Earth Science Honors: Ch. 9 Light and Observations Astronomy – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
black hole
answer
A black hole is a region of space with gravitational force so strong that nothing can escape from it.
question
cosmologist
answer
A cosmologist is a scientist or astronomer who studies large scale structures and dynamics of the universe, including the origins of the universe.
question
dark matter
answer
Dark matter is the name given to the amount of mass whose existence is deduced from the analysis of galaxy rotation curves but which until now has escaped all detection. There are many theories about dark matter, but the subject is still a mystery.
question
electromagnetic radiation
answer
Electromagnetic radiation is energy radiated in the form of waves. It consists of electric and magnetic fields traveling at the speed of light.
question
Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope: what are its 2 parts and what does it do?
answer
Fermi is a space telescope that consists of two parts: the Large Area Telescope, or LAT, and the Fermi Burst Monitor. The LAT has a wide field of view and can detect gamma rays. The Fermi Burst Monitor observes gamma ray bursts which are sudden, brief flashes of gamma radiation that occur about once a day.
question
frequency (v)
answer
Frequency is the number of waves that pass a fixed point in a given period of time.
question
frequency (v): The frequency of electromagnetic radiation is measured in ____________________ which is defined as..... The frequency of a wave is also used to _________________________.
answer
- hertz (Hz) - the number of waves per second. - Compare waves
question
1 Hertz =
answer
1 wavelength/sec.
question
joule (J)
answer
The joule is a unit of energy. One joule is the energy expended when 1 Newton of force is applied to move an object a distance of 1 meter.
question
neutron star is the type of star formed when....
answer
A neutron star is the type of star formed when a massive star explodes as a supernova, leaving behind an ultra dense core.
question
photon
answer
A photon is a quantum, or discrete amount, of light energy. Photons have no mass and behave like both a particle and a wave. - bundle of energy
question
Planck's constant (h)
answer
Planck's constant is a physical constant relating the energy of a photon to its frequency. The value of this constant is approximately 6.626 x 10-34 joule·second.
question
Pulsar
answer
A pulsar is a rotating neutron star which generates regular pulses of radiation.
question
solar flares
answer
Solar flares are violent eruptions of gas on the sun's surface. speed of light (c) - The speed of light is the speed of electromagnetic radiation in a perfect vacuum. The speed of light is the same for all frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, 3.0x108 m/s.
question
wavelength
answer
Wavelength is the length of one wave of radiation, or the distance between two consecutive waves. Wavelength is usually measured in meters.
question
Mechanical vs EM waves: Similarities
answer
Both types of waves transport energy in the world around us.
question
Mechanical vs EM waves: Differences; Mechanical Waves
answer
1. Water and Sound 2. Caused by disturbance or vibration in matter 3. Travel through medium by causing the molecules to bump into each other
question
Mechanical vs EM waves: Differences; Electromagnetic Waves
answer
1. Light 2. Travel through air, solid and vacuum of space 3. Do not require a medium. Magnetic and Electric Fields vibrating back and forth
question
Electromagnetic spectrum is _______________ which is _________________.
answer
radiation light
question
Sound does NOT = ________ all Radiation on EM = _____
answer
EM wave light
question
atmosphere blocks =
answer
Ultraviolet, X-ray, Gamma Rays
question
- Garvit comes in through ____________________. - light can be _______________ or _________________
answer
- radio waves - wave or particle
question
The Nature of Light
answer
Vibrations of electric and magnetic fields
question
The Nature of Light: Wave model- Particle model- Speed-
answer
Wave model: Wavelengths of radiation vary Particle model: Particles called photons-Shorter wavelengths correspond to more energetic photons Speed: the same for all radiation (light)- 300,000,000 meters per second (3.8 x 108) (186,000 miles) per second (To give you an idea of how fast that is, a beam of light could travel from New York to Los Angeles and back again nearly 40 times in just one second)
question
Light is...
answer
- Light is nature's way of transferring energy through space
question
1. A photon- or _____________________________ 2. Each photon energy associated with a.....
answer
1. bundle of energy. 2. particular wavelength of light.
question
Can two wavelengths have the same energy
answer
No
question
The shorter the wavelength the ______________the energy and the longer the wavelength the _______________the energy.
