Mental Health Nursing Exam #1 SXU – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
mental health - WHO
answer
a state of well-being in which each individual is able to realize his or her own potential, cope with the normal stresses of life, work productively and fruitfully, and make a contribution to the community
question
mental illness (Health Canada, 2002)
answer
refers to all mental disorders with definable diagnoses
question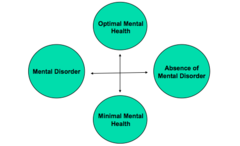
Epp Report - mental health continuum

answer
this depiction of mental health and mental illness allows for 4 possible outcomes: 1. maximal mental disorder and optimal mental health 2. optimal mental health and absence of mental disorder 3. absence of mental disorder and minimal mental health 4. minimal mental health and maximal mental disorder
question
10 components of recovery (SAMHSA, 2011)
answer
1. self-directed 2. individual- and person -centred 3. empowering 4. holistic 5. nonlinear 6. strengths-based 7. peer-supported 8. respect 9. responsibility 10. hope
question
epidemiology
answer
the quantitative study of the distribution of mental disorders in human populations
question
incidence
answer
the number of new cases of mental health disorders in a healthy population within a given period of time
question
prevalence
answer
the total number of cases, new and existing, in a given population during a specific period of time, regardless of when the subjects became ill
question
comorbidity
answer
more than one (mental) disorder at a time
question
Freud's Psychoanalytic Theory
answer
- advanced the first theory of personality development - articulated levels of awareness (unconscious, preconscious and conscious) and demonstrated the influence of our unconscious behaviour on everyday life, as evidence by use of defence mechanisms - identified 3 psychological processes of personality (id, ego, superego) - 5 stages of psychosexual stages articulate developmental theories of personality
question
Erikson's Ego Theory
answer
- expanded on Freud's developmental stages to include middle age through old age - called his stages psychosocial stages and emphasized the social aspect of personality development; development extended beyond the Mother/Father/Child triangle and included society that occurred throughout the lifespan
question
Harry Stack Sullivan's Interpersonal Theory
answer
the foundation of Hildegard Peplau's nursing theory of interpersonal relationships - focuses on interpersonal processes that can be observed in a social framework believing that therapy should educate patients and assist them in gaining personal insight - the nurse must interact with the patient as an authentic human being; mutuality, respect for the patient, unconditional acceptance, and empathy
question
Tidal Model
answer
created by Phill Barker II (used at ROH) focuses on the lived experience of the person-in-care and is based on the assumptions that people are their life stories and that they generate meaning through such stories 10 commitments: -Value the voice -Respect the language -Develop genuine curiosity -Become the apprentice -Reveal (the person's) personal wisdom -Be transparent -Use the available toolkit (the person's story - what has worked) -Craft the gift of time (reframing how we see time - how do we use this time?) -Know that change is constant
question
concurrent disorder
answer
e.g. mental disorder and a coexisting substance disorder
question
Hildegard Peplau's theory of interpersonal relationships in nursing
answer
the theory that is mainly concerned with the processes by which the nurse helps patients make positive changes in their health care status and well-being; illness offers a unique opportunity for experiential learning, personal growth, and improved coping strategies that psychiatric nurses play a unique role in facilitating an interpersonal relations in nursing model that comprises three overlapping themes: 1. the orientation phase 2. the working phase 3. the termination phase
question
pharmacodynamics
answer
refers to the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, which include the mechanisms of drug action and its effect
question
pharmacokinetics
answer
refers to the actions of the body on the drug and involves absorption (how much of the drug enters the circulation) and distribution of an administered drug determines the blood levels of drug, therefore determines dosage
question
Anti anxiety and Hypnotic Drugs
answer
GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS; include 4 types: 1. benzodiazipnes 2. short-acting sedative-hypnotic sleep drugs 3. buspirone hydrochloride 4. SSRI's
question
benzodiazepines
answer
promote the activity of GABA by binding to a specific receptor on the GABA(A) receptor complex and results in inhibited cellular excitation because neurotransmitters cannot be released leading to a calming effect at higher doses, all cause sedation (hypnotic effect); effective as anticonvulsants for their ability to reduce the neuronal overexcitement of alcohol withdrawal
question
benzodiazepines
answer
- diazepam - clonazepam - alprazolam - lorazepam - temazepam - triazolam - nitrazepam - oxazepam
question
zopiclone
answer
