Uptake and Distribution of Inhalation Anesthetics – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
what the body does to the drug
answer
Define pharmacokinetics
question
absorption distribution metabolism excretion
answer
What are the 4 parts of pharmacokinetics
question
What the drug does to the body "The intrinsic sensitivity or responsiveness of receptors to a drug and the mechanisms by which these effects occur"
answer
Define pharmacodynamics
question
from the alveoli into systemic circulation
answer
Where does the pharmacokinetic uptake of inhalation anesthetics occur?
question
movement into the various organ systems
answer
What does the distribution of inhaled anesthetics refer to?
question
Partial pressure gradients
answer
What is responsible for moving the inhaled anesthetics across various barriers in the body?
question
The brain
answer
Where is the site of action of inhaled anesthetics?
question
Dalton's Law
answer
What law describes how we get inhaled anesthetics to the brain?
question
the total pressure of a group of gases is equal to the sum of their individual partial pressures (Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3...)
answer
What is Dalton's Law?
question
to achieve a constant and optimal brain partial pressure
answer
What is the primary action of inhaled anesthetic agents
question
the net movement of gas molecules which proceed from a phase of higher concentration to a phase of lesser concentration
answer
What is partial pressure
question
Anesthesia Gas Machine (PI) Alveoli (PA) Arterial Blood (Pa) Brain (Pbr) = tissues Venous blood (Pv) Alveoli (PA)
answer
What levels does partial pressure equilibrium occur?
question
PI>PA>Pa>Pbr>Pv
answer
What is the order of partial pressures at the induction of anesthesia?
question
when equilibrium is achieved among all phases PI = PA = Pa = Pbr = Pv = PA
answer
When does PA of an inhaled anesthetic reflect Pbr?
question
alveolar partial pressure
answer
What pressure can become a "mirror" of brain partial pressure
question
No, it means that the same PARTIAL PRESSURE exists
answer
Does equilibrium between pressures mean equality of concentration?
question
input factors - uptake factors = alveolar concentration
answer
How do you calculate alveolar concentration of inhaled anesthetics?
question
1) inspired partial pressure (PI) 2) Alveolar ventilation 3) Components of anesthetic breathing system
answer
What are 3 input factors
question
1) solubility 2) cardiac output 3) tissue uptake
answer
What are 3 uptake factors
question
inspired partial pressure (PI)
answer
Which input factor would "concentration effect" fall under?
question
how the inspired partial pressure (PI) of an anesthetic affects the rate at which the alveoli partial pressure (PA) equilibrates with the inspired partial pressure (PI)
answer
What does the concentration effect describe?
question
an increase in inspired partial pressure (PI) concentration. The greater PI the faster the speed at which PA would increase and equilibrates. (this is the concentration effect)
answer
Increasing the concentration set on the vaporizer would result in what?
question
1) Concentration effect 2) Over-pressuring 3) The Second Gas Effect
answer
What are 3 factors that influence inspired partial pressure?
question
Over-pressuring
answer
What is a way to overcome gradients to achieve equilibrium of PI and Pbr?
question
Over-pressuring
answer
What method can be used to increase PI is analogous to an IV bolus?
question
By setting a higher than normal concentration at the vaporizer. This will offset the uptake and speed the equilibrium between PI and Pbr
answer
How do you achieve over-pressuring?
question
the ability of a large volume of one gas to speed the rate of rise of the PA of a second gas
answer
What is the second gas effect?
question
N2O
answer
What is the carrier gas used the achieve the second gas effect?
question
Desflurane - very low blood gas coefficient (already wants to go to the brain and out of the blood)
answer
Which volatile agent is dangerous to overpressure with and why?
question
Increasing alveolar ventilation increases equilibration of PI and PA
answer
Would increasing or decreasing alveolar ventilation speed the rate in which PI will equilibrate with PA?
question
Set ventilator at 14 instead of 6 - the faster you breath the more you bring in
answer
How do you increase alveolar ventilation?
question
1) dead space volume 2) solubility of the agent in the tubing 3) fresh gas flow
answer
What components of the breathing system effect input?
question
Up to 6 liters
answer
How much dead space volume can you have in a breathing circuit?
question
turn up fresh gas flow - the higher the fresh gas flow the faster equilibrium will occur
answer
How can you overcome the anesthesia breathing circuit characteristics?
question
1) Agent solubility 2) Cardiac output 3) Tissue uptake
answer
What factors affect uptake?
question
Uptake = Cardiac Output (Q) x concentration gradient (alveolar to venous partial pressure difference) x blood to gas solubility Note:no uptake occurs if any of these = 0
answer
What is the equation for uptake?