answer
greater lower
question
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Applications; Radio Waves
answer
AM and FM radio; television
question
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Applications; Microwaves
answer
radar; atomic and molecular research: aircraft navigation; microwave ovens
question
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Applications; Infrared (IR) waves
answer
molecular vibrational spectra; infrared photography; physical therapy
question
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Applications; Visible light
answer
visible-light photography; optical microscopy; optical astronomy
question
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Applications; Ultraviolet (UV) light
answer
sterilization of medical instruments; identification of fluorescent minerals
question
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Applications; X rays
answer
medical examination of bones, teeth, and vital organs; treatment for types of cancer
question
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Applications; gamma rays
answer
examination of thick materials for structural flaws; treatment of types of cancer, food irradiation
question
Electromagnetic radiation behaves sometimes like a ________ sometimes like a ___________________________________.
answer
wave stream of particles
question
Polarization: 1. _______________ Property 2. what is it the measurement of 3. what do sunglasses do?
answer
1. Physical 2. Measurement of the electromagnetic field's alignment 3. Think of a throwing a Frisbee at a picket fence. In one orientation it will pass through, in another it will be rejected. This is similar to how sunglasses are able to eliminate glare by absorbing the polarized portion of the light.
question
Light, Electromagnetic waves, and Radiation all refer to the ___________________________________.
answer
electromagnetic energy
question
Electromagnetic Spectrum: 1. ___________ range of electromagnetic radiation 2. name them (6) 3. Characterized by a range of __________________ and _____________________.
answer
1. full 2. Radio waves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays and gamma rays 3. wavelengths and frequencies
question
Electromagnetic Spectrum: 1. _____________ and __________________- terms of frequency (_________) 2. _____________ and ______________-terms of wavelength (___________) 3. ____________ and _______________ -terms of energy (__________________)
answer
1. Radio and Microwaves..............Hertz 2. Infrared and Visible...................meters 3. X-rays and Gamma rays..........electron volts
question
Wave Characteristics: 1. Amplitude? 2. Wavelength?
answer
1. Amplitude - height of the wave measured from the origin to its crest- The brightness or intensity 2. Wavelength - distance between successive crests of the wave-wave travels as it completes one full cycle of upward and downward.
question
Visible light has a wavelength in the range of _______ to _____ nanometers (_______ meter)
answer
400 to 750 10-9 meter
question
Reflection
answer
is when incident light (incoming light) hits an object and bounces off. This reflective behavior of light is used by lasers on board NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter to map the surface of the Moon.
question
Absorption
answer
occurs when photons from incident light hit atoms and molecules and cause them to vibrate. For example, black pavement absorbs most visible and UV energy and reflects very little, while a light-colored concrete sidewalk reflects more energy than it absorbs.
question
Scattering
answer
occurs when light bounces off an object in a variety of directions. The amount of scattering that takes place depends on the wavelength of the light and the size and structure of the object.
question
Why the Sky is Blue?

answer
The sky appears blue because of this scattering behavior. Light at shorter wavelengths—blue and violet—is scattered by nitrogen and oxygen as it passes through the atmosphere. Longer wavelengths of light—red and yellow—transmit through the atmosphere. This scattering of light at shorter wavelengths illuminates the skies with light from the blue and violet end of the visible spectrum. Even though violet is scattered more than blue, the sky looks blue to us because our eyes are more sensitive to blue light.
question
what is Diffraction? - what uses diffraction and how? - A graph of these data is called a ________________________. Patterns in a ____________________________ help scientists how?
answer
is the bending and spreading of waves around an obstacle. - A spectrometer uses diffraction (and the subsequent interference) of light from slits or gratings to separate wavelengths. - spectral signature, help identify the physical condition and composition of stellar and interstellar matter.
question
eV (electron volts)
answer
amount of kinetic energy needed to move an electron through one volt potential
question
1. Radio Station: equation
answer
93.1 megahertz= 93.1 x 106 cycles per second
question
Visible light: equation
answer
4 x 1014 s-1 to 7 x 1014 s-1
question
Spectroscopy: Most stars have a ________________ spectrum
answer
dark-line
question
Continuous spectrum
answer
Blackbody emits light at all wavelengths
question
Dark-line spectrum: what is it also called?
answer
atoms in gas cloud absorb light of certain specific wavelengths, producing dark lines in spectrum. - Absorption
question
Bright-line spectrum: what is it also called?
