Organic Chem Chapter 6 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
what type of reaction
answer
nucleophilic substitution reaction or methyl transfer reaction
question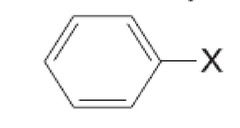
name

answer
phenyl halide or aryl halide
question
...
answer
vinylic halide
question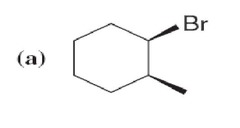
name

answer
6.1 (a) cis-I-Bromo-2-methylcyclohexane
question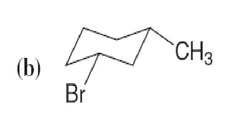

answer
(b) cis-1-Bromo-3-methylcyclohexane
question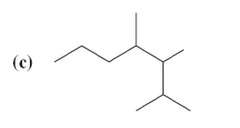

answer
(c) 2,3,4-Trimethyllieptane
question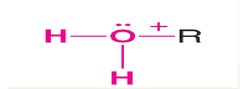

answer
Alkyloxonium ion
question
Consequently, the carbon-halogen bond length increases and carbon-halogen bond strength decreases as we go down the periodic table
answer
true
question
1 step; Favoured in polar aprotic solvents; Most stable 1 > 2 > 3 Least stable; rate = k[Nu][RX]; Optically active/inverted products
answer
SN2 reaction
question
A backside attack occurs when a concerted displacement of one nucleophile by another on a sp3 hybrid atom.
answer
SN2 reaction
question
all bond breaking and bond making occurs in a single step
answer
concerted reaction
question
reactions that release energy
answer
exergonic
question
chemical reaction; requires energy to proceed.
answer
endergonic
question
Two step process where the first step is a carbo cation formed and the second step is the reaction of the nucleophile.
answer
SN1 reaction
question
2 Steps; Favoured in polar protic solvents; Most stable 3 > 2 > 1 > methyl Least stable; rate = k[RX]; racemic products; favoured with the use of bulky nucleophiles
answer
SN1 reaction
question
when two hydrogens are attached to a carbon with 2 different groups
answer
enantiotopic hydrogens
question
# of pi bonds and rings in an alkene
answer
degree of unsaturation
question
In chemistry refers to partial conversion of one enantiomer into another, which often occurs in SN1 substitution.
answer
Racemization
question
rank them
answer
...
question
A solvent containing a hydrogen easily lost as a proton. Examples are water and most alcohols.
answer
protic solvent
question
To impede or hamper the function or activity of: hinder, to impede, hold back
answer
encumber
question
a compound formed by solvation (the combination of solvent molecules with molecules or ions of the solute)
answer
solvate
question
solvents that do not perform H-bonding
answer
Aprotic solvents
question
The rates of SN2 reactions generally are vastly increased when they are carried out in polar aprotic solvents. The increase in rate can be as large as a millionfold.
answer
true
question
Use of a polar protic solvent will greatly increase the rate of carbocation formation of an alkyl halide in any SN1 reaction because of its ability to solvate cations and anions so effectively.
answer
true
question
ability to dissolve polar compounds
answer
dielectric constant
question
Water is the most effective solvent for promoting ionization, but most organic compounds do not dissolve appreciably in water. They usually dissolve, however, in alcohols, and quite often mixed solvents are used. Methanol-water and ethanol-water are common mixed solvents for nucleophilic substitution reactions.
answer
notes
question
the best leaving groups are those that can be classified as
answer
weak bases after they depart.
question
best leaving group for acidity
answer
...
question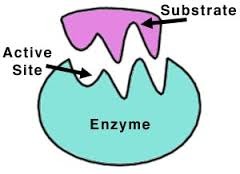
1

answer
substrate
question
2
answer
nucleophile
question
delocalization of electrons by overlap of carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon sigma bonds with an empty p orbital
answer
Hyperconjugation
question
a reaction between a compound and the solvent at which is dissolved
answer
solvolysis
question
Vinylic and phenyl halides are generally unreactive in SN1 or SN2 reactions
answer
true
question
an elimination in which the two atoms lost are a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom
answer
Dehydrohalogenation
question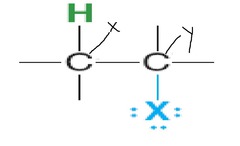
x

answer
beta carbon
question
y
answer
alpha carbon
question
what type of reaction
answer
E2
question
draw
answer
...
question
name reaction
answer
sn1
question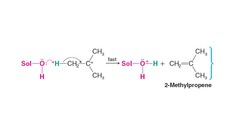
name reaction

answer
Elimination reaction
question
nucleophile better for E2 or SN2
answer
E2
question
Use of a weakly basic ion such as a chloride ion (Cl) or an acetate ion (CH3CO2 ) or a weakly basic and highly polarizable one such as Br, I, or RS increases the likelihood of substitution (SN2).
answer
True
question
If an elimination product is desired from a tertiary substrate, it is advisable to use a strong base so as to encourage an E2 mechanism over the competing E1 and SN1 mechanisms
answer
true



