Nursing 131: therapeutic relationships – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Orientation Working Termination
answer
The three phases of the nurse-patient relationship.
question
Review Table 9-1 Common Patient Behaviors and Nurse Responses
answer
Identify common patient behaviors a nurse may encounter in the clinical setting.
question
•Consistency includes ensuring that a nurse is always assigned to the same patient and that the patient has a regular routine for activities. Interactions are facilitated when they are frequent and regular in duration, format, and location. Consistency also refers to the nurse being honest and consistent (congruent) in what is said to the patient. •Pacing includes letting the patient set the pace and letting the pace be adjusted to fit the patient's moods. A slow approach helps reduce pressure, and at times it is necessary to step back and realize that developing a strong relationship may take a long time. •Listening includes letting the patient talk when needed. The nurse becomes a sounding board for the patient's concerns and issues. Listening is perhaps the most 145 146 important skill for nurses to master. Truly listening to another person, attending to what is behind the words, is a learned skill. •Initial impressions, especially positive initial attitudes and preconceptions, are significant considerations in how the relationship will progress. Preconceived negative impressions and feelings toward the patient usually bode poorly for the positive growth of the relationship. In contrast, the nurse's feeling that the patient is "interesting" or "a challenge" and a positive attitude about the relationship are usually favorable signs for the developing therapeutic alliance. •Comfort and control, that is, promoting patient comfort and balancing control, usually reflect caring behaviors. Control refers to keeping a balance in the relationship: not too strict and not too lenient. •Patient factors that seem to enhance the relationship include trust on the part of the patient and the patient's active participation in the nurse-patient relationship.
answer
Explore aspects that foster a therapeutic nurse-patient relationship
question
inconsistency and unavailability (e.g., lack of contact, infrequent meetings, meetings in the hallway) on the part of the nurse, patient, or both.
answer
Factors that are inherent in a non-therapeutic nursing interactive process.
question
three personal characteristics that help promote change and growth in patients, which are classic guidelines that are vital components for establishing a therapeutic alliance or relationship: (1) genuineness, (2) empathy, and (3) positive regard.
answer
Define and discuss the role of empathy, genuineness, and positive regard on the part of the nurse in a nurse-patient relationship.
question
A well-defined therapeutic relationship allows the establishment of clear patient boundaries that provide a safe space through which the patient can explore feelings and treatment issues. The nurse's role in the therapeutic relationship is theoretically rather well-defined. The patient's needs are separated from the nurse's needs, and the patient's role is different from that of the nurse. Therefore the boundaries of the relationship seem to be well stated. In reality, boundaries are at risk of blurring, and a shift in the nurse-patient relationship may lead to nontherapeutic dynamics. Examples of circumstances that can produce blurring of boundaries include the following: •When the relationship slips into a social context •When the nurse's needs are met at the expense of the patient's needs
answer
Establishing boundaries
question
When situations such as these arise, the relationship has ceased to be a helpful one and the phenomenon of control becomes an issue. Role blurring is often a result of unrecognized transference or countertransference.
answer
influence of transference and countertransference on boundary blurring.
question
Values and Cultural Influences With in a Relationship
answer
Discuss the influences of different values and cultural beliefs on the therapeutic relationship
question
Working under supervision is an excellent way to keep the focus and boundaries clear. Communication skills and knowledge of the stages of and phenomena occurring in a therapeutic relationship are crucial tools in the formation and maintenance of that relationship. Within the context of a helping relationship, the following occur:
answer
Discuss the importance of nurse self awareness on professional practice and explain the role of clinical supervision.
question
in empathy we understand the feelings of others. In sympathy we feel the feelings of others. When a helping person is feeling sympathy for another, objectivity is lost, and the ability to assist the patient in solving a personal problem ceases. Furthermore, sympathy is associated with feelings of pity and commiseration.
answer
Empathy versus sympathy
question
the focus is on the nurse's behavior in the nurse-patient relationship. The nurse and the supervisor examine and analyze the nurse's feelings and reactions to the patient and the way they affect the relationship.
answer
clinical supervision
question
The patient has a right to know who else will be given the information shared with the nurse and that the information may be shared with specific people, such as a clinical supervisor, the physician, the staff, or other students in conference. The patient also needs to know that the information will not be shared with relatives, friends, or others outside the treatment team, except in extreme situations.
