United States vs USSR: Cold War – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Superpower

answer
An extremely powerful nation, especially one capable of influencing international events and the acts and policies of less powerful nations. After World War II - the United States and the Soviet Union.
question
Joseph Stalin
answer
Russian leader who succeeded Lenin as head of the Communist Party and created a totalitarian state by purging all opposition Bolshevik revolutionary, head of the Soviet Communists after 1924, and dictator of the Soviet Union from 1928 to 1953. He led the Soviet Union with an iron fist, using Five-Year Plans to increase industrial production and terror to crush opposition.
question
Dumbarton Oaks Conference
answer
A meeting near Washington, D.C., held from August 21 to October 7, 1944, U.S., Great Britain, U.S.S.R. and China met to draft the constitution of the United Nations. Conversations on International Peace and Security Organization was an international conference at which the United Nations was formulated and negotiated among international leaders.
question
Yalta Conference

answer
Meeting of FDR, Winston Churchill, and Joseph Stalin, in February 1945 at an old Tsarist resort on the Black Sea, where the Big Three leaders laid the foundations for the postwar division of power in Europe, including a divided Germany an territorial concessions to the Soviet Union.
question
Cold War

answer
The 45 year diplomatic tension between the US and the Soviet Union that divided much of the world into polarized camps, capitalist against communist.
question
Iron Curtain
answer
A term popularized by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill to describe the Soviet Union's policy of isolation during the Cold War. The barrier isolated Eastern Europe from the rest of the world.
question
Containment
answer
America's strategy against the Soviet Union based on ideas of George Kennan, and declared that the Soviet Union and communism were inherently expansionist and had to be stopped from spreading through both military and political pressure.
question
Berlin Airlift
answer
Year-long mission of flying food and supplies to blockaded West Berliners, whom the Soviet Union cut off from access to the West in the first major crisis of the Cold War.
question
Berlin Wall

answer
Fortified and guarded barrier between East and West Berlin erected on orders from Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev in 1961 to stop the flow of people to the West. Until its destruction in 1989, the wall was a vivid symbol of the divide between the communist and capitalist worlds.
question
Cuban Missile Crisis
answer
Standoff between John F. Kennedy and Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev in October 1962 over Soviet plans to install nuclear weapons in Cuba. Although the crisis was ultimately settled in America's favour and represented a foreign policy triumph for Kennedy, it brought the world's superpowers perilously close the brink of nuclear confrontation.
question
Fidel Castro
answer
Cuban revolutionary who overthrew Batista dictatorship in 1958 and assumed control of the island country. His connections with the Soviet Union led to a cessation of diplomatic relations with the United States in such internationl affairs as the Bay of Pigs invasion and the Cuban Missile Crisis. Oversaw his country through the end of the Cold War and through nearly a half-century of trade embargo with the US.
question
John F. Kennedy

answer
President of the United States who narrowly defeated the incumbent vice-president Nixon in 1960 to become the youngest person ever elected president. Launched New Frontier programs and urged legislation to improve civil rights; assumed the blame for the Bay of Pigs ivasion and was credited as well for the superb handling of the Cuban Missile Crisis. He was assasinated in Dallas, Texas, on November 22, 1963, by Lee Harvey Oswald
question
Korean War

answer
First "hot war" or the Cold War. Began in 1950 when the Soviet-backed North Koreans invaded South Korea before meeting a counter-offensive by UN Forces, dominated by the US, and the war ended in stalemate in 1953.
question
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)

answer
Military alliance of Western European powers and the US and Canada established in 1949 to defend against the common threat from the Soviet Union, marking a giant stride forward for European unity and American internationalism.
question
Nikita Khrushchev

