with cancerous cells that grow & divide indefinitely Certain B cells & myeloma cells will fuse to create hybridomas
question
What are myeloma cells?
answer
Cancerous cells that grow & divide indefinitely
question
What are hybridomas?
answer
hybrid cells that act as factories for making antibodies
question
How are hybridomas grown?
answer
chemically selected and grown in liquid culture
question
What do hybridomas do?
answer
secrete antibodies into liquid culture surrounding cells
question
What is an advantage of hybridomas?
answer
can be transferred and frozen (so permanent stock always available)
question
Where are antibodies isolated in/from?
answer
cultures in large batches using bioreactors
question
What are some MAbs attached to?
answer
snake venom (to cause lysis of the cell)
question
What further research is need regarding MAbs?
answer
ensure that they only attack intended cells
question
How do MAbs have value in therapy?
answer
treating people addicted to harmful drugs (preventing damage)
question
What MAbs applicational products are on the market now?
answer
strep tests and home pregnancy kits
question
What does ELISA stand for?
answer
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
question
What is the ELISA technique?
answer
fundamental tool of clinical immunology
question
For what is ELISA technique used?
answer
initial screen for HIV detection
question
What principle is the ELISA technique based upon?
answer
antibody-antibody interaction
question
What does ELISA allow for?
answer
easy visualization of results without use of radioactive materials
question
In what is the ELISA technique performed?
answer
microplates
question
What are the first steps in the procedure of the ELISA technique?
answer
Bottom of each well is coated with a protein (ex. antigen) (which will bind the antibody you want to measure) Whole blood is allowed to clot and the cells are centrifuged out to obtain the clear serum with antibodies (called primary antibodies) Serum is incubated in a well, and each well contains a different serum. (Positive and negative control serum samples tested)
question
What are the next steps in the procedure of the ELISA technique?
answer
The serum is removed and weakly adherent antibodies are washed off with a series of buffer rinses To detect the bound antibodies, a secondary antibody is added to each well The secondary antibody would bind to all human antibodies and is typically produced in a rodent
question
What are the final steps in the procedure of the ELISA technique?
answer
Attached to the secondary antibody is an enzyme such as peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase These enzymes can metabolize colorless substrates (sometimes called chromagens) into colored products
question
What is indirect ELISA?
answer
After an incubation period, the secondary antibody solution is removed and loosely adherent ones are washed off as before The final step is the addition the enzyme substrate and the production of colored product in wells with secondary antibodies bound The amount of color produced is proportional to the amount of primary antibody bound to the proteins on the bottom of the wells
question
What is gene therapy?
answer
Involves delivery of therapeutic genes into the human body to correct disease conditions created by faulty genes
question
What are the two primary strategies of gene therapy?
answer
Ex vivo gene therapy and In vivo gene therapy
question
Ex vivo gene therapy
answer
cells from diseased person are removed and are treated in a lab (using techniques similar to bacterial transformation) and reintroduced to the patient
question
T or F: Ex vivo is more effective than in vivo.
answer
True
question
What is transfection?
answer
introduction of DNA into animal or plant cells
question
In vivo gene therapy
answer
introducing genes directly into tissues or organs without removing body cells
question
What is the challenge of In vivo gene therapy?
answer
delivery to only intended tissues
question
What do viruses act as for gene delivery?
answer
Vectors (HW chart) but some are injected directly into tissue
question
What is payload?
answer
therapeutic genes
question
What do payloads possibly require?
answer
May require long-term expression of corrective gene Others require rapid expression for short periods of time
question
What do viral vectors do?
answer
use viral genome to carry therapeutic gene(s) and to infect human body cells
question
What are the types of viral vectors?
answer
Adenovirus (common cold) Adeno-Associated Virus Retrovirus (HIV) Herpes simplex virus (cold sores)
question
Why must viruses be engineered for viral vectors?
answer
so that they can neither produce disease nor spread (extremely effective at infecting human cells)
question
Describe Adenoviruses.
answer
infect both dividing & non-dividing cells effectively
question
Describe Adeno-Associated viruses.
answer
do not cause illness in humans, can infect a wide variety of cells, & integrate 95% of time in same location
question
Describe Retroviruses.
answer
of interest because they insert DNA into the genome of host where it remains permanently (integration), but often, randomly
question
Describe Herpes virus (HSV-1)
answer
strain primarily affects central nervous system (CNS) and may help develop treatments for Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and other genetic neurodegenerative diseases
question
What is one major setback to viral vectors?
answer
not easily transfected
question
Describe Liposomes.
answer
small diameter, hollow particles made of lipid molecules and packaged with genes - injected into tissues (gene guns also used)
question
Describe "Naked" DNA.
answer
DNA injected directly into body tissues (ex. effective in liver/muscle), but not enough cells express gene to have affect
question
Describe Artificial chromosomes.
answer
Non-protein coding DNA with therapeutic gene with a similar construction to normal chromosomes (designed for permanent incorporation)
question
About how many genetic disease conditions are caused by single genes?
answer
More than 3,000
question
Candidates for treatment by gene therapy include:
answer
Cystic Fibrosis Huntington's disease Tay-Sachs Hemophilia Sickle cell disease Phenylketonuria (PKU)
question
Who was Ashanti de Silva?
answer
(4 years old) with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) treated in 1990 at NIH in Maryland Lack functioning immune system because of defect in gene called adenosine deaminase (ADA), which is involved in metabolism of dATP (nucleotide precursor used for DNA synthesis) Accumulations of dATP are toxic to T cells Normal gene cloned into vector introduced into nonpathogenic retrovirus
question
First human gene therapy success
answer
Ex vivo approach used T cells isolated from blood Multiple treatments required Within a few months, T cell numbers increased After 2 years, ADA enzyme activity was high
question
Cystic Fibrosis
answer
occurs with 2 defective copies of gene encoding the protein called cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance (CFTR) serves as a pump at the cell membrane to move chloride ions out of the cells if cells can't move chloride out, they absorb water trying to dilute the chloride in the cell. leads to the production of thick sticky mucus that clogs airways; ideal environment for infections (leading to pneumonia, etc...)
question
Treatments for Cystic Fibrosis
answer
Back clapping Drugs that thin mucus Antibiotic treatment (to fight infections) One form of gene therapy has helped
question
Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy
answer
Uses viruses and liposomes sprayed into nose & mouth Expensive treatment NOT a reliable cure yet Requires multiple applications (DNA doesn't integrate) May not produce adequate protein
question
Risk of Gene Therapy
answer
Discussions of safety intensified when 18-year-old Jesse Gelsinger died during a clinical trial @ Upenn in 1999 Complications related to adenovirus vector that was used Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (affects ability to break down dietary amino acids) 1st person to die as a result of gene therapy
question
Success of Gene Therapy
answer
Success in Rhys Evans, a child born with X-linked Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Syndrome (SCIDS - aka bubble boy), in 2002 The team took stem cells that give rise to immune cells from the boy's bone marrow They used a modified form of a retrovirus as a vector The engineered stem cells were then returned to the boy's body Now, he has normal levels of T cells
question
Unresolved Questions
answer
Can gene expression be controlled in the patient? What happens if normal gene is overexpressed? How long will the therapy last? What is the best vector to use? What is the minimum number of cells needed to infect to achieve success?
question
God Bless America.
answer
And God Bless Phusko Pharmaceuticals.