a short-acting sedative-hypnotic sleep drug, termed z-drug it is unrelated to existing hypnotics, but promotes GABA and inhibits the release of neurotransmitters with a fast onset of action 2 hour half-life; causes unpleasant bitter taste upon awakening
question
buspirone hydrochloride
answer
an anxiolytic drug that is used for the short-term relief of excessive anxiety without having strong sedative-hypnotic properties; does not leave the pt sleepy or sluggish (not a CNS depressant) mechanism is not clearly understood, but seems to moderately enhance the effects of serotonin; so-called a partial serotonin agonist
question
anti-depressant drugs
answer
1. tricyclic antidepressants 2. selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) 3. Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
question
monamine hypothesis of depression
answer
there is a deficiency in one or more of the three neurotransmitters - serotonin, norepinephrine, or dopamine; theory suggests increasing these alleviates depression
question
monamine receptors hypothesis of depression
answer
suggest that low levels of neurotransmitters cause postsynaptic receptors to be up-regulated (increased in sensitivity or number) increasing of neurotransmitters by antidepressants results in down-regulation (desensitization) of key receptors; delayed length of time for down-regulation may explain why it takes so long for antidepressants to work, especially if they rapidly increase neurotransmitters
question
tricyclic antidepressants
answer
widely used prior to SSRIs; no longer considered first-line treatment (advert effects) thought to act primarily by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine for the secondary amines and of both norepinephrine and serotonin for the tertiary amines which prevents NE from coming into contact w/its degrading enzyme, MAO - nortriptyline hydrochloride - amitriptyline hydrochloride - imipramine hydrochloride
question
SSRIs
answer
preferentially block the reuptake and, therefore, the destruction of serotonin; have less ability to block the acetylcholine muscarinic and histamine-1 than TCAs, therefore more selective action. adverse effects may include spinal reflexes of orgasm, apathy, low libido and nausea/vomitting -Fluoxetine hydrochloride -Paroxetine hydrochloride -Citalopram hydrobromide -Escitalopram oxalate -Fluvoxamine maleate -Sertraline hydrochloride
question
SNRIs
answer
medications that increase both serotonin and norepinephrine venlafaxine hydrochloride venlafaxine succinate duloxetine hydrochloride
question
venlafaxine hydrochloride and venlafaxine succinate
answer
potent inhibitor of neuronal serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake and weak inhibitor of dopamine reuptake has the flexibility of working as an SSRI at lower doses and as an SNRI at higher doses
question
duloxetine hydrochloride
answer
an SNRI that has an equal balance of inhibitor effects of norepinephrine and serotonin reuptake; greater noradrenergic effect that does velafaxine hydrochloride indicated for acute and maintenance treatment of major depressive disorder, for acute treatment of generalized anxiety disorder, for managing neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, and for managing fibromylagia
question
SNDIs
answer
class that only has one drug, Mirtazapine increases norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin (5-HT) transmission by blocking central presynaptic alpha-adrenergic inhibitory receptors has a rapid onset and has anti anxiety and antidepressant effects
question
MAOIs
answer
a group of anti-depressant drugs that prevent the destruction of monamine by inhibiting the action of monoamine oxidase phenelzineu sulfate tranylcypromine selegiline hydrochloride
question
monoamines
answer
a type of organic compound and include the neurotransmitters NE, E, dopamine and serotonin, as well as many different food substances and drugs
question
monoamine oxidase (MAO)
answer
an enzyme that destroys monamines
question
bupropion hydrochloride
answer
effective both as an antidepressant and for smoking cessation seems to act as a dopamine-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and also inhibits nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to reduce the addictive action of nicotine does not cause sexual adverse effects (no serotonin action), but may cause insomnia, tremor, anorexia and weight loss
question
trazodone hydrochloride
answer
a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) and is not a first choice for antidepressant treatment; often given with another antidepressant drug because sedation
question
mood stabilizers
answer
lithium carbonate anticonvulsant drugs: - valproate - carbamazepine - lamotrigine - gabapentin - topiramate - oxcarbazepine
question
lithium carbonate
answer
a mood stabilizer used to treat patients with bipolar disorders mechanism of action is far from understood; may interact with the electrical impulses along neurons
question
first generation antipsychotics
answer
conventional antipsychotics that are strong antagonists at the D2 dopamine receptors by binding to these receptors and blocking the attachment of dopamine, they reduce dopaminergic transmission
question
second generation antipsychotic drugs
answer