answer
atoms in gas cloud re-emit absorbed light energy at the same wavelengths at which they absorbed it. - Emission
question
1. Spectral lines are produced how? 2. The ____________ of an atom is surrounded by _________ that occupy only certain orbits or energy levels 3. When an electron jumps from one energy level to another, it emits or absorbs a ___________ of appropriate energy (and hence of a specific wavelength). 4. The spectral lines of a particular element correspond to the various _____________ transitions between __________________________ in atoms of that element. 5. __________ model of the atom correctly predicts the wavelengths of hydrogen's spectral lines.
answer
1. when an electron jumps from one energy level to another within an atom 2. nucleus electrons 3. photon 4. electron energy levels 5. Bohr's
question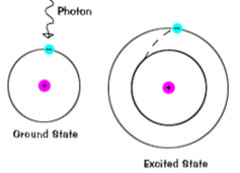
Incoming photon

answer
Ground state = incoming photon - atom absorbs a 656.3-nm photon;absorbed energy causes electron to jump from the n = 1 orbit up to the n = 2 orbit
question
emitted photon
answer
Electron falls from the n = 3 orbit to the n = 2 orbit; energy lost by atom goes into emitting a 656.3-nm photon.
question
The apparent change in wavelength of radiation caused by the ____________________________ and ______________
answer
relative motions of the source AND observer
question
_______________________ determines the main type of radiation emitted
answer
Temperature
question
Visible: Near Infrared: Mid-Infrared:
answer
Visible: dark nebula, heavily obscured by interstellar dust Near Infrared: dust is nearly transparent, embedded proto-stars can be observed Mid- and far-Infrared: glow from cold dust is directly observable
question
Telescopes: Refracting
answer
lenses bring visible light to a focus-The telescope that Galileo used was a tube with two convex glass lenses inside. A telescope that uses only convex lenses is called a refracting telescope
question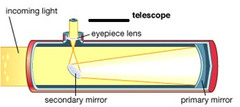
Telescopes: Reflecting

answer
mirrors bring visible light to a focus-English scientist Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727). In a reflecting telescope, light from a distant object is reflected from a curved mirror into a lens. Because they can be made much larger than refractors, the reflectors can gather light more efficiently
question
Telescopes: what do Radio telescopes detect
answer
radio waves, X-Ray Telescopes etc. GARVT
question
Benefits: wavelengths: One of the most useful telescope attachments is the _________________, what is it?
answer
Benefits: have the ability to attach different detectors to telescopes to observe all. wavelengths: spectroscope, is a device that separates white light into different colors. (Each color represents a different wavelength.)
question
Radio radiation: Gathered by "_____________" called _________________________
answer
big dishes radio telescopes
question
what is a radio telescope
answer
is a special receiver that collects radio waves generated by the sun and distant stars
question
Radio Telescopes: 1. is it Small or Big? explain 2. what is it made out of? 3. does it have good or bad resolution? 4. Can be wired together into a network called a ___________________________________.
answer
1. Large because radio waves are about 100,000 times longer than visible radiation 2. Often made of a wire mesh 3. Have rather poor resolution 4. radio interferometer
question
Radio Telescopes: Advantages over optical telescopes
answer
1. Less affected by weather 2. Less expensive 3. Can be used 24 hours a day 4. Detects material that does not emit visible radiation 5. Can "see" through interstellar dust clouds
question
what can Hubble Telescopes detect?
answer
Hubble can detect all the visible wavelengths of light plus many more that are invisible to human eyes, such as ultraviolet and infrared light.
question
what is a typical Hubble image made from?
answer
from a combination of black-and-white images representing different colors of light.
question
what do the Hubble telescope cameras record
answer
light from the universe with special electronic detectors
question
what is the Chandra Observatory designed to observe?
answer
X-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as the remnants of exploded stars.
question
Chandra detects and images X-ray sources that are ____________________________________________________ away.
answer
billions of light years
question
Chandra Observatory: NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory is a telescope specially designed to detect _____________________ from very ______ regions of the Universe such as _____________________, ___________________________, and __________________________________________________________. Because X-rays are absorbed by Earth's _______________________, Chandra must orbit ___________ it, up to an altitude of 139,000 km (86,500 mi) in space. As its mission progresses, Chandra will continue to discover startling new science about our ___________________________________________. (from Chandra Observatory)
answer
1. X-ray emission 2. hot 3. exploded stars 4. clusters of galaxies 5. matter around black holes 6. atmosphere 7. above 8. high-energy Universe
question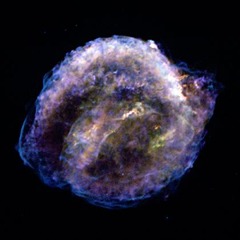
Kepler's supernova remnant:

answer
Red represents low-energy X-rays and shows material around the star -- dominated by oxygen -- that has been heated up by a blast wave from the star's explosion. The yellow color shows slightly higher energy X-rays, mostly iron formed in the supernova, while green (medium-energy X-rays) shows other elements from the exploded star. The blue color represents the highest energy X-rays and shows a shock front generated by the explosion.