answer
confidentiality
question
A contract emphasizes the patient's participation and responsibility because it shows that the nurse does something with the patient rather than for the patient. The contract, either stated or written, contains the place, time, date, and duration of the meetings.
answer
contract
question
refers to the tendency of the nurse to displace onto the patient feelings related to people in his or her past.
answer
countertransference
question
Therefore, empathy signifies a central focus and feeling with and in the patient's world. According to Mercer and Reynolds (2002) it involves the following: •Accurately perceiving the patient's situation, perspective, and feelings •Communicating one's understanding to the patient and checking with the patient for accuracy •Acting on this understanding in a helpful (therapeutic) way toward the patient
answer
empathy
question
Genuineness, or self-awareness of one's feelings as they arise within the relationship and the ability to communicate them when appropriate, is a key ingredient in building trust. When a person is genuine, one gets the sense that what is displayed on the outside of the person is congruent with the internal processes.
answer
genuineness
question
in the United States is 0 to 18 inches and is reserved for those we trust most and with whom we feel most safe.
answer
intimate distance
question
It is the first time the nurse and the patient meet, and they are strangers to each other. When strangers meet, they interact according to their own backgrounds, standards, values, and experiences.
answer
orientation phase
question
18 to 40 inches) is for personal communications such as those with friends or colleagues
answer
personal distance
question
Recording all communication verbal and nonverbal
answer
process recordings
question
12 feet or more) relates to public space (e.g., public speaking). In public space one may hail another, and the parties may move about while communicating with one another.
answer
public distance
question
major emphasis during the first few encounters with the patient is on providing an atmosphere in which trust and understanding, or rapport, can grow.
answer
rapport
question
4 to 12 feet) is applied to strangers or acquaintances, often in public places or formal social gatherings.
answer
social distance
question
Both peoples needs are met
answer
social relationship
question
The termination phase is the final, integral phase of the nurse-patient relationship. Termination is discussed during the first interview, and again during the working stage at appropriate times. Termination may occur when the patient is discharged or when the student's clinical rotation ends. •Summarizing the goals and objectives achieved in the relationship •Discussing ways for the patient to incorporate into daily life any new coping strategies learned during the time spent with the nurse •Reviewing situations that occurred during the time spent together •Exchanging memories, which can help validate the experience for both nurse and patient and facilitate closure of that relationship
answer
termination phase
question
the relationship is consistently focused on the patient's problem and needs.
answer
therapeutic encounter
question
The nurse-patient relationship is often loosely defined, but a therapeutic relationship incorporating principles of mental health nursing is more clearly defined and differs from other relationships. A therapeutic nurse-patient relationship has specific goals and functions. Goals in a therapeutic relationship include the following: •Facilitating communication of distressing thoughts and feelings •Assisting patients with problem solving to help facilitate activities of daily living •Helping patients examine self-defeating behaviors and test alternatives •Promoting self-care and independence
answer
therapeutic relationship/partnership
question
Clients sometimes work in opposition to their therapists, a phenomenon known as "resistance." Such behavior is not simply an impediment to treatment, but also a potentially rich source of information about each client.
answer
resistance
question
is the process whereby a person unconsciously and inappropriately displaces (transfers) onto individuals in his or her current life those patterns of behavior and emotional reactions that originated in relation to significant figures in childhood. The patient may even say, "You remind me of my ______" (e.g., mother, sister, father, brother).
answer
transference
question
Values are abstract standards and represent an ideal, either positive or negative. Our values are usually culturally oriented and influenced in a variety of ways through our parents, teachers, religious institutions, workplaces, peers, and political leaders, as well as through films and the media.
answer
values
question
During the working phase, the nurse and patient together identify and explore areas in the patient's life that are causing problems. •Maintain the relationship. •Gather further data. •Promote the patient's problem-solving skills, self-esteem, and use of language. •Facilitate behavioral change. •Overcome resistance behaviors. •Evaluate problems and goals, and redefine them as necessary. •Promote practice and expression of alternative adaptive behaviors.
answer
working phase
question
Positive regard implies respect. It is the ability to view another person as being worthy of caring about and as someone who has strengths and achievement potential.
answer
Positive regard
question
Teaching: This means giving the patient specific information Advising: This means suggesting certain solutions to a problem Psychotherapy: This is examining the impact of experiences from the distant past.
answer
The therapeutic relationship does NOT involve
question
The therapeutic relationship is contractual. It is an explicit agreement that the nurse will be the helper/advocate, and the patient, the "helpee". There are no role shifts.
