Geology – week 7 – Geo-time – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Oldest rock on Earth
answer
4.28 billion years
question
Geology is...
answer
The science of time
question
Radioactivity was discovered in...
answer
1910
question
1920
answer
Was when Earth was first dated by radiometric dating
question
2 ways to analyze time
answer
- relative dating - radiometric dating
question
Relative dating
answer
Uses reasoning to determine chronological sequence of geological events
question
Radiometric Decay (dating)
answer
Determines age through radioactive decay. Measures the decay time of uranium into lead. Gets us more of an exact date.
question
Stratigraphy
answer
- study of strata (layers) in order to interpret geological history - closely tied to dating methods - involved with oil
question
Stratigraphy dating methods
answer
- fossils - stable isotopes - paleomagnetism - sedimentary cycles
question
Basin analysis
answer
Usually sedimentary. Works out sequence and deposition of rocks.
question
Facies
answer
"Aspect" or "appearance" of something.
question
Biostratigraphy
answer
If 2 rocks contain the same fossil they must be the same age.
question
Index fossil
answer
Useful fossils in rock dating.
question
Best index fossils?
answer
- fast evolving - easy to recognize - short duration - widespread geographic distribution
question
Pelagic
answer
Lives on the bottom of a body of water (lake, pond, ocean ect.)
question
Time
answer
Divided into intervals defined by specific fossils and strata.
question
4.6-4.2 BY
answer
- Earth and moon formed - end of heavy extraterrestrial bombardment - molten Earth - oldest known mineral
question
4.2-3.8 BY
answer
- oldest rock - oldest probable micro fossil
question
3.8-3.4 BY
answer
- oldest O2 producing bacteria (start of the atmosphere?) - oldest known microfossil - oldest craton
question
3.4-3.0 BY
answer
- first stromatolites (colonial Cyanobacteria) - oldest microfossil
question
3.0-2.6 BY
answer
- continental accretion events (orogeny's) (plate tectonics - first super continent
question
Oldest geological era
answer
Precambrian Era
question
Period of time
answer
The basic unit of geological time in which a single type of rock system is formed. Two or more periods comprise a geological Era. Some periods are divided into epochs.
question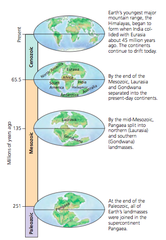
Eon

answer
A unit of geological time equal to a billion years, or a very long period of time. An example of an eon is the unit of measure used when talking about how long ago the solar system was created. Two or more Eras form an Eon, the largest division of geologic time.
question
Era
answer
A subdivision of geologic time that divides an eon into smaller units of time. The Phanerozoic Eon is divided into three such time frames: the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic represent the major stages in the macroscopic fossil record.
question
Paleozoic era
answer
The Paleozoic Era, which ran from about 542 million years ago to 251 million years ago, was a time of great change on Earth. The era began with the breakup of one supercontinent and the formation of another. Plants became widespread. And the first vertebrate animals colonized land.
question
Mesozoic era
answer
Dominate life form was reptiles. The dinosaurs and the mammals appeared during the Triassic period, roughly 225 million years ago. The dinosaurs went extinct 65 million years ago. The Mesozoic Era lasted about 180 million years, and is divided into three periods, the Triassic, the Jurassic, and the Cretaceous.
question
Cenozoic era
answer
Homo Sapiens are present. The Cenozoic spans only about 65 million years, from the end of the Cretaceous Period and the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs to the present. The Cenozoic is sometimes called the Age of Mammals, because the largest land animals have been mammals during that time.
question
What events separates each era of geologic time?
answer
Mass extinctions of life
question
Earliest life
answer
3.9 billions years ago
question
Early land plants
answer
420 million years
question
Mass extinction
answer
248 million years ago
question
Dinosaur extinction
answer
65 million years ago
question
Phanerozoic eon
answer
The Phanerozoic, the eon of visible life, is divided into three major spans of time largely on the basis of characteristic assemblages of life-forms: the Paleozoic (541-252 million years ago), Mesozoic (252-66 million years ago), and Cenozoic (66 million years ago to the present) eras.
