Anesthesia Mgnt Monitored Anesthesia Care MAC – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Are there differences in standards or care comparing General Anesthesia vs Monitored Anesthesia Care vs Regional Anesthesia?
answer
Preoperative evaluation, intraoperative monitoring & the continuous presence of a member of the anesthesia care team are *No different* from GA to MAC to Regional
question
What is the general rule of dosing MAC cases of how to avoid excessive levels of sedation?
answer
drugs should be titrated in small increments or by adjustable infusions rather than administered in larger doses according to predetermined notions of efficacy
question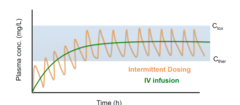
Which dosing method uses less drug and results in less episodes of excess/inadequate sedation? Intermittent dosing or continuous infusion?

answer
Continuous infusions use less overall drug and have less risk of excess or inadequate sedation
question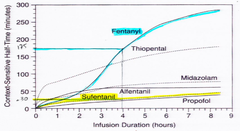
define context sensitive half-life

answer
time necessary for the plasma drug concentration to decrease by 50% or more after a continuous infusion is stopped
question
what makes a context sensitive half-life longer? (2
answer
1. The duration of an infusion; as the infusion duration increases so does the context sensitive half-life. 2. Lipopgilic nature causes the storage & later release of the drug, like fentanyl, from peripheral binding sites
question
Does context sensitive half-life describe time to awake?
answer
No, it describes the time it takes for plasma concentration to be reduced by 50%. there are many other factors that influence that. Awake is Effect Site Concentration Decay
question
What two drugs have particularly marked [long] context sensitive half-lives? Why?
answer
fentanyl & thiopental. Fentanyl returns from the peripheral compartments.
question
Is there a drug that can provide needed therapy for MAC (i.e. analgesia, anxiolysis & hypnosis
answer
No single drug can provide all componesnts of MAC while maintaining safety. That is why multiple anesthesia drugs are combined.
question
Propofol infusion dosing
answer
25 to 75 mcg/kg/min
question
Ketamine dose I.V.
answer
0.25 to 1 mg/kg
question
What is Ketofol? advantages?
answer
Combination of Ketamine and Propofol. Advantages are its ability to balance out the negative side effects of one another. [Hemodynamic stability, decreased N/V, & decreased airway complications]
question
Opioids alone will cause what adverse effects? So they are recommended to be combined with?
answer
Alone Opioids cause cardiorespiratory interactions, so they are combined with benzodiazepines at lower doses, to achieve hypnosis, amnesia and analgesia.
question
Why is it that by combining Opioids and Benzos can you reduced doses? How much?
answer
The drugs display marked synergy [1+1=4]. Hypnosis can be reached [in 50% of Pts] with a dose that is ~25% of the median effective dose of the drugs individually. That means about 75% less of each drug without the cardiorespiratory side effects.
question
1681: What is the definition of deep sedation?
answer
Deep sedation is a drug-induced state where the patient cannot be easily aroused, but responds purposefully to painful stimuli. Ventilatory function may be impaired and the patient may require assistance in maintaining a patent airway. Cardiovascular function is usually unaffected.
question
1682: What are the monitoring standards for MAC cases?
answer
According to the standards set forth by the ASA, the patient's oxygenation, ventilation, and circulation shall be continually monitored. This includes pulse oximetry, ECG, and blood pressure (which must be assessed at least every five minutes). During monitored anesthesia care cases, capnography is not required, but ventilation must be assessed, at least, by continual observation of qualitative clinical signs (e.g. chest rise and breath sounds). The temperature is to be monitored any time clinically significant changes in body temperature are intended or anticipated.
question
1721: What is the definition of minimal sedation?
answer
Minimal sedation, also known as anxiolysis, is a drug-induced state where the patient's cognitive function may be impaired, but he/she can still respond verbally and ventilatory and cardiovascular function is unchanged.
question
In a Moderate Sedation Case, some patients continue to move, can a RN take the sedation procedure to a deeper plane of anesthesia?
answer
No, only those trained in anesthesia techniques can do those kinds of sedation cases the become MAC cases
question
MAC & GA similarities of our role?
answer
you still need a pre-OP assessment, you still must be present, and still need perioperative monitoring
question
GA vs MAC vs Regional, do they all need an anesthesia provider? Why/Why not?
answer
Yes, in the event the sedation goes deeper or needs to be deeper
question
Can RN's give pressors if pt's BP drops?
answer
No, they will need to get an order unlike CRNAs who can give medications like pressors
question
physiological benefit of MAC over GA (2
answer
1. Less physiological changes occur with a MAC, an may be better for patients with underlying cardiovascular disease and will cause less stress on CV system. 2. And allow for a more rapid recovery.
question
Should a pt in a MAC be able to respond to you?
answer
yes, in theory, because if they do not sense anything at all they are now in a general
question
name a way you may know the Pt is deeper then desired? intervention?
answer
pt begins to obstruct their airway or cannot maintain airway. Consider: Jaw-thrust, or nasal/oral airway
question
Can you do a monitored anesthesia care (MAC case with only Valium (diazepam?
answer
You MAY be able however it is unlikely to do it because you must keep the patient from moving
question
What do we give in MAC cases?
answer
Sedation, analgesia, amiolytics and hypnosis in any number of combinations
question
Pre-OP assessment for MAC what are we trying to assess or decide, name 4 questions we should assess
answer
1. Is MAC appropriate for this patient? 2. Can this patient lie still? 3. Is this proceedure appropriate for an unprotected airway? 4. Is the patient's physiologic status going to allow MAC?
question
What is the tight rope balance of MAC that we must walk?
answer
the balance between keeping the patient from moving and allowing them to keep their airway protected
question
do you have to have an ETT in for the case to be considered a general anesthesia
answer
No
question
What about the patient that needs to lie still but they have a cough? what is your intervention?
answer
That patient may need to be cancelled sent home to get better but if it is a case that must happen, the will need to become a GA case, to stop the coughing reflex and secure the airway
question
With a reactive airway like an EGD case where the scope goes into the mouth & down to the stomach, if they start coughing upon insertion what is our intervention?
answer
have the surgeon pull out the scope, get the patient deeper with your propofol and try again
question
What is our desired goal with any anesthesia?
answer
Safe and comfortable, control pain (analgesia, anxiety (anxiolytic, Sedation and hypnosis
question
with MAC will they remember it? How do you address that?
answer
Yes, it is possible, so tell your patients that it is not uncommon to remember things that were said during a MAC case.
question
What do we commonly give with Propofol during a MAC case? Why?
answer
Lidocaine, it helps get the Pt a little deeper, numbs the vein where the propofol is pushed and it helps to stabilize the heart.
question
What kinds of things aggitate our patients?
answer
obviously the surgery, positioning, tourniquets, full bladder etc.
question
Therapeutic range and subsequent dosing: what is the ideal way?
answer
1 larger dose to begin the case with subsequent smaller doses to keep the patient within the therapeutic range throughout the case
question
Initial dose of propofol for healthy guy for MAC
answer
about 1 mg/kg initial dosing followed by subsequent doses to keep the patient in the therapeutic range
question
Propofol onset of action
answer
about 30 to 60 seconds
question
Fentanyl onset of action
answer
5 minutes
question
effect site equilibration definition
answer
Time between dosing and clinical effect... The delay between dosing and onset reflects the time necessary for the circulation to deliver the drug to its site of action
question
Where is the site we as C.R.N.A.s are concerned with for effect site equilibration?
answer
the Brain
question
The time necessary for the plasma concentration of a drug to decline 50% during the elimination phase?
answer
elimination half time