answer
Role shifts
question
The therapeutic relationship is goal-oriented and purposeful. It is not social. REMEMBER TO KEEP THE FOCUS ON THE PATIENT!
answer
Orientation
question
The therapeutic relationship is current. It focuses on what is happening for the patient at the present time.
answer
Timing
question
1. A patient seeking assistance and is ready to work. 2. A nurse willing and capable of giving assistance. 3. A safe environment for the process to occur.
answer
There are three requirements for a therapeutic relationship.
question
1. When the patient is experiencing a marked change in mental status. 2. When the patient is experiencing an acute physical problem. 3. When the patient needs intensive psychotherapy.
answer
Therapeutic communication is always appropriate, but there are times when it may be inappropriate or impossible to use these skills effectively. Here are three examples of situations in which the patient may NOT be ready to work with you:
question
Nurse-patient partnership •One of several types of professional relationships (educator, advocate) •Focus is on the patient's problems and needs, goal directed, purposeful, planned, patient centered-not social or reciprocal, the patient implements the solutions •Basis of all psychiatric nursing treatment interventions
answer
Nurse patient partnership Examples of types of professional relationships.. Focus in on... It is the ....
question
No matter what they do or how they act they deserve our attention and respect
answer
Positive regard
question
Empathy- understand the feelings of others. Much more apt to keep focus on the patient. Sympathy- feel the feelings of others. Often perceived as pity. Boundaries blur.
answer
Empathy Vs Sympathy
question
•Facilitate communication •Assist with problem solving •Help patients examine self defeating behaviors and explore alternatives •Promote self-care and independence
answer
Goals of Therapeutic Relationship: (4)
question
Self awareness. Values clarification.
answer
Pre orientation
question
•These patient situations can challenge us the most
answer
What happens when the nurse's beliefs, values, and interpretive system are very different from those of a patient?
question
Reflect our own culture ; experience. •Are those we have chosen for ourselves from a variety of influences and role models.
answer
It is helpful to realize that our values and beliefs:
question
Understand and accept our own values and beliefs. •Are sensitive to and accepting of the unique and different values and beliefs of others.
answer
•It is critical that we:
question
A meaningful therapeutic relationship is facilitated when values and cultural influences are considered. It is the nurse's responsibility to seek to understand the patient's perceptions.
answer
What helps a meaningful therapeutic relationship
question
•The more self aware one is the better able to analyze behavior ; reactions, to suspend judgment and focus on the needs of the client even if their values differ greatly from one's own •Supervision/mentoring •Countertransference
answer
Self Awareness
question
The first connections between the nurse and patient are to establish an understanding that the nursing relationship is: •Safe, confidential, reliable, and consistent. •Rapport building •Trust, genuineness, honesty, compassion •Testing behavior common •Resistance
answer
Phase 2: Orientation Phase
question
•Addressing needs and goals of the patient •Conducted within appropriate and clear boundaries. •Initially, one of the biggest boundary issues is over-connecting with patients. Intensity.
answer
Phase 3: Working Phase
question
Transference Counter transference
answer
Role and boundary blurring are often a result of unrecognized:
question
Transference- patient unconsciously projects intense feelings onto the therapist related to unfinished work from previous relationships •Countertransference-unconscious emotional response of the therapist projected onto the patient.
answer
Transference Counter transference
question
Although the boundaries of the nurse-patient relationship are generally clearly define, they can become blurred. •This can be insidious and may occur on an unconscious level. •Usually the transference and countertransference phenomena are operating when boundaries are blurred.
