WBC Disorders (210 Hematology) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion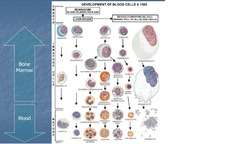
Hematopoiesis

answer
Blood cells are formed in bone marrow, where they mature Stem cells give rise to all blood cells, including RBCs, WBCs & platelets Progenitor cells differentiate Precursor cells acquire morphologic features of each cell type Cells enter bloodstream
question
Normal Peripheral White Blood Count
answer
4,800-10,800 cells/µL (adult) Slightly lower in blacks Slightly higher during pregnancy Much higher in infants & young children
question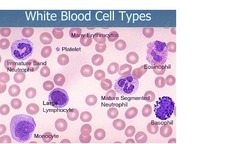
WBC Types (Peripheral Blood)

answer
Segmented Neutrophils Band Neutrophils Lymphocytes Monocytes Eosinophils Basophils
question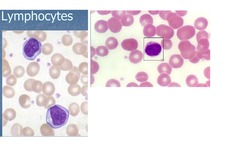
Lymphocytes

answer
13-46% of WBCs Small, dark blue Scant cytoplasm INCREASE in acute viral illness such as EBV, CMV Reactive lymphocytes (normal response to infection) -Plasma cells: thought to be progeny of B lymphocytes, not in peripheral blood, live in tissues -Stimulated in infection
question
T Cells
answer
Cytotoxic T cells -bind to antigens on plasma membrane of target cells (cancer, virus-infected, foreign tissue) & directly destroy cells Helper T cells -secrete cytokines, activating B cells, cytotoxic T cells, NK cells & macrophages NK cells -bind directly & nonspecifically to virus infected & cancer cells to kill them, function as killer cells in Ab-dependent cellular toxicity
question
B Cells
answer
Initiate Ab-mediated immune responses by binding specific antigens to B cell plasma membrane receptors (immunoglobulins) Transform into plasma cells after activation Present antigen to helper T cells
question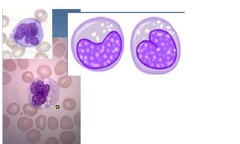
Monocytes

answer
3-9% of WBCs Largest WBC, irregular shape, light blue cytoplasm May be increased in some chronic bacterial infections (TB), or during recovery from acute infections Phagocytic Extracellular killing via secretion of toxic chemicals Process & present antigen to helper T cells Secrete cytokines involved in inflammation, activation & differentiation of helper T cells, & systemic responses to infection or injury (the acute phase response) Enter tissue & transform into macrophages Macrophages perform same functions in TISSUES
question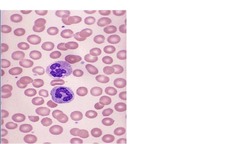
Neuitrophils

answer
Granulocytes 53-79% of WBCs Granules stain neutral Light pink cytoplasm Phagocytize debris & bacteria, kill microbes Pathognomonic of acute inflammation Release chemicals involved in inflammation (vasodilators, chemotaxins, etc.)
question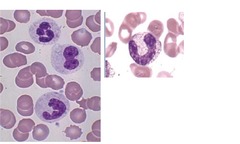
Bands

answer
Immature neutrophils 0-10% of WBCs Nucleus shape not segmented INCREASE in peripheral blood is called "left shift"
question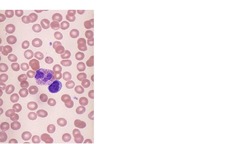
Eosinophils

answer
Granulocytes 0-4% of WBCs Granules stain reddish-orange Modulate immunologically mediated inflammation Participate in immediate hypersensitivity reactions Destroy multicellular parasites
question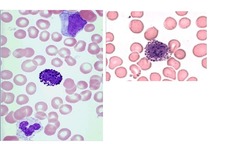
Basophils

