ACS Organic Chemistry II Final Examination – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is the IUPAC priority for naming?
answer
Carboxylic acid > Ketone > Aldehyde > Alcohol
question
In IUPAC naming, what is the suffix used for ketone groups?
answer
-one
question
In IUPAC naming, what is the suffix used for alcohol groups?
answer
-nol
question
In IUPAC naming, what is the suffix used for esters?
answer
-noate
question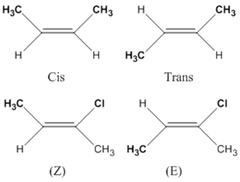
(E) isomers vs. (Z) isomers. Which one is observed when the higher ranked molecules are on the same side? opposite?

answer
highest on same side: Z highest on opposite sides: E
question
Electron-withdrawing groups are what type of directors? What is the one and only exception?
answer
Meta (deactivators) Halogens
question
If the atom directly attached to the aromatic ring has lone pairs what type of director is it? what if it does not have lone pairs?
answer
lone pairs: activating, ortho, para director no lone pairs: deactivating, meta director
question
When are the terms ortho, meta, para used?
answer
when there are 2 substituents on the aromatic ring
question
In IUPAC naming, what is NH2 on a phenyl ring referred to as?
answer
aniline
question
If there is a NO2 group present, what IUPAC prefix will also be evident?
answer
nitro
question
What is the predicted reaction? 1º alkyl halide with a strong base? weak base? poor nucleophile?
answer
strong base: Sn2 favored but E2 with strong non-nucleophilic bases weak base: Sn2 poor nucleophile: no reaction
question
What is the predicted reaction? 2º alkyl halide with a strong base? weak base? poor nucleophile?
answer
strong base: mostly E2 strong non-nucleophilic bases: mostly Sn2 poor nucleophile: Sn1/E2 (slow) in polar, protic solvents
question
What is the predicted reaction? 3º alkyl halide with a strong base? weak base? poor nucleophile?
answer
strong base: E2 strong non-nucleophilic bases: Sn1/E1 in polar protic solvents poor nucleophile: Sn1/E1 in polar, protic solvents
question
What is the configuration of the product in the base-catalyzed hydrolysis of (R)-1-choloro-1-deuteriobutane?
answer
(S)-1-deuterio-1-butanol (Sn2)
question
Where is the largest molecule on the periodic table?
answer
Bottom lefthand corner
question
Nucleophilic strength increase with increasing what?
answer
atomic size
question
Which alkyl valid would you expect to undergo Sn1 hydrolysis most rapidly? I, Br,Cl, or F?
answer
I
question
In which reaction is a racemic mixture obtained? In which reaction is an inversion of chirality obtained?
answer
inversion: Sn2 racemic mix: Sn1
question
Cleavage of an ether usually requires a strong acid that has a conjugate base which is a strong nucleophile, such as...? Depending on the type of alkyl group, the acid reaction with the halide ion produces what?
answer
HBr HI alkyl halide and an alcohol
question
When chirality rotates clockwise the chirality is...
answer
R
question
When chirality rotates counterclockwise the chirality is...
answer
S
question
A solution containing equal amounts of both enantiomers is called a..?
answer
racemic mixture
question
A meso compound contains multiple __________ centers but is nevertheless ________ because it possesses reflection symmetry
answer
chirality achiral
question
For each chirality center Fischer projection - the horizontal lines are considered to be coming _______ of the page and the vertical lines are considered to be going ______ the page _
answer
horizontal - coming out of the page (towards you) vertical - going out of the page (away from you)
question
A racemic mixture of enantiomers is optically _________.
answer
inactive
question
Based off chirality, how can you tell if two molecules are enantiomers?
answer
If they contain the same molecules but one is S and the other is R
question
How do you convert a fischer projection to a wedge and dash diagram?
answer
1. place lowest priority on dash 2. place highest priority up
question
The _____________ a molecule is, the better/stronger nucleophile it is
answer
larger
question
Which type of reaction involves a carbocation intermediate?
answer
Sn1
question
Which type of reaction involves a transition state
answer
Sn2
question
What is the rate determining step in an Sn1 reaction?
answer
the loss of the leaving group to form the intermediate carbocation.
question
What is the rate determining step in an Sn2 reaction?
answer
the concentration of substrate and the nucleophile
question
which reaction will occur if the substrate is 1º?
answer
Sn2
question
which reaction will occur if the substrate is 3º?
answer
Sn2
question
Nucleophiles can behave as bronsted-lowry ________ because of their ability to pick up a H+
answer
bases
question
E2 reactions occur in ________ step(s) E1 reactions occur in ________ step(s)
answer
E2: 1 step E1: 2 steps
question
Which elimination reaction has a unimolecular rate law determination?
answer
E1
question
What does the rate of an E1 reaction depend upon?
answer
the concentration of the substrate only (unimolecular)
question
Which elimination reaction has a bimolecular rate law determination?
answer
E2
question
What does the rate of an E2 reaction depend upon?
answer
the concentration of the substrate and the base (bimolecular)
question
What is the rate determining step in an E1 reaction?
answer
the formation of the carbocation
question
What is the rate determining step in an E2 reaction?
answer
concerted (bimolecular) happens all at once
question
Which elimination reaction requires a strong base?
answer
E2
question
Which elimination reaction requires the stereochemistry of the hydrogen to be removed to be anti to the leaving group
answer
E2
question
The more substituted product is called the..?