question
blood-gas partition coefficient (BGPC)
answer
How is solubility of an anesthetic agent measured?
question
the distribution ratio of molecules (agent) at equilibrium (when the partial pressures have equilibrated between arterial blood and gas)
answer
What is BGPC?
question
a RAPID equilibration between the alveolus and the arterial blood
answer
What does a low BGPC mean?
question
12
answer
BGPC of methoxyflurane
question
2.54
answer
BGPC of Halothane
question
1.90
answer
BGPC of Enflurane
question
1.46
answer
BGPC of isoflurane
question
0.69
answer
BGPC Sevoflurane
question
0.46
answer
BGPC Nitrous Oxide
question
0.42
answer
BGPC Desflurane
question
rapid
answer
Would a low BGPC result in slow or rapid equilibration and speed of induction?
question
SLOW! Results in rapid uptake by the circulation (wash out) so that the rate of rise in the PA and speed of induction is slow - think more blood dilutes
answer
If you have increased CO what will happen to the speed of induction?
question
FAST! results in a slow uptake by the circulation so that the rate of equilibration between PA and Pa is enhanced
answer
If you have decreased CO what will happen to the speed of induction?
question
Pa to Pv partial pressure difference
answer
What partial pressure difference describes tissue uptake?
question
DECREASE!
answer
Will tissue uptake result in a decrease or increase in PA
question
DECREASE PA and thus Pbr
answer
Will Agents with high tissue solubility partition coefficients increase or decrease PA and Pbr?
question
Cardiac Output - the higher the % of cardiac output to a specific tissue group the quicker the equilibration.
answer
What factor can increase the equilibration between Pa and Pv?
question
Brain Heart Liver Kidneys
answer
What tissues are known as the vessel rich group?
question
Vessel Rich Group
answer
Which group equilibrates Pa and Pv the quickest?
question
75% CO at 10% body weight
answer
How much CO does the Vessel Rich Group Receive?
question
Muscle at 19% CO and 50% body weight
answer
What group receives the next largest CO after the VRG?
question
6% CO at 20% body weight
answer
How much CO does Fat get?
question
Vessel rich group Muscle Fat Vessel Poor Group: Bone and cartilage
answer
What are the areas considered in tissue uptake
question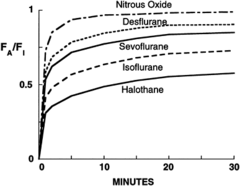
1st: rapid rise of FA toward FI before uptake begins (no concentration gradient exists) Bend: rapid uptake into the blood and distribution to vessel-rich group 2nd seg: dist and uptake muscle 3rd seg: dist and uptake fat

answer
FA/FI Curve name what each represents (1st segment, bend, 2nd segment, 3rd segment)
question
Time constants
answer
How do we measure inhalation agents?
question
The time until a 63% change of the system toward equilibrium occurs
answer
What is the time constant for inhaled anesthetics defined as?
question
By tissue groups: Capacity of tissue/blood flow to tissue
answer
How do we calculate time constants
question
Lambda or tissue to blood solubility for a specific tissue bed x K ( a constant representing 100 ml of tissue)
answer
What is the Definition of capacity?
question
flow/100 ml of tissue/minute
answer
How is blood flow to a tissue defined?
question
low tissue to blood partition coefficient- takes longer to equilibrate because high percentage of body composition combined with lower perfusion of 3 ml per 100 ml of muscle tissue
answer
Why does the muscle group take longer to equilibrate?
question
the movement of inhalation anesthetic into muscle and fat (slow in, slow out)
answer
What can be the potential cause of post-aneshteic sedation?
question
About 2 hours
answer
How long does it take for muscle equilibration to occur?
question
4 hours and up
answer
how long does it take for fat equilibration to occur?
question
PI<PA<Pa<Pbr<Pv
answer
What would the partial pressures look like during reversal?
question
the rate at which PA decreases over time
answer
How do you define recovery?
question
1) Inspired partial pressure - PI<PA 2) Tissue to venous partial pressure difference Pbr<Pv 3) Alveolar ventialtion 4) Cardiac Output 5) Metabolism of Agent
answer
What are factors that influence a decline in PA during recovery?
question
20%
answer
What percentage of halothane is metabolized?
question
3%
answer
what percentage of enflurane is metabolized?
question
0.2%
answer
What percentage of isoflurane is metabolized?
question
0.02%
answer
What percentage of Desflurane is metabolized?
question
3-5%
answer
What percentage of Sevoflurane is metabolized?