question
Eons from oldest onwards...
answer
Pre-Archean (ends at 3.8 BY), Archean (starts at 3.8 BY), Proterozoic (starts at 2.5 BY), Phanerozoic (starts at 570 million years)
question
Eons
answer
- Pre-Archean - Archean - Proterozoic - Phanerozoic
question
Eras from oldest onwards...
answer
Paleozoic (541 -252 million years), Mesozoic (252-66 million years), Cenozoic (66 million years and onward)
question
Eras
answer
- Paleozoic - Mesozoic - Cenozoic
question
Paleozoic periods

answer
Cambrian (570-500 MY), Ordovician (500-435 MY), Silurian (435-410 MY), Devonian (410-360 MY), Carboniferous (360-290 MY), Permian (290-240 MY)
question
Mesozoic periods
answer
Triassic (240-205 MY), Jurassic (205-138 MY), Cretaceous (138-66 MY)
question
Cenozoic periods
answer
Tertiary (66-1.6 MY), Quaternary (1.6 MY-present)
question
Periods throughout the development of the Earth
answer
- Cambrian - Ordovician - Silurian - Devonian - Carboniferous - Permian - Triassic - Jurassic - Cretaceous - Tertiary - Quaternary
question
Cambrian period
answer
This Period is the first geological time period of the Paleozoic Era (the "time of ancient life"). This period lasted about 53 million years and marked a dramatic burst of evolutionary changes in life on Earth, known as the "Cambrian Explosion." Among the animals that evolved during this period were the chordates — animals with a dorsal nerve cord; hard-bodied brachiopods, which resembled clams; and arthropods — ancestors of spiders, insects and crustaceans.
question
Ordovician period
answer
This Period lasted almost 45 million years, beginning 488.3 million years ago and ending 443.7 million years ago.* During this period, the area north of the tropics was almost entirely ocean, and most of the world's land was collected into the southern supercontinent Gondwana.the Ordovician is marked by the appearance of the oldest bony vertebrates whose appearance is completely known. These were jawless, armored fish informally called ostracoderms, but more correctly placed in the taxon Pteraspidomorphi.
question
Silurian period
answer
This period (443.7 to 416.0 million years ago)* was a time when the Earth underwent considerable changes that had important repercussions for the environment and life within it. One result of these changes was the melting of large glacial formations. This contributed to a substantial rise in the levels of the major seas. The Silurian witnessed a relative stabilization of the Earth's general climate, ending the previous pattern of erratic climatic fluctuations. Coral reefs made their first appearance during this time, and the Silurian was also a remarkable time in the evolution of fishes.
question
Devonian period
answer
This Period occurred from 416 million to 358 million years ago. It was the fourth period of the Paleozoic Era. It was preceded by the Silurian Period and followed by the Carboniferous Period. It is often known as the "Age of Fishes," although significant events also happened in the evolution of plants, the first insects and other animals. The supercontinent Gondwana occupied most of the Southern Hemisphere, although it began significant northerly drift during the Devonian Period. Eventually, by the later Permian Period, this drift would lead to collision with the equatorial continent known as Euramerica, forming Pangaea.
question
Carboniferous period
answer
This Period is famous for its vast swamp forests, such as the one depicted here. Such swamps produced the coal from which the term Carboniferous, or "carbon-bearing," is derived. The Carboniferous Period lasted from about 359.2 to 299 million years ago* during the late Paleozoic Era.