producer fewer extrapyramidal effects; target both the negative and positive symptoms; often chosen as first-line treatment; associated with significant weight-gain and metabolic syndrome clozapine risperidone quietapine olanzapine ziprasidone hydrochloride monohydrate paliperidone paliperidone palmitate
question
third-generation antipsychotic drug
answer
aripiprazole: a dopamine stabilizer
question
mental status exam
answer
a systematic assessment of an individual's appearance, affect, behaviour and cognitive processes reflects examiners observations and impressions making it highly subjective
question
milieu therapy
answer
managing the environment in which treatment takes place so that patients feel comfortable, safe and respected management includes orientating patients to their rights and responsibilities, selecting specific activities that meet patients physical and mental health needs and ensuring the least restrictive environment as possible informs patients about the needs for limits and conditions
question
delusion
answer
a fixed belief, based on an incorrect inference about reality not shared by others and is inconsistent w/the individual's intelligence or cultural background and cannot be corrected by reasoning
question
hallucination
answer
false sensory perceptions (not associated with external stimuli and not shared by others) Auditory, visual, tactile, olfactory, gustatory, command
question
delusion of control
answer
belief that one's thoughts are controlled by an outside force
question
thought insertion
answer
belief that thoughts are being inserted into one's mind by someone else
question
thought broadcasting
answer
the belief that one's thoughts are obvious to others or are being broadcast to the world
question
ideas of reference
answer
the belief that other people, objects and events are related to or have a special significance for one's self e.g. a person on a television is talking to or about them
question
illusion
answer
misperception or misrepresentation of real sensory stimuli
question
paranoid delusions
answer
an irrational distrust of others and/or the belief that others are harassing, threatening, etc.
question
bizarre delusions
answer
an absurd or implausible belief e.g. the electricity is making me gain weight
question
somatic delusions
answer
a false belief in involving the body or bodily functions
question
delusions of grandeur
answer
an exaggerated belief of one's importance or power (reference to sovereignty or super powers)
question
religious delusions
answer
the belief that one is an agent of or specially favoured by a greater being
question
erotomania
answer
the belief that someone (often a public figure) unknown to the individual is in love w/them or in a relationship w/them e.g. Tom Cruise is in love with me and my baby is his baby
question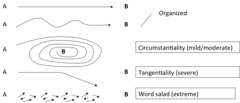
disturbances in thought process

answer
a number of mental disorders are characterized by disturbances in the process of normal thinking
question
loosening of associations
answer
lack of logical relationship between thoughts and ideas; conversations shift from one topic to another in a completely unrelated manner, making it confusing and difficult to follow
question
Circumstantiality
answer
the individual takes a long time to make a point because his or her conversation is indirect and contains excessive and unnecessary detail (over inclusive)
question
Tagentiality
answer
similar to circumstantiality, except that the speaker does not return to a central point
question
thought blocking
answer
an abrupt pause or interruption in one's train of thoughts, after which the individual cannot recall what he or she was saying
question
neologisms
answer
the creation of new words
question
flight of ideas
answer
rapid, continuous verbalization, w/ frequent shifting from one topic to another
question
perseveration
answer
a persisting response to a stimulus even after a new stimulus has been presented
question
clang associations
answer
the use of words or phrases that have similar sounds but are not associated in meaning; may include rhyming or puns
question
echolalia
answer
the persistent echoing or repetition of words or phrases said by others
question
verbigeration
answer
the meaningless repetition of incoherent words or sentences; typically associated w/psychotic states and cognitive impairment
question
transference
answer
client unconsciously and inappropriately displaces onto nurse, feelings and behaviours, related to significant figures in the patient's past
question
countertransference
answer
when the nurse displaces their own feelings related to people in nurses's past onto client
question
boundary violations
answer
boundary crossings occur when the nurse becomes over/under-involved w/ the client and the relationship enters into the personal domain
question
defence mechanism
answer
automatic psychological process protecting the individual against anxiety and from the awareness of internal or external dangers or stressors
question
Form 1
answer
initiated by an MD (of any kind who has examined the patient within the last 7 days). This form allows the police to apprehend a person and bring them to a hospital ED for a psychiatric evaluation. The person can be held involuntarily for 72 hours for this eval.
