Neurology Exam 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Anterior/Posterior
answer
Closer to the front side/closer to the back side
question
Superior/Inferior
answer
Above, further from the ground/ below, slower to the ground
question
Superficial/Deep
answer
On or near the surface/further from the surface
question
Medial/Lateral
answer
Toward the midline/away from the midline
question
Rostral
answer
Toward nose
question
Caudal
answer
Toward tail
question
Dorsal
answer
Toward back
question
Ventral
answer
Toward belly
question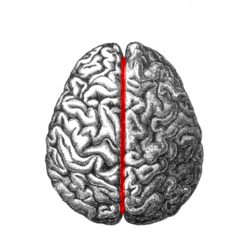
Sagittal Slice

answer
Separates right half from left half
question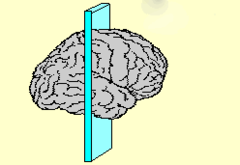
Coronal Slice

answer
Separates front from back
question
Horizontal Slice
answer
Separates top from bottom
question
Transverse Slice
answer
Showing the middle of object at an angle
question
Efferent Nervous System
answer
From CNS to body
question
Afferent Nervous System
answer
From body to CNS
question
Gyrus
answer
Hill
question
Sulcus
answer
Valley
question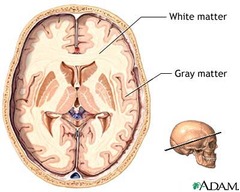
White Matter

answer
Made up of axons, in the inside of the brain and on the outside of the spinal column
question
Grey Matter
answer
Made up of cell bodies, on the outside of the brain and on the inside of the spinal column
question
Neocortex
answer
-90% -newest -6 layers of cells -80% excitatory neurons -20% inhibitatory interneurons
question
Allocortex
answer
-10% -oldest -3-5 layers of cells
question
Basal Ganglia
answer
Network of structures that form a ring around the thalamus and control movement/body position, sense of direction/distance, inhibitors, and the reward center
question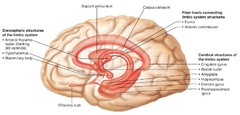
Limbic System

answer
Form a ring around the brainstem; control emotion memory and learning processes Includes - hippocampus, cingulate gyrus, amygdala, olfactory bulb, hypothalamus
question
Hippocampus
answer
Long term memory
question
Cingulate Gyrus
answer
Feeling reward/punishment
question
Amygdala
answer
Agression and fear
question
Olfactory Bulb
answer
Smell
question
Hypothalamus
answer
Behavior, homeostasis, metabolic functions, ANS
question
Thalamus
answer
Relay station between brain and senses (NOT SMELL), regulates emotion, attention, and consciousness
question
Pituitary Gland
answer
Regulates blood pressure, water balance in body, sex organs
question
Pineal Gland
answer
Melatonin (for sleep)
question
Sylvian or Lateral Fissure
answer
Separates temporal from frontal and parietal lobes
question
Longitudinal Fissure
answer
Line that divides the right and left hemisphere
question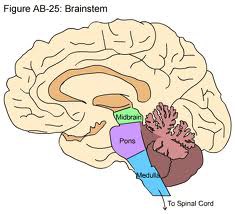
Brainstem Parts

answer
All information to and from the body-brain passes through the brainstem -Midbrain -Pons -Medulla
question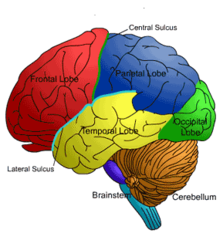
Lobes of the Brain

answer
1. Frontal Lobe 2. Parietal Lobe 3. Occipital Lobe 4. Temporal Lobe 5. Insular Lobe
question
Frontal Lobe
answer
Motor/Speech; higher executive functioning; judgement
question
Parietal Lobe
answer
Spatial information; attention; sensory
question
Occipital Lobe
answer
Vision
question
Temporal Lobe
answer
Language; comprehension; auditory; memory
question
Insular Lobe
answer
Homeostasis; emotion
question
Precentral Gyrus
answer
Primary motor strip
question
Postcentral Gyrus
answer
Primary sensory strip
question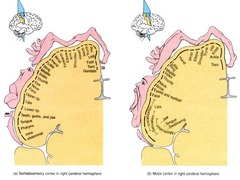
Homunculus

answer
Neutral representation of motor and sensory info maps onto the body
question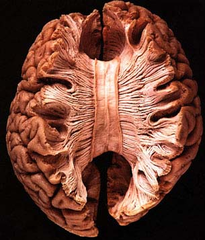
Corpus Callosum

