Anatomy and Physiology for vet techs – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Physiology
answer
The functions of the body; how things work, what they do
question
Anatomy
answer
Form and structure of body. What it looks like and where is it
question
Macroscopic Anatomy (Gross Anatomy)
answer
See with naked eye without microscope. (muscles, organs, bones)
question
Microscopic Anatomy (Histology)
answer
Look through microscope. Ex. tissues, cells
question
Regional
answer
Look at all components of single region. Ex. Horse leg
question
Systematic
answer
Look at SYSTEMS in body (cardiovascular, etc.)
question
Main Body Systems
answer
Skeletal, integumentary, nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, muscular, sensory, endocrine, urinary, reproductive.
question
Skeletal
answer
Bones and joints
question
Integumentary
answer
Skin, hair, nails, and hooves
question
nervous
answer
central nervous system and peripheral nerves
question
Cardiovascular
answer
heart and blood vessels
question
respiratory
answer
lungs and air passages
question
digestive
answer
gastrointestinal tube and accessory digestive organs
question
muscular
answer
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle
question
sensory
answer
organs of general and special sense
question
endocrine
answer
endocrine glands and hormones
question
urinary
answer
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra
question
reproductive
answer
male and female reproductive structures
question
anatomic planes of reference
answer
imaginary slices through the body. 4 planes
question
Saggital plane
answer
divide the body into right and left parts(not equal)
question
median plane
answer
divides body into EQUAL left and right parts.
question
Transverse Plane
answer
divides in cranial and caudal
question
Cranial
answer
towards head
question
caudal
answer
towards tail
question
Dorsal Plane
answer
Divides body into dorsal and ventral
question
Dorsal
answer
towards animals back
question
ventral
answer
towards animals belly
question
left
answer
animals left
question
right
answer
animals right
question
rostral
answer
towards nose (when on animals head)
question
medial
answer
towards median plane (inside of leg)
question
lateral
answer
away from median plane (outside of leg)
question
Deep
answer
internal; towards center
question
superficial
answer
external; away from center
question
Proximal
answer
towards body (extremities)
question
Distal
answer
Away from body (extremities)
question
common regional terms
answer
shorthand way of naming things
question
barrel
answer
trunk (body w/o head, legs, tail)
question
brisket
answer
base of neck b/w front legs
question
flank
answer
lateral surface of abdomen b/w last rib and pelvis/ rear limb bones soft part
question
hock
answer
"ankle" tarsus
question
knee
answer
"wrist" carpus of large animal
question
muzzle
answer
most rostral part of face (nasal bone, maxillary bone)
question
poll
answer
top of head b/w ears
question
stifle
answer
"knee" joint b/w femur and tibula/fibula
question
tailhead
answer
dorsal surface where tail meets body
question
withers
answer
area dorsal to shoulder blades (scapula)
question
bilateral symmetry
answer
L and R 1/2 mirror images
question
paired organs
answer
(lungs, kidneys, eyes) found on 1 on right and 1 on left
question
single organ
answer
(heart, stomach) found on or near median plane
question
2 main body cavities
answer
dorsal and ventral
question
dorsal body cavity
answer
contains brain and spinal cord
question
ventral body cavity
answer
larger than dorsal cavity, contains all of the viscera (soft organs)
question
viscera
answer
soft organs
question
thoracic cavity
answer
Organs- heart, lungs, major blood vessels (aorta) Pleura