question
Form 2
answer
Initiated by a friend/family member/person other than MD. They go to a justice of the peace and plead their case. The Justice issues the form 2, which then allows the police to apprehend a person and bring to hospital for a psychiatric evaluation (same 72 hours timeframe as a form 1).
question
Form 3
answer
this is issued by a psychiatrist (usually the one who did the psych eval from the form 1 or 2), if they feel the person needs to be kept in hospital involuntarily. It lasts up to 2 weeks.
question
Form 4
answer
the renewal of a Form 3
question
Form 45
answer
community treatment order (CTO)
question
Form 47
answer
apprehension orders for when a patient does not comply with their CTO
question
Section 17
answer
when a police officer determines that a patient needs immediate psychiatric care. They bring them directly to the ED for evaluation. The police officer must remain with the patient until their custody is transferred to a physician.
question
tort
answer
a civil wrong for which money damages may be collected by the injured party (plaintiff) from the responsible party (defendant)
question
intentional tort
answer
willful or intentional acts that violate another person's rights or property - assault - battery - false imprisonment - invasion of privacy - defamation of character
question
unintentional tort
answer
unintended acts against another that produce injury or harm - negligence - malpractice
question
General Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
answer
In contrast to everyday worries, GAD must be excessive, persistent and pervasive. The amount of time spent on worrying; the degree of control over one's worrying; and the impact on personal, social, and occupational functioning are key components of the assessment. GAD affects nearly 4% of the population at any given time (very common).
question
allostasis
answer
the body's normal adaptive processes to keep (chemical) homeostasis
question
allostatic overload
answer
the cumulative wear and tear of the biologic system - may lead to stress-related disorders
question
OCD
answer
Psychiatric disorder characterized by severe obsessions and compulsions that significantly interfere normal daily living The typical age of onset of OCD is in the early 20s to mid - 30s (although symptoms begin in childhood). - Ritualistic behaviors are typical of childhood (magical thinking, superstition) and disorder may go unnoticed. - Parents often notice social, academic (failing grades, decreased concentration), and personal impairments which help differentiate OCD from common behaviours.
question
obsessions
answer
Unwanted, intrusive and persistent thoughts, impulses, or images that cause anxiety and distress.
question
compulsions
answer
Behaviours that are performed repetitive, in a ritualistic fashion, with the goal of preventing or relieving anxiety and distress caused by obsessions.
question
PTSD
answer
Affects roughly 8% of the population PTSD doesn't only develop after a personal experience but may also include witnessing an event. Individuals with PTSD have four core symptoms cluster: 1. Re-experiencing 2. Avoidance 3. Numbing 4. Heightened arousal
question
Acute stress disorder
answer
Share the same symptom clusters as PTSD Differs in duration (symptoms emerge 2 to 4 days after exposure and lasts up to 1 month) Differs also by including dissociative symptoms (ex. Depersonalization, dissociative amnesia, etc.)