answer
Boundaries Although they are generally ____ they may become ____ This may be ____ This may lead to ____
question
feel close, have confided, developed trust, have been accepted and held in esteem-perhaps for the first time. •Fearful of loosing the therapeutic relationship •Fearful of being without the nurse
answer
Phase 4: Termination Difficulties for patients (3)
question
maintain the role of importance in the patient's life •Feels gratitude for the learning experience •Narcissism- "only one" who can help this patient
answer
Termination: Difficulties for the professional: (3)
question
•Consistency •Active listening •(First) impressions •Pacing •Comfort •Patient factors
answer
What helps: (6)
question
•Avoidance •Premature discharge ("kicked out") •Humor •Anger •Chaos at time of d/c
answer
Tendency not to terminate
question
Making self available and showing interest and concern "I will walk with you"
answer
Offering self
question
Observe verbals and non verbals Maintain eye contact and remarks to clarify and encourage further communication
answer
Active listening
question
"Tell me more about your son"
answer
Exploring
question
What do you want to talk about today
answer
Broad openings
question
Planned absence of verbal remarks to allow patient and nurse to think over what is being discussed
answer
Silence
question
Apprehension, uncertainty resulting from a real or perceived threat Can be acute or chronic
answer
Anxiety:
question
reactionary to situation
answer
Acute Anxiety (state)
question
on-going, possibly characterological
answer
Chronic Anxiety (trait)
question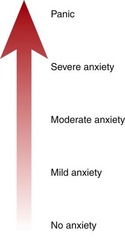

answer
The Four Levels of Anxiety
question
Perceptual field: heightened, on alert, able to process information from the environment.
answer
Mild Anxiety perceptual field
question
Cognition/learning: able to work effectively towards a goal, develop and identify alternatives.
answer
Mild Anxiety cognition/learning
question
slight discomfort, restless, irritable, tap fingers, chew lip, jingle change in pocket, pen clicking (exhibits what are known as nervous habits)
answer
Mild Anxiety behavioral
question
Perceptual: narrowing of perceptual field, less able to attend to environmental stimuli unless prompted by someone (selective inattention).
answer
Moderate anxiety perceptual
question
Cognition/learning: problem solving present but less effective; benefits from guidance and cues from others
answer
Moderate anxiety cognition/learning
question
Behavioral: voice tremors, change in pitch, poor concentration, shaky, repetitive questions, some diaphoresis, ? RR, pulse and muscle tension, pacing, banging and somatic complaints begin.
answer
Moderate anxiety behavioral
question
Perceptual field: greatly reduced, hyper-focused on details, self-absorbed, scattered attention, poor environmental attention even with cueing.
answer
Severe anxiety perceptual
question
•Cognition/learning: events and details are not connected, perceptual distortions are great (interpretations become skewed).
answer
Severe anxiety cognition/learning
question
Behavioral: feelings of dread, confusion, ineffective functioning, describes "impending doom", wanders aimlessly, absence of purposeful activity, intense somatic complaints, hyperventilation, tachycardia, withdrawal, loud and rapid speech; may become demanding or threatening
answer
Severe anxiety behavioral
question
Perceptual: unable to focus on the environment, terror, environmental paralysis, feels (s)he "ceases to exist", hallucinations or delusions may take the place of reality.
answer
PANIC perceptual
question
Cognition/learning: may be mute, extreme psychomotor agitation to the point of exhaustion, disorganized or irrational reasoning.
answer
PANIC cognition/learning
question
Behavioral: experience of terror, immobility, "freeze", severe hyperactivity or flight, dilated pupils, unintelligible communication or inability to speak, severe shakiness, sleeplessness, severe withdrawal, hallucinations, delusions, flashbacks, dissociation.
answer
PANIC behavior
question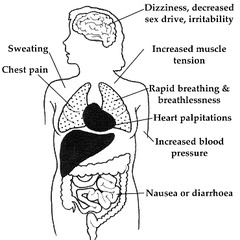
Inability to focus Nausea-severe Diarrhea- severe Rapid heart rate Etc... Look at levels above for more details

answer
Levels of Anxiety: Assessment Signs and Symptoms
question
•Assist with problem-solving efforts to cope with anxiety •Benefits from presence/guidance of others •Help the client understand the cause of the anxiety and learn new ways of controlling it. •Provide physical outlets •C.B.T. can be used and also promotion of the relaxation response
answer
Interventions for moderate levels of anxiety:
question
Cognitive behavioral therapy Using your mind to adjust your behaviors Useful in circumstances where they have control over their mind ex not using it for a skitzophrenic with hallucinations
answer
C.B.T.
question
Long term goals include client education, recognition of the anxiety, insight into the anxiety, and coping with anxiety.