question
Pleura
answer
thin membrane covering everything in thoracic cavity
question
visceral pleura
answer
covers organs in thoracic cavity
question
parietal pleura
answer
covers thoracic cavity
question
Abdominal Cavity
answer
organs- intestine, kidney, stomach peritoneum
question
peritoneum
answer
thin membrane covering everything in abdominal cavity
question
visceral peritoneum
answer
covers organs in abdominal cavity
question
parietal peritoneum
answer
covers peritoneum cavity
question
cells
answer
basic unit of life, smallest thing in body can still have life, some very specialized(ex. neuron, muscle cells, red blood cells)
question
epithelial tissue
answer
composed of only cells. covers and protects (surfaces) secretes (glands) absorbs (intestinal lining)
question
connective tissue
answer
composed of living cells and non-living intercellular substances. bind cells and structures together and supports the body
question
muscle tissue
answer
skeletal (voluntary) movements cardiac (heart) smooth (involuntary)
question
nervous tissue
answer
Composed of nerve cells (neurons) and supporting cells. Transmits info around body; coordinates and controls activities
question
element
answer
simplest component of matter cannot be divided further by a chemical process
question
matter
answer
occupies space and has mass
question
major elements
answer
H, C, N, O. 96% living matter
question
minor elements
answer
Na, Mg, K, Ca, P, S, Cl
question
trace elements
answer
Boron, Flourine, Vanadium, Chromium, Manganese, Iron, Cobalt, Copper, Zinc, Serenium, Maybdenum, Tin, Iodine
question
atoms
answer
smallest unit of an element retains unique properties of the element
question
protons
answer
positive electrical charge
question
neutrons
answer
no electrical charge
question
electrons
answer
negative electrical charge remain in constant motion "electron cloud"
question
atomic weight
answer
atomic nucleus sum of protons and neutrons
question
atomic number
answer
# of protons also # of electrons
question
ion
answer
atom may gain or lose an electron may have a (+) or (-) electrical charge
question
molecule
answer
atoms joined together by chemical bond smallest unit of a compound that retains properties of the compound.
question
solutions
answer
solute is dissolved and uniformly distributed within the solvent. homogeneous
question
colloids
answer
emulsions. large sized solutes- do not precipitate out- jello appear translucent
question
suspensions
answer
large sized solutes- readily precipitate out "shake well"
question
ionic bond
answer
formed when electrons are transfered from one atom to another. one has a few electrons while other has many.
question
cation
answer
positively charged ion
question
anion
answer
negatively charged ion
question
hydrogen bond
answer
type of weak ionic bond- formed between molecules bond between H+ atoms that are already in a covalent bond.
question
chemical reaction
answer
energy released formation & breaking of chemical bonds reactants and products
question
synthesis
answer
energy released new, more complex chemical made from multiple, simpler chemicals
question
decomposition
answer
energy released single, more complex chemical broken into multiple, simpler chemicals.
question
exchange
answer
no net energy exchanged certain atoms are exchanged between molecules
question
role of energy
answer
energy is either required or released
question
concentration
answer
availability of reactants. more reactants= higher chance of chemical reaction
question
environmental temperature
answer
higher temperature = higher rate of reactions = higher soeed of molecule movement
question
enzyme
answer
special protein that holds reactants together so they may interact.