answer
Granulocytes 0-1% of WBCs Granules stain deep blue/purple ?? Function in CIRCULATION INCREASE in CML, UC Related to mast cells in chemical characteristics & function (mast cells do not circulate, are found in most connective tissues & organs) Acute & delayed allergic reactions Mast cells release histamine & other inflammatory substances
question
Diagnostic Methods for WBCs (Tests)
answer
CBC (complete blood count) WBC differential Bone marrow evaluation Lymph node biopsy Protein electrophoresis (PEP): Serum (SPEP) Urine (UPEP) Special stains
question
2 Parts of WBC COUNT
answer
Total number of WBCs -Per 1mm^3 (µl) peripheral blood Differential count -% each type of leukocyte in same specimen
question
MANUAL Differential

answer
Stain whole blood film Microscopic exam Scan film with low magnification Estimate WBC count & platelet count
question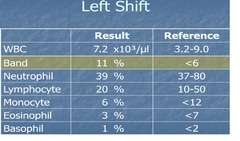
Left Shift

answer
increased prominence of immature WBCs in differential, usually from acute bacterial infection
question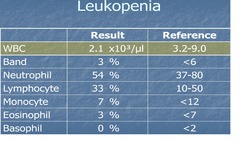
Leukopenia

answer
decrease in total WBC count; seen in viral infections, radiation, drugs, or chemical exposure
question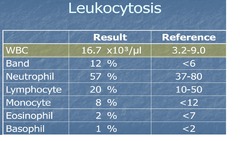
Leukocytosis

answer
increase in total WBC count; seen in infectious disease (esp. bacterial) or leukemia
question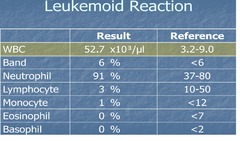
Leukemoid Reaction

answer
EXTREME increase in WBC count (to levels seen in leukemia, but caused by infection, esp. sepsis); RESOLVES with treatment
question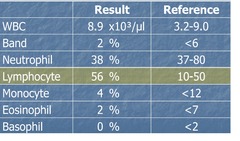
Lymphocytosis

answer
lymphocyte value is higher than reference range
question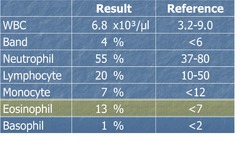
Eosinophilia

answer
high eosinophils
question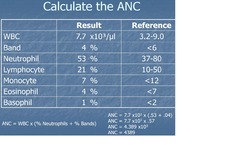
Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)

answer
One measure of risk for infection ANC = WBC x (% Neutrophils + % Bands) Immunocompromised if ANC < 1000
question
5 Abnormal WBC Inclusions (Morphology)
answer
Auer rods Döhlebodies Toxic granulation Neutrophil hypersegmentation Vacuoles
question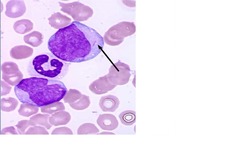
Auer Rod

answer
Red/pink narrow rod in cytoplasm Found in blasts Suggests AML
question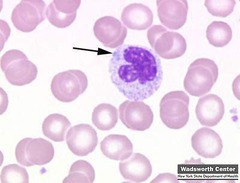
Dohle Body

answer
Blue irregular patch or patches Near edge of neutrophil Associated with infection
question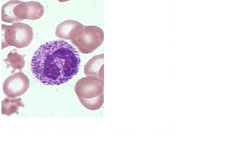
Toxic Granulation

answer
Prominent purple/blue-black granules Seen in neutrophils Severe systemic infection & toxic states
question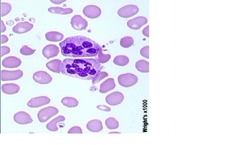
Hypersegmentation

answer
6 or more lobes or >3% with 5+ lobes In neutrophils Megaloblasticanemia, B12-folate deficiency, myeloproliferative d/o
question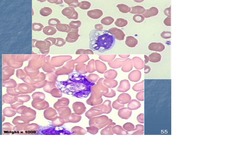
Vacuoles

answer
Degenerative changes In monocytes & neutrophils May suggest sepsis
question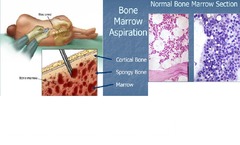
Bone Marrow Aspiration/Biopsy