answer
Zaitsev product
question
The less substituted product is called the..?
answer
Hoffmann product
question
Which isomer is more stable than the other: E or Z?
answer
E
question
List common base only reagents
answer
NaH DBN or DBU tertbutyl (KO+) triethyl amine (Et3N)
question
How do all base only reagents reactions proceed (1º, 2º, 3º)
answer
E2
question
HOCH3
answer
weak nu weak base
question
List the two ways 2 water molecules can be added across an alkene in a syn addition manner
answer
1)KMnO4 2)H2O or 1)OsO4 2) H2O2
question
List the reagents necessary to add two water molecules across an alkene in an anti fashion
answer
MCPBA, H3O+
question
The majority of E2 eliminations require a transition state conformation in which the B-hydrogen atom and the leaving group are _____ to each other
answer
anti
question
T/F conjugated alkenes are more stable and favored in E2 reactions
answer
True
question
NaCC(R)
answer
Strong nucleophile/strong base
question
Why would concentrated hydrobromic acid be an inappropriate catalyst for the dehydration of alcohols
answer
Because the conjugate base (Br-) is a good nucleophile and it would attack the carbocation to form an alkyl bromide
question
To double the volume of the solvent, you would multiply the reaction rate by a factor of what?
answer
1/4
question
Under basic conditions, nucleophiles will attack the epoxide at the _______ substituted position
answer
least
question
under acidic conditions, the epoxide becomes __________ and then the nucleophile attacks the more ________ carbon
answer
protonated substituted
question
primary alcohol treated with PCC yields? secondary alcohol treated with PCC yields?
answer
1º = aldehyde 2º = ketone
question
What two reagents can be used to convert a primary alcohol into a carboxylic acid?
answer
KmNO4 or Na2Cr2O7/H2So4
question
What reagent can be used to reduce an ether to an alcohol?
answer
1) LiAlH4 2) H2O
question
What reagent can be used to reduce a carboxylic acid to an alcohol?
answer
1) LiAlH4 2) H2O
question
What two reagents can be used to reduce aldehydes and ketones to alcohol?
answer
NaBH4 or 1)LiAlH4 2)H2O
question
What are the two rules for Diels Alder reactions?
answer
1. The diene must always be in the "s-cis" conformation 2. Stereochemistry in the dienophole is always preserved
question
Under normal Diels Alder conditions, which product dominates?
answer
Endo (everything on wedge or everything on dash)
question
On the chair conformation, which way does endo point? exo?
answer
endo = down exo = up
question
Besides H2O, H30+ what is another way to add OH markovnikov across an alkene?
answer
Hg(OAC)2, H2O followed by NaBH4
question
What is the stereochemistry for water being added anti-markovnikov?
answer
syn addition
question
Br2 adds bromines in what fashion across an alkene?
answer
anti addition
question
What is formed when an alkene is treated with a peroxyacid? (R'COOOH)
answer
an epoxide branching from the alkene bond
question
What is the FINAL product when an alkyne is treated with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4
answer
a ketone
question
What must you keep in mind with addition reactions?
answer
METHYL OR PROTON TRANSFER / CARBOCATION REARRANGEMENTS
question
Under which set of conditions is a Diels Alder reaction best carried out?
answer
heating in hexanes
question
Which carbonyl compound would exist to the greatest extent as its hydrate when dissolved in aqueous solution? Why?
answer
An aldehyde would exist at a greater concentration due to electronic and steric effects
question
when an ether (acetal) is treated with H2O, H3O+ in the presence of heat, what occurs?
answer
ketone
question
are the reaction conditions TsOH, C6H6 (heat) considered acidic or basic conditions
answer
acidic
question
What can/cannot NaBH4 be used to reduce?
answer
ketones or aldehydes not esters or carboxylic acids.
question
Methyl vinyl ketone is a conjugated ketone that may undergo 1,2 or 1,4 addition. if the nucleophile is strongly basic (LiAlH4, Ch3MgBr, phosphonium ylide) what type of addition occurs? What about if its not as basic (NaCN)? Which type of reagent is more reversible?
answer
strongly basic: 1,2 addition Not as basic: 1,4 addition Not as basic: NaCN
question
List 4 carboxylic acid derivatives starting most reactive to least reactive
answer
acyl chloride acid anhydride ester amide
question
Best way to convert a carboxylic acid to an ester
answer
SOCl2
question
Which type of polymer could be readily prepared by condensation polymerization?
answer
Any amine containing compound --> peptide
question
activator or deactivator: CH3
answer
weak activator: para, oath director
question
conjugation causes a shift to a lower/higher wavenumber?
answer
lower wavenumber
question
strong absorption at 1720
answer
ketone
question
strong band 2500-3300
answer
OH - carboxylic acid
question
broad with spikes 3300
answer
amine or amide
question
3300 sharp
answer
CH (sp)
question
just above 3000
answer
CH (sp2)
question
just below 3000
answer
CH (sp3)
question
2700 ; 2800 both
answer
aldehyde
question
1735 strong
answer
C=O ester
question
1710 very strong
answer
C=O aldehyde, ketone, or carboxylic acid
question
1660 usually strong
answer
C=N
question
1660 moderate to weak
answer
C=C nonaromatic
question
1600
answer
C=C aromatic