answer
Connects the right and left hemisphere; made of white matter
question
8 Core Concepts of the Brain
answer
1. Brain interconnectivity 2. Centrality of CNS 3. Hierarchically organized levels 4. Laterality organized 5. Functional networking 6. Topographical organization 7. Plasticity 8. Culturally neutral brain
question
Brain Interconnectivity
answer
Brain is connected to itself; there is constant interactivity for information integration
question
Centrality of CNS
answer
Decision maker, integration of incoming/outgoing information, analyze/synthesize information, generates a response
question
Hierarchically Organized Levels
answer
Complexity increases with ascending level (Lowest level = spinal cord) (Highest level = cerebral cortex)
question
Laterality Organization
answer
-bilateral anatomic symmetry (except enlarged left temporal planum) -unilateral function differences -contralateral sensorimotor control
question
Functional Networking
answer
Distinct parallel pathways conducting different types of information (Sensory fibers = touch) (Motor Efferent = limbs)
question
Topographical Organization
answer
Selectivity of organization
question
Plasticity
answer
Brain's ability to reorganize and modify due to adaptations from external/internal changes
question
Culturally Neutral Brain
answer
Impartiality -Brain potential is independent of gender, race, and culture -Variations in size , shape, and weight -Differences don't change functionality
question
Central Nervous System (CNS)
answer
Brain and spinal cord; enclosed within the meninges and BBB. Responsible for higher cognitive functions
question
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
answer
Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia; found outside the meninges and BBB
question
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
answer
Part of PNS, control involuntary actions (like heart racing, mouth drying), affects glands and smooth muscles, survival
question
3 Division of ANS
answer
1. Sympathetic 2. Parasympathetic 3. Enteric
question
Sympathetic Nervous System
answer
Prepares you body for action -Flight -Fight -Fright -Fornication
question
Parasympathetic Nervous System
answer
Conserves energy -Salivation -Lacrimation (crying) -Urination -Defecation
question
Enteric Nervous System
answer
Runs the gut - digestion; very little input from the CNS
question
Somatic Nervous System
answer
The somatic system is the part of the PNS that is responsible for carrying motor and sensory information both to and from the CNS.
question
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
answer
Insulation of capillaries in brain so blood does not mix with cerebrospinal fluid
question
Meninges
answer
Membranes that envelop CNS to keep in cerebrospinal fluid; provides supporting framework for CNS vessels; 3 layers of protection
question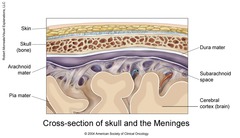
3 Layers of Meninges

answer
1.Dura Mater (dense, most protective) 2. Arachnoid Mater (like a spider web, in the middle) 3. Pia Mater (softest, adheres directly to brain/spine)
question
Cell Membranes
answer
Made up of pumps, channels, and an impermeable phospholipid bilayer
question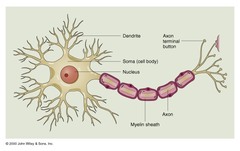
Neurons

answer
Primary nerve cells of CNS. Process info, specialize in communication. Have excitable membranes, dendrites, soma, axons, carry electical currents, capable of chem transmission.
question
Types of Neurons
answer
-Sensory Neurons: receive info (translate info) -Motor Neurons: provoke behavior (move muscles) -Interneurons: support staff, organized as networks for perception, cognition etc.
question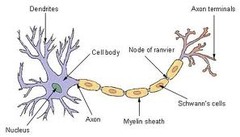
Parts of a Neurons

answer
1. Cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) 2. Soma 3. Axon 4. Dendrite 5. Mitochondrion
question
Soma
answer
-Cell body of neuron -Functions = protein synthesis and cell maintenance
question
Axon
answer
-Originates at axon hillock, ends at axon terminal; branches into synaptic terminals -Function = conducts electric signal away from cell body
question
Dendrites
answer
-Covered in receptor proteins -Function = receive chemical messages across synapses
question
Mitochondrion
answer
Organelles that produce ATP
question
ATP
answer
Cell's energy source; produced by mitochondrion
question
Receptors
answer
Consisting of molecules located on cellular surface; binds to neurotransmitters which travel across synaptic cleft
question
Transporters
answer
Gated cell membrane channels gated by electric potential or neurotransmitters. Flow of ions depend on density of channels, size, ion concentration gradient, and electrical gradient
question
Glial Cells
answer
Cells that provide support for the brain -Structural support -Chemical support -Insulation (myelin) -Debris removal -Form BBB -Development (guide neuron migration and growth) -Information processing
question
Myelin Sheath
answer
Sheath of lipid and cell membrane wrapped around an axon and contributes to speed of impulse transmission
question
Resting Potential
answer
A neuron "resting" is when it is not generating an electrical impulse but has the potential to act; intracellular cytosol is about 70mV more negative than extracellular (more K, less Na)
question
3 Forces that Act on Ions
answer
Concentration, Concentration Gradient, & Electrical Force
question
Concentration
answer
Ions will move from a higher concentration of that ion to a lower concentration of that ion
question
Concentration Gradient
answer
-Difference in concentration of molecules in space. -Resting potential means more K+ in and more Na+ out
question
Electrical Force
answer
OPPOSITES ATTRACT. Negative ions move toward positive charges and positive ions move toward negative charges
question
Electrical Current
answer
Current is the movement of charged ions. Electric current is the language of neurons
question
Sodium Potassium Pump
answer
Protein machine in the membrane that actively pumps against concentration gradient. Pump continually kicks 3 sodium for every 2 potassium ions it brings in
question
Nongated Sodium or Potassium Channel
answer
Channels that are specially designed to only allow these ions to pass through the membrane. There are more potassium channels than sodium channels. Pumps for ions opposite of concentration gradient to maintain concentration
question
Depolarization
answer
Inside of cell becomes less negative (or more positive like -50mv)
question
Polarization
answer
Resting Potential (-70 mv)
question
Hyperpolarization
answer
Inside of cell becomes more negative (-80 mv)
question
Action Potential
answer
How electrical messages are transmitted within the neuron; a rapid change across neural membrane caused by movement of ions
question
Synaptic Vesicle
answer
Found within synaptic terminals - filled with neurotransmitters that mediate connection between cells - small bubbles that transport material to terminal
question
Postsynaptic Receptor
answer
Membrane of postsynaptic cell; contains receptor proteins, the sites for binding neurotransmitter molecules
question
Neurotransmitters
answer
Help regulate brain mechanisms that control cognition, language, speech, moods, attention, etc. Released at a synapse and transmits a signal across neurons