answer
Premier of the Soviet Union from 1958-1964, he was a communist party offical who emerge from the power struggle after Stalin's death in 1953 to lead the USSR. He crushed a pro-Western uprising of Hngary in 1956, and, in 1958, issued an ultimatum for Western evacuation of Berline. Defended Soviet-style economic planning in the Kitchen Debate with Richard Nixon in 1959 and attempted to send missiles to Cuba in 1962 but backed down when comfronted by JFK.
question
Warsaw Pact
answer
A military alliance of communist nations in eastern Europe. Organized in 1955 in answer to NATO, the Warsaw Pact included Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and the Soviet Union. Organization of communist countries set up to counter NATO
question
Alliance for Progress

answer
A program in which the United States tried to help Latin American countries. JFK's "ten-year plan for americans" promised Latin American leaders that U.S. would reverse the cycle of poverty and stimulate exonomic growth at the cost of $20 billion.
question
Bay of Pigs Invasion
answer
CIA plot in 1961 to overthrow Fidel Castro by training Cuban exiles to invade and supporting them with American air power. The mission failed and became a public relations disaster early in John F. Kennedy's presidency.
question
Truman Doctrine

answer
1947; Truman's policy of providing economic and military aid to any country threatened by communism or totalitarian ideology
question
Harry S. Truman

answer
The 33rd U.S. president, who succeeded Franklin D. Roosevelt upon Roosevelt's death in April 1945. Truman, who led the country through the last few months of World War II, is best known for making the controversial decision to use two atomic bombs against Japan in August 1945. After the war, Truman was crucial in the implementation of the Marshall Plan, which greatly accelerated Western Europe's economic recovery.
question
Potsdam Conference
answer
From July 17 to August 2, 1945, President Harry S Truman met with Soviet leader Joseph Stalin and British leaders Winston Churchill and later Clement Attlee near Berlin to deliver an ultimatum to Japan: surrender of be destroyed.
question
West Berlin
answer
The part of the capital city of Berlin that was under control of the Americans, Brits and French after World War II.
question
East Berlin
answer
The part of the capital city of Berlin that was under control of the Soviet Union World War II.
question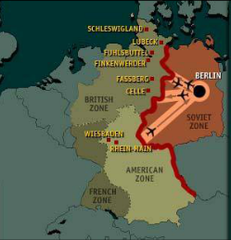
Berlin Blockade

answer
An attempt in 1948 by the Soviet Union to limit the ability of France, Great Britain and the United States to travel to their sectors of Berlin, which lay within Russian-occupied East Germany. Eventually, the western powers instituted an airlift that lasted nearly a year and delivered much-needed supplies and relief to West Berlin. Coming just three years after the end of World War II, the blockade was the first major clash of the Cold War and foreshadowed future conflict over the city of Berlin.
question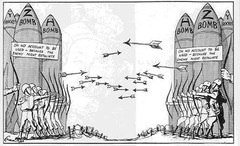
Arms Race

answer
The buildup of arms was also a characteristic of the Cold War between the U.S. and the Soviet Union, though the development of nuclear weapons changed the stakes for the par.
question
Nuclear Proliferation
answer
The spread of nuclear weapons to new nations. Treaty to limit the spread (proliferation) of nuclear weapons. The treaty came into force on 5 March 1970 and currently there are 189 states party to the treaty, five of which are recognized as nuclear weapon states: the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, and China (also the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council)
question
General Douglas MacArthur
answer
Was an American general and field marshal of the Philippine Army who was Chief of Staff of the United States Army during the 1930s and played a prominent role in the Pacific theater during World War II. He was one of only five men ever to rise to the rank of General of the Army in the U.S. Army, and the only man ever to become a field marshal in the Philippine Army.
question
Dwight Eisenhower
answer
Supreme Commander of the US Forces in Europe during World War II; became President of the US and during his two terms presided over the conomically prosperous 1950s. He was praised for his dignity and decency, though critcized for not being more assertive on civil rights
question
Eisenhower Doctrine

answer
Policy of the US that it would defend the Middle East against attack by any communist country. Restatement of the containment policy.