answer
Interventions for moderate levels of anxiety: long term goals
question
•Stay with the client and provide support ?Reduce environmental stimuli ?Keep demands to a minimum ?Calm, simple, clear statements ?Encourage physical activity like walking ?Administer meds in a timely manner ?Assist in simple relaxation breathing techniques ?Teach to limit nicotine, caffeine ?Promote sleep with comfort measures ?Attend to physical needs Make them comfortable and assure the. That they are not alone
answer
For severe to panic anxiety levels: (10)
question
•Are normal behaviors which operate on an unconscious level and tend to deny or distort reality ?Help the individual cope with anxiety and prevent the person from being overwhelmed ?Have adaptive value if they do not become a style of life used to avoid facing reality ?May be maladaptive depending on frequency, intensity and duration of use
answer
Ego Defense Mechanisms (review): Are ...... Behaviors Helps them to ..... May be ...... Depending on frequency
question
HEALTHY INTERMEDIATE IMMATURE
answer
3 CLASSIFICATIONS
question
altruism, sublimation, suppression, humor.
answer
HEALTHY (4)
question
displacement, reaction formation, somatization, undoing
answer
INTERMEDIATE (4)
question
passive aggression, rationalization, acting out, dissociation, devaluation, idealization, splitting, projection, denial and regression
answer
IMMATURE (9)
question
Denial: "I'm not mad at you." Won't even let themselves believe that the unpleasing thought exists
answer
Denial
question
Displacement: "I'm not mad at you. I'm mad at the dog." Substitute a different target for impulses when the original would be dangerous or unacceptable
answer
Displacement
question
Projection: "I'm not mad at you. You are mad at me."
answer
Projection
question
Rationalization: "I'm not mad at you. I'm just tired."
answer
Rationalization
question
Regression: "I'm taking my toys and going home." Ex bed wetting You retreat to an earlier level of development or to less demanding habits or situations Ex a 16 year old gets in a fight with their parents but instead of talking it out like a young adult they slam their door
answer
Regression
question
Ex a little kid being bullied doesn't want to go to school because his stomach hurts
answer
Somatization
question
Suppression: "I'll deal with my anger tomorrow."
answer
Suppression
question
Unconsciously preventing painful or dangerous thoughts from entering your awareness
answer
Repression
question
Attributing ones own personal feelings, shortcomings, or unacceptable impulses on others Ex if you have a huge crush on somebody on Valentine's Day and they send valentines to everybody including you, so you think that they have a huge crush on you too because they sent you a valentine
answer
Projection
question
Prevents dangerous impulses from being expressed in behavior by exaggerating opposite behavior Ex if somebody blows you off and you are upset instead of saying you are upset you say "oh no I'm totally fine, I'm happy you didn't want to hang out I'm busy anyways"
answer
Reaction formation
question
Justify your behavior by giving reasonable and rational, but false, reasons for it Ex: you can't hand in your homework because your printer broke
answer
Rationalization
question
Working off unmet desires, or unacceptable impulses in activities that are constructive Ex: if they are mad at someone they go running instead of fighting
answer
Sublimation
question
Counteracting real or imagined weaknesses by emphasizing desire able traits or seeking to excel in the area of weakness or other areas
answer
Compensation
question
An immature unconscious defense mechanism in which the person deals with emotional conflict or stress by actions rather than reflection or feelings; The person is trying to feel less powerless or helpless by acting out.
answer
Acting out
question
Used as people were either really good or really bad. Ex if they broke up with the boyfriend they would say "he was really awful and bad" Pitting one against the other Ex if a mother has a gentle and harsh side and they refer to them as "good mommy" or "bad mommy" Splitting (also called black and white thinking or all-or-nothing thinking) is the failure in a person's thinking to bring together both positive and negative qualities of the self and others into a cohesive, realistic whole. It is a common defense mechanism used by many people.[1] The individual tends to think in extremes (i.e., an individual's actions and motivations are all good or all bad with no middle ground).
answer
Splitting
question
Always use the interventions that are most effective and least restrictive. Interventions are most effective and least restrictive when implemented early in the cycle of aggression.
answer
MANAGING AGGRESSIVE BEHAVIOR
question
?Individual Psychotherapy ?Group/Family Therapy ?Cognitive Behavior Therapies ?Relaxation and Stress Reduction Activities
answer
Non-Pharmacological Treatment Modalities of Mild to Moderate Anxiety (4)
question
Medications are not indicated for mild to moderate anxiety, additionally, meds can be easily abused if people have a low tolerance for this level of anxiety if they are fearful of escalation. ?Anxiety can escalate quickly. Monitor closely. ModerateSeverePanic ?Anxiety is "contagious". Stay calm. Be self aware.
answer
Medication and mild or moderate anxiety Indication Escalation Contagion



