Nursing process, communication, nursing diagnosis – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Nursing Process: why does Nursing need its own process?
answer
Identifying a process for our own profession *assists in clarifying the scope of our practice * identifies what is unique to our practice *facilitates dialogue in provision of interdisciplinary patient care
question
Steps of Nursing Process
answer
-Assessment -Nursing Dx -Outcome identification -Planning -Implementation -Evaluation
question
Assessment
answer
- systematic collection of subjective and objective data -goal = make clinical nursing judgement about indiv, fam or community -physical, psychological, emotional, sociocultural and spiritual factors considered for total client situation appraisal
question
Who is your primary source in an assessment?
answer
the client
question
Who is you secondary source?
answer
family significant others healthcare workers health records literature review
question
What should the assessment include
answer
Observation Interviewing Examining the client Interpreting laboratory data, diagnostic data
question
why is the assessment/ initial database so important?
answer
= reference point for all further nursing assessments and is crucial in determining plan of care.
question
Outcome identification must be
answer
- measurable -realistic -client focused
question
Rationale of interventions
answer
Must know why you are providing every intervention that you provide
question
Somatic
answer
well localized; stabbing, aching, throbbing; damage to skin, bone, muscle; peripheral nociceptors.
question
Visceral
answer
poorly localized; dull, aching, crampy, referred; injury to organs; nociceptors in skin.
question
Neuropathic
answer
can follow nerve path; sharp, shooting, burning; injured or dysfunctional PNS or CNS; aberrant somatosensory processing
question
Nociceptive pain
answer
-Damage to somatic or visceral tissue -Surgical incision, broken bone, or arthritis -Usually responsive to opioids and nonopioid medications *Somatic *Visceral
question
Somatic Nociceptive pain
answer
Localized Arises from bone, joint, muscle, skin, or connective tissue Somatic pain often is categorized as superficial or deep. Superficial pain arises from skin, mucous membranes, and subcutaneous tissues, and often is described as sharp, burning, or prickly. Deep pain is often characterized as deep, aching, or throbbing and originates in bone, joint, muscle, skin, or connective tissue.
question
Visceral Nociceptive pain
answer
*Tumor involvement or obstruction *Arises from internal organs such as the intestine and bladder *Comes from the activation of nociceptors in the internal organs and lining of the body cavities (ex: the thoracic and abdominal cavities). *Visceral nociceptors respond to: * inflammation * stretching *ischemia. *Stretching of hollow viscera in the intestines and bladder that occurs from tumor involvement or obstruction can produce intense cramping pain.
question
Neuropathic Pain
answer
*Damage to peripheral nerve or CNS *Numbing, hot-burning, shooting, stabbing, or electrical in nature *Sudden, intense, short-lived, or lingering Common causes of neuropathic pain: - trauma -inflammation -metabolic disease: DM, infections of NS, tumors, toxins, and neurologic disease such as MS. *Neuropathic pain often is not well controlled by opioid analgesics alone. Treatment is typically augmented with adjuvant therapies
question
Acute pain
answer
Improves over time Usually less than 3 months Mild - Severe Serves as a warning Anxiety Common
question
Chronic pain
answer
*Worsens and intensifies with the passage of time *Usually greater than 3 months *Moderate - Severe *Serves no purpose *Frustration common
question
T/F: Increase in vital signs are an indication that the patient is experiencing pain.
answer
Vital signs may increase for brief periods of acute pain, but this may not occur in patients with chronic pain. Besides pain, an increase in VS can signal many other problems, such as anxiety or deterioration in the patient's clinical status
question
Manifestations of pain
answer
*Physiologic responses *Increased blood pressure *Increased heart rate *Increased respiratory rate *Neuroendocrine and metabolic responses
question
T/F: Depression is common in patients who have chronic pain
answer
True. Many patients with chronic pain suffer from depression; as a patient group, they have an increased risk of suicide. A long period of pain coupled with deterioration in the patient's functional ability and relationships can cause a situational depression that affects pain relief, rest and interpersonal relationships.
question
Assessment of Client Experiencing Pain
answer
*Subjective data -Normal pattern identification: Location, intensity, quality, and temporal pattern of pain *Objective data -Physical assessment -Diagnostic tests and procedures *Functionality -Measure how chronic pain is effecting life
question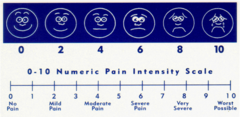
Pain Assessment tool for patients 12 y and older who are able to self report:

answer
*The Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) *For patients 12 years or older. *Patients are asked to rate their pain on a scale of 0-10. *0 represents no pain and a 10 represents the worst pain possible.
question
Pain Assessment tool for patients between 3 and 12 yo who are able to self report:

answer
*The FACES scale (0-10) (The Modified Wong-Baker) *For patients over the age of 3 who are unable to comprehend the Numerical Rating Scale. *The Bieri Faces Scale-Revised is used by Radiation Oncology in the pediatric population.
question
Pain Assessment of patients who are able to self report but unable to use other tools
answer
The Verbal Descriptor Scale (VDS) May be used in place of the NRS when patients are unable to provide a number to describe pain intensity. The following words may be used to quantify pain: no pain, mild, moderate, severe, very severe, or worst possible pain. This scale may be converted to the corresponding numbers on the WILDA Pain Assessment Guide for documentation.