question
inorganic compounds
answer
do not contain hydrocarbon groups (water salt acid base buffer)
question
organic compounds
answer
contain hydrocarbon groups, usually covalently bonded (carbohydrates, lipids (fats), protein
question
solute
answer
chemicals added to a solvent
question
solvent
answer
fluids in which chemicals are dissolved
question
solution
answer
solute+solvent=solution
question
hydrophilic
answer
water loving-polar molecules or ions
question
hydrophobic
answer
water hating- neutral, non-polar molecules
question
universal solvent
answer
most chemicals are dissolved in water
question
transport medium
answer
acts as a blanket, molecules can move freely & are cushioned
question
heat capacity and vaporization
answer
chemical reactions generate heat. water can absorb fairly high temp needed for water to vaporize
question
lubrication
answer
surround molecules to allow cells and tissues to move freely
question
salts
answer
mineral compounds w/ ionic bonds principal form of minerals within the body when added to water, separate(ionize) into ions
question
electrolytes (ions)
answer
salts in their ionic form. Able to transmit an electrical charge
question
acids
answer
ionically bonded substances that release H+ when added to water H+ donors/ proton donors
question
bases
answer
ionically bonded substances that release OH- when added to water. H+ acceptors/ proton acceptors
question
PH scale
answer
1(most acidic)--7(neutral)--(most alkaline) normal body PH 7.4
question
buffers
answer
weak acids and bases that dont completely ionize in water help keep pH in neutral range (Bicarbonate HCO3-)
question
Carbohydrates (CHO)
answer
used for energy, storage of energy and cellular structure made of C,H, and O
question
amino acids
answer
20 differnt amino acids, all have same basic structure. building blocks of proteins
question
proteins
answer
speed up chemical reactions. act upon substrates
question
taurine
answer
cats dont make. lack causes weight loss, muscle weakness
question
epithelial cells
answer
line and cover organs
question
macrophage
answer
fights disease
question
fibroblasts
answer
build scar tissue
question
neuron

answer
(nerve cell) sends electrical impulses
question
erythrocyte
answer
(red blood cell) carries oxygen
question
neutrophil
answer
(white blood cell) fights disease
question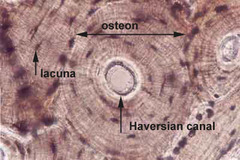
osteocyte

answer
(bone cell) builds bone
question
adipocyte
answer
stores fat
question
myocyte
answer
(muscle cells) move body parts
question
3 basic structures in all cells
answer
cell membrane (plasmalemma), cytoplasm, nucleus
question
cell membrane
answer
purpose is to form barrier between cytoplasm (intracellular) and outside environment (extracellular)
question
membrane structure
answer
lipid bilayer
question
fluid mosaic
answer
floating freely
question
cell membrane proteins
answer
55% lots proteins
question
2 types of functioning proteins
answer
integral and peripheral
question
integral
answer
span the width of membrane
question
peripheral
answer
bound to intra or extracellular surface
question
integral proteins
answer
can form channels through bilayer that other molecules can pass through
question
selective
answer
only certain molecules
question
nonselective
answer
form "pores" anything right size (or charge) passes through
question
peripheral protein
answer
on surface not passing all the way through the inside and outsidesurfaces of the cell differ
question
intracellular
answer
parts cytoskeleton. act as catalyst (speed up reaction) for cellular proteins enzymes
question
extracellular
answer
many are attached "sugar groups" form sugar coating= glycocalyx
question
glycocalyx
answer
improve cell to cell adhesion
question
cell adhesion molecules (CAMS)
answer
responsible for cell to cell adhesion -help cells bond to extracellular molecules
question
membrane receptors
answer
peripheral proteins, integral act as binding sites on cell surfaces
question
chemical signaling
answer
ex. hormones; neurotransmitters
question
contact signaling
answer
bacteria viruses find their cells
question
cytoplasm
answer
substance in the cell thats not nucleus
question
cytosol
answer
jelly substance "liquid" in the cell
question
cytoskeleton
answer
flexible structure helps shape cell. support organelles
question
cell membrane
answer
phospholipid bilayer with integral and peripheral proteins; a fluid mosaic with discrete areas of stiff "rafts", covered in sugary glyocalyx
question
cell membrane function
answer
boundary between extracellular and intracellular compartments; controls passage of substances into and out of cell; maintains membrane receptors for attachment of ligands
question
cilia
answer
many fine hairlike structures on luminal surface of cells that beat rhythmically in unison
question
cilia function
answer
fast phase of rhythmic beat propels mucus and fluid across luminal surface of cell in one direction
question
flagellum
answer
single long hairlike structure found in sperm, cells and some pathogens
question
flegellum function
answer
thrashing movement of flagellum propels cell forward
question
nucleus
answer
site of transcription; (transfer of genetic code from DNA to mRNA) and production of ribosomal subunits
question
nuclear envelope
answer
separates nucleus from surrounding cytosol; restricts movement of molecules into and out of nucleus