answer
Bone marrow aspiration -Dry tap may require repositioning needle or biopsy procedure -Iliac Crest Bone marrow biopsy If marrow is hypoplastic or hyperplastic (& unable to aspirate)
question
Special Stains
answer
Used to identify & diagnose specific conditions Many available Ex: leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) -Low in CML -High in leukemoid reactions
question
Myelodysplastic Syndromes
answer
Cytopenia with a hypercellular bone marrow Morphologic abnormalities in two or more hematopoietic cell lines Cytogenetic abnormalities Despite adequate numbers of progenitor cells, ineffective hematopoiesis occurs Sometimes termed "preleukemia"
question
Immunoproliferative Diseases
answer
Multiple Myeloma (more common) Monoclonal Gammopathy of Uncertain Significance (MGUS) Waldenström's macroglobinemia
question
Multiple Myeloma
answer
Excess plasma cell clone production Collection in bone marrow = myeloma Multiple collections = multiple myeloma, seen as multiple bone lesions Findings: anemia, hypercalcemia, marked monoclonal spike in IgG ;/or IgA on SPEP, monoclonal proteins on UPEP (Bence-Jones proteins), lytic lesions on skeletal radiograph
question
4 Types of Leukemias
answer
ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia AML: acute myelogenousleukemia CLL: chronic lymphocytic leukemia CML: chronic myelogenousleukemia
question
Leukemia
answer
Definitive diagnosis of leukemia: blasts on bone marrow; most often presents as blasts in peripheral blood Findings: -INCREASE WBC on CBC -DECREASE PLT (acute), NL (chronic) -Hct/Hgb: normocytic normochromic anemia CLLs ; CMLs characterized by gradually increasing #s of mature cells in marrow
question
Leukemia Evaluation
answer
Morphology of WBCs Cytochemistry (special stains) Genetic analysis (chromosomal, molecular) Immunology / Serology
question
Acute Leukemias
answer
Rapid onset with symptoms common Pancytopenia with circulating blasts Bone marrow hypercellular ; dominated by blasts
question
Chronic Leukemias
answer
Slow onset, many patients asymptomatic Disorders of middle age
question
2 Major Lymphomas
answer
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) -Classification controversial, recently based on both clinical ; pathologic features
question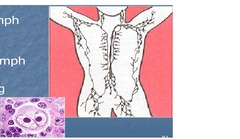
Hodgkin Lymphoma

answer
Arises from lymph tissue Pathologic diagnosis by lymph node biopsy Reed-Sternberg cells present in peripheral blood
question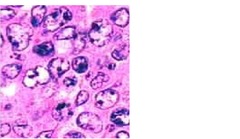
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma

answer
Peripheral blood may be normal, some have leukemic phase INCREASED serum LDH Lymph node biopsy required for diagnosis ; staging
question
Infectious Diseases with WBC Findings
answer
Infectious Mononucleosis Ehrlichiosis Histoplasmosis Cryptococcus Neoformans HIV (covered in Infectious Disease unit of ClinMed)
question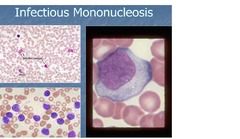
Infectious Mononucleosis

answer
Cause: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Findings: Lymphocyte pleomorphismon blood film with lymphocytosis ; 10% reactive lymphocytes! INCREASED EBV titer Heterophile Ab Bone marrow = normal
question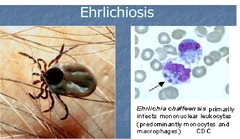
Ehrlichiosis

answer
Cause: tick-borne Ehrlichiaebacteria Findings: Clustered bacteria in vacuoles in neutrophils, or monocytes ; macrophages on blood film (depends on type of Ehrlichia) Thrombocytopenia Leukopenia with left shift in neutrophils Rising Ab immunofluorescence titer
question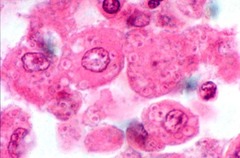
Histoplasmosis

answer
Cause: intracellular fungus Histoplasma capsulatum Findings: Usually in immunocompromised patients Organism in neutrophils ; monocytes on Wright-Giemsa stained blood film Organism in macrophages on bone marrow smear



