Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Economic Perspective
answer
The economic way of thinking that has several critical and closely interrelated features
question
Scarcity
answer
Goods and services that are in limited supply. Restricts options and demand choices
question
Opportunity Costs
answer
The loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen. A sacrifice
question
Utility
answer
The pleasure, happiness, or satisfaction obtained from consuming a good or service
question
Marginal Analysis
answer
Refers to the "additional" analysis that focuses on the comparisons of marginal benefits and marginal costs - usually for decision making
question
Scientific Method
answer
1. Observing real-world behaviour and outcomes 2. Formulating a hypothesis 3. Testing the explanation through experimentation 4. Accepting, rejecting and modifying the hypothesis 5. Continuing to to test the hypothesis
question
Economic Principle
answer
A very well-tested and widely accepted theory that is a statement about economic behaviour
question
Generalisations
answer
General ideas and habits relating to economic behaviour or the economy itself. For example, it is a common fact that consumers buy more of a product when its price falls
question
Other-things-equal assumption
answer
The assumption that factors other than those being considered do not change. For example, the relationship between the price of Pepsi and the amount of it purchased - the price varies
question
Graphical Expression
answer
Many economic models are expressed through graphs
question
Microeconomics
answer
The part of economics concerned with decision making by individual customers, workers, house-holds, and business firms
question
Aggregate
answer
A collection of specific economic units treated as if they were one unit
question
Macroeconomics
answer
The part of economics that examines the performance and behaviour of the economy as a whole. It focuses on economic growth, the business cycle, interests rates, inflammation, and the behaviour of major economic aggregates such as the government, household, and business sectors
question
Positive Economics
answer
Focuses on facts and cause-and-effect relationship. It includes description, theory development, and theory testing. It avoids value judgements
question
Normative Economics
answer
Incorporates value judgements about what the economy should be like or what particular policy actions should be recommended to achieve a desirable goal
question
Economising Problem
answer
The need to make choices because economic wants exceed economic means
question
Budget Line
answer
A curve that shows various combinations of two producers a consumer can purchase with a specific money income
question
Resource Categories
answer
Economists classify economic resources into four general categories: 1. Land (includes natural resources used in production process) 2. Labour (consists of the physical actions and mental activities that people contribute to the production of goods and services) 3. Capital (includes all manufactured aids used in producing consumer goods and services) 4. Entrepreneurial Ability (human resource) - Also called factors of production or "inputs"
question
Investment
answer
Spending that pays for the production and accumulation of capital goods
question
Entrepreneurs
answer
Employees who perform important economic functions such as: taking the initiative in combining all four resource categories and creating the strategic business decisions. They focus on innovation and the risks and benefits that come with it.
question
Consumer Goods
answer
Products that satisfy our wants directly (e.g. pizza)
question
Capital Goods
answer
Products that satisfy our wants indirectly by making possible more efficient production of consumer goods (e.g. industrial robots that make cars)
question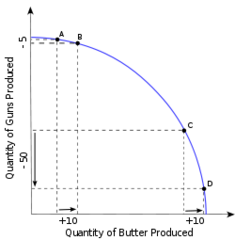
Production Possibilities Model/Curve

answer
A curve that displays the different combinations of goods and services that society can produce in a fully employed economy, assuming a fixed availability of supplies of resources and fixed technology
question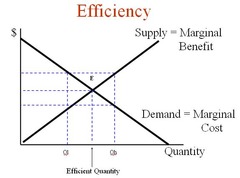
Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs

answer
As the production of a particular good increases, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit rises
question
Unemployment and the production possibilities curve
answer
Any point inside the production possibilities curve, such as "D", represents unemployment or a failure to achieve full employment
question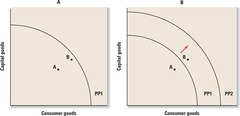
Economic growth and the production possibilities curve

answer
The increase in supplies of resources, improvements in resource quality, and technological advances that occur in a dynamic economy move the production possibilities curve outward and to the right, allowing the economy to have larger quantities of both types of goods