question
Social phobias
answer
(social anxiety disorder) involve persistent fear of social or performance situations in which embarrassment occurs. Many individuals who meet the criteria do not get diagnosed. Exposure to the social or performance situation nearly always provokes immediate anxiety or triggers a panic attack. Individuals with social phobias also fear that others will judge them and will go to great lengths to avoid feared situations. There are two subtypes of this disorder: 1. Generalized social phobias - most social situations 2. Specific social phobias - one or two social situations
question
Panic disorder
answer
Extreme overwhelming form of anxiety when individual is placed in a life-threatening situation (real or perceived) A chronic condition that has exacerbations and remissions. It is characterized by the appearance of disabling attacks of panic (with or without agoraphobia). Both types include recurrent and unexpected panic attacks followed by 1 month or more of consistent concern about: - having another attack - worrying about another - attack or changing behaviour because of fear of the attacks
question
Panic attack
answer
Discrete periods of fear or discomfort (usually peaks at 10 minutes but the effects can last as long as 30 minutes) Physical (palpitations, rapid pulse, trembling, SOB, paresthesia). Cognitive (depersonalization, derealization, fear of going crazy or going to die) Similar to cardiac emergencies (heart attack). Recognition of the seriousness of panic attacks should be communicated to the patient. can lead to the development of phobias, or persistent, unrealistic fear of situations, objects or activities
question
agoraphobia
answer
intense, excessive anxiety or fear about being in places or situations from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing or in which help might not be available if a panic attack were to occur feared places are avoided
question
Schizophrenia
answer
Phase 1 - Premorbid - Preschizophrenic presentation - characterized by some form of maladjustment Phase 2 - Prodromal - Signs and symptoms that precede the characteristic manifestations of an acute, fully developed illness Phase 3 - Schizophrenia - Active phase of the disorder Phase 4 - Residual - Schizophrenia is characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation. During the residual phase, symptoms of the acute stage are either absent or no longer prominent. Negative symptoms may remain.
question
psychosis
answer
a state in which the individual is experiencing hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized thoughts, speech or behaviours
question
schizophrenia - dopamine theory
answer
drives from the study of the action of the conventional (first-generation) antipsychotics; these block dopamine-2 receptors in brain limiting the activity of dopamine and reducing some symptoms
question
positive symptoms
answer
symptoms that exist that should not; reflect an excess or distortion of normal functions, including delusions and hallucinations are associated with: - acute onset - normal premorbid functioning - normal social functioning during remissions - normal CT findings - normal neuropsych test results - favourable response to antipsychotic
question
negative symptoms
answer
symptoms that should be there but are not; reflect a lessening or loss of normal functions, such as: - affective flattening or blunting - alogia - avolition - anhedonia they impede one's ability to: - initiate and maintain conversations and relationships - obtain and maintain a job - make decisions and follow through on plans - maintain adequate hygiene and grooming contribute to poor social functioning and social withdrawal
question
cognitive symptoms
answer
evident in most people with schizophrenia; include difficulty with attention, memory, info processing, cognitive flexibility and executive functions
question
affective symptoms
answer
symptoms that increase a person's suffering (e.g. depression)
question
anosognosia
answer
an inability to realize you are ill
question
recovery model
answer
outcomes should be consistent in that they stress hope, living a full and productive life and eventual recovery rather than focusing on controlling symptoms and adapting to a disability
question
metabolic syndrome
answer
includes weight gain, dyslipidemia and altered glucose metabolism caused by atypical anti-psychotic medications (second and third generation)
question
EPS
answer
a nerve tract which functions to control automatic movements required for postural adjustment; more likely in the use of antipsychotics must look for signs of: - dystonic reaction - akathisia - pseudoparkinsonism
question
dystonic reaction
answer
involuntary muscle spasm especially in head and neck
question
akathisia
answer
inability to sit still
question
pseudoparkinsonism
answer
rigidity, slowed movements and tremor; can be observed by the loss of spontaneous movements
question
neuroleptics
answer
reflects the common and often significant neurologic side effects produced by these medications (EPS ; TD)