question
Permian period
answer
This Period was the final period of the Paleozoic Era. Lasting from 299 million to 251 million years ago, it followed the Carboniferous Period and preceded the Triassic Period. By the early Permian, the two great continents of the Paleozoic, Gondwana and Euramerica, had collided to form the supercontinent Pangaea. Pangaea was shaped like a thickened letter "C." The distinction between the Paleozoic and the Mesozoic is made at the end of the Permian in recognition of the largest mass extinction recorded in the history of life on Earth. It affected many groups of organisms in many different environments, but it affected marine communities the most by far, causing the extinction of most of the marine invertebrates of the time.
question
Triassic period
answer
This was a Period when life outside of the oceans began to diversify. Climate was generally very dry over much of Pangaea with very hot summers and cold winters in the continental interior. A highly seasonal monsoon climate prevailed nearer to the coastal regions. Late in this Period, seafloor spreading in the Tethys Sea led to rifting between the northern and southern portions of Pangaea, which began the separation of Pangaea into two continents, Laurasia and Gondwana, which would be completed in the Jurassic Period. The oceans had been massively depopulated by the Permian Extinction when as many as 95 percent of extant marine genera were wiped out by high carbon dioxide levels.
question
Jurassic period
answer
It occurred from 199.6 to 145.5 million years ago, following the Triassic Period and preceding the Cretaceous Period. During the Jurassic Period, the supercontinent Pangaea split apart. The northern half, known as Laurentian ,the southern half, Gondwana. This rifting, along with generally warmer global temperatures, allowed for diversification and dominance of the reptiles known as dinosaurs. By the Mesozoic Era, living things had evolved the capability of living on the land rather than being confined to the oceans.
question
Cretaceous period
answer
The last and longest segment of the Mesozoic Era. It lasted approximately 79 million years, from the minor extinction event that closed the Jurassic Period about 145.5 million years ago to the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event dated at 65.5 million years ago. In the early Cretaceous, the continents were in very different positions than they are today. Sections of the supercontinent Pangaea were drifting apart. The Tethys Ocean still separated the northern Laurasia continent from southern Gondwana. One of the hallmarks of the Cretaceous Period was the development and radiation of the flowering plants. The oldest angiosperm fossil that has been found to date is Archaefructus ljiaoningensis.
question
Tertiary period
answer
This period has five principal subdivisions, called epochs, which from oldest to youngest are the Paleocene (66-55.8 mya), Eocene (55.8-33.9 mya), Oligocene (33.9-23 mya), Miocene (23-5.3 mya, and Pliocene (5.3-2.6 mya). This period was an interval of enormous geologic, climatic, oceanographic, and biological change. It spanned the transition from a globally warm world containing relatively high sea levels and dominated by reptiles to a world of polar glaciation, sharply differentiated climate zones, and mammalian dominance. It began in the aftermath of the mass extinction event that occurred at the very end of the Cretaceous Period (the so-called K-T boundary), when as much as 80 percent of species, including the dinosaurs, disappeared. The Tertiary witnessed the dramatic evolutionary expansion of not only mammals but also flowering plants, insects, birds, corals, deep-sea organisms, marine plankton, and mollusks (especially clams and snails), among many other groups. The Tertiary Period saw huge alterations in Earth's systems and the development of the ecological and climatic conditions that characterize the modern world. The end of the Tertiary is characterized by the growth of glaciers in the Northern Hemisphere and the emergence of primates that later gave rise to modern humans (Homo sapiens), chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), and other living great apes.
question
Quaternary period
answer
Part of the Cenozoic Era, the period is usually divided into two epochs — the Pleistocene Epoch, which lasted from approximately 2 million years ago to about 12,000 years ago, and the Holocene Epoch, which began about 12,000 years ago. This Period has involved dramatic climate changes, which affected food resources and brought about the extinction of many species. The period also saw the rise of a new predator: man. Scientists have evidence of more than 60 periods of glacial expansion interspersed with briefer intervals of warmer temperatures. The entire Quaternary Period, including the present, is referred to as an ice age due to the presence of at least one permanent ice sheet (Antarctica); however, the Pleistocene Epoch was generally much drier and colder than the present time.



