Action Potential/Neurochemistry/Development/Sleep – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
An abrupt depolarization (spike) of the membrane potential.
answer
Action Potential
question
Step 1:
answer
EPSPs caused by ligand-gated Na+ channels opening to depolarize the cell toward threshold.
question
Step 2:
answer
EPSPs summate to reach threshold and voltage-gated Na+ channels open.
question
Step 3:
answer
Once voltage gated Na+ channels open, Na+ rushes into the cell causing rapid depolarization.
question
Step 4:
answer
As the cell depolarizes Na+ channels close and K+ voltage-gated channels open. K+ flows out and makes makes neuron less positive.
question
Step 5:
answer
Na+ channels are closed and K+ is leaving the cell, the cell is going back toward its resting potential. During this time, the cell can't fire another action potential because the Na+ channels are "inactivated."
question
Step 6:
answer
Hyperpolarization - The cell overshoots its normal resting potential, during this time it is harder for the neuron to fire again, but possible if the signal is "important" enough (very strong EPSPs).
question
Step 7:
answer
Restoration - K+ voltage gated channels close again. Membrane permeability back to resting state, Na+/K+ pumps work to restore ion concentration gradients.
question
The _____ the axon, the ___ the conduction.
answer
Thicker, faster
question
Gaps between Schwann Cells.
answer
Nodes of Ranvier
question
Contain most of the ion channels of the axon
answer
Nodes of Ranvier
question
Acetylcholine
answer
Attention and memory, formed in basal forebrain, projects everywhere, acetate comes from acetyl CoA and choline comes from diet.
question
What enzyme combines acetyl and choline?
answer
Choline acetyl transferase
question
What is acetylcholine correlated with?
answer
Expectation. These neurons are degenerated in Alzheimer's patients and they don't expect things.
question
Dopamine
answer
Reward, made from substantial nigra and VTA, projects to frontal lobe.
question
Frontal Lobes are ______, Nucleus accumbens ________
answer
Angel, devil
question
Frontal lobe _______ impulsivity, nucleus accumbens _________ impulsivity.
answer
Discourage, encourage.
question
Norepinephrine
answer
Arousal, made from locus coereleus
question
Acetylcholine neurons project to brain areas with ?
answer
Diverse functions
question
How to make dopamine?
answer
Tyrosine to DOPA to dopamine
question
What does cocaine do?
answer
Blocks the dopamine transporter so it is left in synaptic gap.
question
How to make norepinephrine?
answer
Tyrosine to DOPA to dopamine to norepinephrine.
question
Norepinephrine is the brain's _________
answer
on switch
question
Serotonin.
answer
Sleep, dreaming, and moods. Made from raphe nuclei, too much can lead to death, too little can lead to depression.
question
How much serotonin activity is there in REM?
answer
None
question
GABA
answer
Inhibition, major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, everywhere.
question
How's GABA synthesized?
answer
Glutamate to GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase) to GABA
question
__________ increase GABA
answer
Benzodiazepines
question
Anxiety-reducing effects of alcohol, benzodiazepines, and barbiturates all depend upon _______?
answer
GABA
question
Glutamate
answer
Neuroplasticity, makes connections stronger, dysfunctions could be the cause of schizophrenia
question
Endogenous marijuana
answer
Anandamide
question
What do ventricles form from?
answer
Remnants of the original neural tube of the developing embryo.
question
What are the ventricles?
answer
Hollow space in the middle of the brain.
question
Within a region, ___________ are produced before most ___________
answer
Neurons, glial cells
question
How is brain size determined?
answer
Total number of cell cycles in the ventricular zone.
question
If the generation time of the VZ cells double, then the final output of neurons produced by them ___________?
answer
Quadruples
question
Ventricular zone is ________ the neocortex
answer
Under
question
Animals with bigger brains live ________?
answer
Longer
question
Small brains have a ________ of offspring
answer
a lot
question
Our cortex may be as thick as it can get, so the idea is to keep thickness _________, and increase ______________
answer
constant, surface area
question
What kills of neurons you no longer need?
answer
Glutamate or apoptosis
question
Number of neurons + wiring complexity = ?
answer
Intelligence
question
Primary motor and sensory areas myelinate ________, while association cortex myelinate _________.
answer
First, last
question
In the ______, the myelin sheath can remain _______ after injury and help guide the regrowing nerve axon to the correct site of action.
answer
PNS, intact
question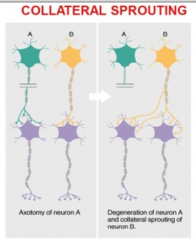

answer
Collateral sprouting
question
Development, maturation, maintenance, and recovery from injury of the _______ depends upon the presence of ________.
answer
CNS, stem cells
question
Stem cells originate in the __________, and are guided on their migration by _________.
answer
Proliferative zone, glial cells
question
Neurons are born throughout their life in the _________ and _________ can stimulate their production.
answer
Hippocampus, anti-depressant drugs.
question
Damage to the ______ disrupts sleep-wake patterns
answer
SCN (superchiasmatic nuclei)
question
Three phenomena linked with sleep?
answer
Memory enhancement (slow wave oscillations in brain electrical activity), reactivation of recent experiences, and changes in synaptic connectivity.
question
Slow, synchronized firing neurons that fire as a group is due to GABA. What is this?
answer
Coma, deep sleep
question
Fast, desynchronized neural activity is very active neurons, glutamate or acetylcholine. What is this?
answer
Awake
question
Beta waves?
answer
Alert/Working
question
Alpha waves?
answer
Relaxed/Reflecting
question
Theta waves?
answer
Drowsy/Idealing
question
Delta waves (2-3 Hz)
answer
Dreamless/Deep sleep
question
Delta waves (15-30 Hz)
answer
REM sleep/Dreaming
question
Progressive REM stages become ________ as SWS becomes _________.
answer
Longer, lighter
question
________ projections from ________ slow the neuronal activity and EEG.
answer
GABA, thalamus
question
With age, ______ decreases _____ while ______ decreases _______.
answer
SWS; somewhat, REM; significantly
question
_______ takes you into REM, while ______ takes you out of it.
answer
Acetylcholine, amines.
question
Any neuron in the cortex that is activated by acetylcholine (REM) is inactivated by ____,_____, ; ______
answer
DA, NE, and 5 HT
question
What is the difference between REM and being awake?
answer
Frontal lobes are quiet in REM
question
______ is a result of a disordered sleep pattern?
answer
Depression
question
_______ is influenced by sunlight and promotes ________.
answer
Orexin, wakefulness
question
Blocking orexin may treat?
answer
Insomnia
question
During REM, what excites neurons that will inhibit motor neurons.
answer
Glutamate
question
Abnormal, flailing movements occurring during sleep, with sleep-related injuries, or movements that are potentially injurious or disruptive
answer
REM Behavior Disorder
question
During ____ the ________ shows movies to the frontal cortex in very compressed packets of info.
answer
SWS, hippocampus
question
Activity in the what causes dreams to have a big fear component?
answer
Amygdala
question
You wake up drowsy because of the ________ in your brain
answer
Adenosine debris
question
Scorpion toxin
answer
MTX, blocks K+ channels - cell can't get back to RMP, stuck at excited state
question
Puffer fish toxin
answer
(TTX) Na+ - depolarization can't occur.
question
Saltatory conduction
answer
Jumping from one node to another
question
Iron is in ______, copper is in _______
answer
Dopamine, norepinephrine