question
WILDA pain assessment
answer
The WILDA© pain assessment guide is used for patients who are able to self-report pain. This guide includes the following elements: *Words to describe pain *Intensity *Location of pain *Duration of pain (continuous, intermittent) *Aggravating and alleviating factors
question
FLACC
answer
5 categories: 0-2 points- higher score is better *Face (expression?) *Legs (position) *Activity (lethargic?) *Cry *Consolability
question
OLD CART pain assessment
answer
Onset Location Duration Characteristics Accompanying symptoms Radiation Treatment (what makes it better) or "Time"
question
Pain assessment of patient unable to self-report
answer
*Premature Infant Pain Profile (PIPP) -For neonates in the NICU per department guidelines *Neonatal Infant Pain Scale (NIPS) -For newborns in the nursery and up to one month of age. -A score greater than 3 indicates pain *Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability Observational Tool (FLACC) *Used in ages one month to 18 years for procedural/surgical and acute pain.
question
Pain Management Reassessment Requirements
answer
-Ongoing pain reassessment is required to evaluate the changing nature of pain and to determine the response to treatment. -Reassessment of pain intensity is done a minimum of every 4 hours, or more often as warranted by the patient's condition. -Following an intervention for relief of pain, a reassessment of pain intensity should be done within one hour
question
Non-Pharmacologic Psychological Nursing Interventions for Pain
answer
Cognitive-behavioral therapy Relaxation Meditation Hypnosis Music therapy Biofeedback
question
Non-Pharmacologic Complementary Modalities Nursing Interventions for Pain
answer
Traditional Chinese medicine Acupuncture Hypnosis Therapeutic message Aromatherapy
question
GFR
answer
According to the National Kidney Foundation, normal results range from 90 - 120 mL/min/1.73 m2. Older people will have lower normal GFR levels, because GFR decreases with age.
question
BUN
answer
10-20 mg/dL
question
Cr
answer
0.5/0.6-1.1/1.2mg/dL females
question
Bolus or loading dose
answer
One-time dose of medication that may be given at the start of a PCA infusion or can be given as an additional dose to supplement PCA therapy
question
Basal or continuous rate
answer
The amount of medication automatically infused per hour
question
Incremental or PCA dose
answer
The amount of medication infused when the patient presses the control button
question
Lockout or delay time
answer
. Of time that must pass between the completion of one PCA dose and the initiation of the next
question
Patient controlled analgesia PCA
answer
Delivery of opioids via an electronic pump which enables the patient to self administer small doses usually IV at frequent intervals maintaining blood levels of opioids within an effective range
question
PCA by proxy
answer
Unauthorized administration of a PCA dose by anyone other than the patient such as family members caregivers clinicians
question
PCA therapy verification of orders
answer
The physicians order should contain the following: *name and strength of drug (mg/ml or mcg/ml *Bolus or loading dose (mg or mcg) * Basal or continuous rate (mg/he or mcg/hr) *Incremental or PCA dose (mg or mcg) *lockout or delay time (min) *monitoring instructions (respiratory rate sedation pain intensity etc.)
question
Two RNs must verify and document orders and PCA pump settings when
answer
-Initiating the PCA infusion -accepting patient from another floor -changing shift -changing any settings (dose, concentration)
question
Suitable candidates for PCA
answer
Patients with pain who are mentally alert and able to comprehend and to comply with instructions and procedures regarding it's use
question
Patients who may not be suitable candidates include
answer
-Infants and young children -patients with altered mental status -patient with decreased level of consciousness -patients who are not psychologically stable -patients without intellectual capacity to understand and operate the PCA
question
PCA side effects
answer
Nausea and or vomiting Itching urinary retention constipation
question
PCA pt at increased risk for respiratory depression
answer
-pt receiving other sedating drugs (benzodiazepines, antibiotics, and antihistamines) -renal or hepatic insufficiency leading to potential delayed excretion of narcotics -respiratory problems sleep apnea, depressed mental status, or metabolic disease -greater than 65 years old or debilitated -obesity; a dose that is based on total body weight rather than lean body mass can lead to a relative overdosage
question
PCA complications; emergency respiratory depression
answer
If respiratory rate less than eight per minute or sedation level of one not able to arouse: "less then eight intubate" -stop infusion -administer naloxone 0.1mg IV STAT -May repeat every 3-5 minutes x three doses to a total of 0.4mg
question
Epidural analgesia
answer
Method of regional anesthesia that involves the administration of medications as a single injection or a continuous infusion via an epidural pump into the epidural space. The epidural space is a potential space that lies superficial to the Dura mater surrounding the spinal cord
question
Neuromotor blockade
answer
unwanted side effects of epidural anesthesia from local anesthetics that is characterized by muscle weaknessmales)
question
Maintenance of epidural catheter insertion site
answer
-Reinforced dressing as needed monitor site for redness swelling tenderness drainage -report drainage if other than serosanguinous or greater than the size of a silver dollar to physician -Report unusual findings to physician
question
Safety concerns for epidural patients
answer
Patients on anticoagulants are at risk of bleeding into epidural space so should not be on anticoagulants and epidural concurrently Monitor patients for neuromotor blockade. These side effects can cause significant weakness with position changes and ambulation: At risk for falls All patients must ambulate initially with assistance
question
PCA and EPCA patient documentation
answer
The nurse is responsible to document the following on the appropriate patient information record: -RR and sedation level everyone 1 hr x 4 hours, then every 2 hours -pain intensity every four hours -Side effects/complications -evaluation of patient response to interventions
question
PCA and EPCA documentation on IV/Epidural PCA & Controlled Substance
answer
Medication and PCA settings at initial set up, shift change, patient transfer, change in settings; to nurse criteria for all these times Start of infusion container and wasting of unused medication The number of PCA button demands/deliveries and the total amount of medication used every four hours. After recording these amounts clear the four hour shift total to reset the pump for the next four hour total
question
Sympathetic blockade
answer
Sympathetic nerve fibers are responsible for several physiologic parameters including vascular tone. Blockade of the sympathetic fibers with local anesthetics especially in lower extremities can lead to vasodilation this may make a patient prone to low blood pressure especially if partially dehydrated or elderly