question
Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC)
answer
In this composite image the Chandra data is shown in purple, optical data from Hubble is shown in red, green and blue and infrared data from Spitzer is shown in red. - The Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) is one of the closest galaxies to the Milky Way.
question
what is the James Webb Space Telescope
answer
(sometimes called JWST) will be a large infrared telescope with a 6.5-meter primary mirror. The project is working to a 2018 launch date.
question
Several innovative technologies have been developed for Webb, including....
answer
a folding, segmented primary mirror, adjusted to shape after launch; ultra-lightweight beryllium optics; detectors able to record extremely weak signals, microshutters that enable programmable object selection for the spectrograph; and a cryocooler for cooling the mid-IR detectors to 7K.
question
Kepler Telescope: what is the Kepler Mission
answer
is a NASA Discovery Program for detecting potentially life-supporting planets around other stars.
question
Has the Kepler Mission found any planets if so explain.
answer
All of the extrasolar planets detected so far by other projects are giant planets, mostly the size of Jupiter and bigger. Kepler is poised to find planets 30 to 600 times less massive than Jupiter.
question
The Kepler satellite has a _______________ diameter telescope that is a ____________________ having a field of view a bit over 10 degrees square (and area of sky the size of about two open hands).
answer
0.95-meter photometer
question
what is the Kepler satellite designed to do?
answer
It is designed to continuously and simultaneously monitors brightnesses of 100,000 stars brighter than 14th magnitude in the constellations Cygnus ; Lyrae.
question
BACKGROUND TO TELESCOPES: A light ray ___________ as it enters glass and _____________ again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an ___________ that appears ___________, ___________, ____________, or ___________ than the object being viewed.
answer
bends bends image larger smaller closer farther
question
How does a lens form an image?

answer
by bending parallel rays of light that pass through it.
question
what is a lens?
answer
is a piece of glass or plastic that refracts light.
question
The incoming parallel rays _______________ to a ____________ point. A converging lens, also known as a ________________________, is _____________ in the middle, causing rays of light that are initially parallel to meet at a ____________ point
answer
- converge - single - convex lens - thicker - single
question
The principal axis of the lens is ...
answer
Is the line joining the centers of curvature of its surfaces
question
What is the focal point of a converging lens?
answer
the point at which a beam of light parallel to the principal axis converges.
question
What is the focal plane of a converging lens?
answer
a plane perpendicular to the principal axis that passes through either focal point of a lens.
question
A lens has ____ focal points and _____ focal planes.
answer
two and two
question
What happens with light rays in a refracting telescope?
answer
light rays from a distant object (such as a planet or star) are first collected by an object lens, or objective, located at the far end of the tube. The objective then bends and concentrates light rays from the distant object to a single point inside the telescope.
question
what happens to the image in an astronomical telescope?
answer
The image is inverted, which explains why maps of the moon are printed with the moon upside down.
question
In the terrestrial telescope, a _____ lens or a pair of reflecting prisms is used which produces an image that is right side up.
answer
A third lens.
question
In a reflecting telescope, light rays from a star are ...
answer
collected by one or more curved, or concave, mirrors.
question
what are two main kinds of reflecting telescopes?
answer
single mirror and multiple mirror reflectors.
question
Describe a single mirror reflector.
answer
In a single-mirror reflector, a large concave mirror is located at the far end of the telescope tube. The mirror is curved so that all incoming light rays are reflected toward a single focal point. A flat, smaller mirror inside the telescope then reflects the converging light rays to an eyepiece lens, which magnifies the image .
question
In a multiple mirror reflector, several smaller concave mirrors are arranged ...
answer
In a ring. An image is formed when the light rays from each of the mirrors are combined and focused on a single focal point.
question
Multiple mirror reflectors are easier to build because ...
answer
It's simpler and less expensive to build a large curved mirror then to make a convex mirror from large piece of glass.



