Geriatric Anesthesia – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The percent maximum physiologic function decreases with age after _____ years.
answer
The percent maximum physiologic function decreases with age after 25-32 years (30 years).
question
Pulmonary complications with surgery increase in elderly based on :
answer
Pulmonary complications with surgery increase in elderly based on duration of surgery, obesity and patient age greater than 70. .
question
These Increase in geriatric cardiovascular : .
answer
-LV wall thickness - Left ventricular wall hypertrophy can exist without arterial hypertension. LV wall is thicker and less elastic exhibiting symmetric hypertrophy and an increase in collagen cross linking in the myocardial cytoskeleton. -LV hypertrophy results from chronic increase in afterload to left ventricular ejection imposed by elevations in PVR (decreased arterial compliance) -LV wall tension -Due to chronic increase in afterload seen in elderly; The law of Laplace applies. Stiffer vessels (harder to receive blood) like PVC pipe. Ventricle doing more work. Large arteries and the aorta do not have the ability to store energy during systole (the windkessel effect); this will elevate the ventricular wall tension and cardiac workload -heart size and tissue mass -Afterload - due to decrease in arterial compliance and impedence to LV output increases -Cardiac workload - decrease in arterial compliance results in increases in afterload , systolic pressure, and LV hypertrophy ; -Systemic BP -systolic arterial hypertension due to fibrotic replacement of elastic tissues. (vessels become less compliant); decrease in arterial compliance -Systolic BP - usually seen with increased arterial pulse pressure. Peripheral Vascular Resistance - The increase in peripheral vascular resistance is greater than the decrease seen in cardiac output, because blood vessels are less compliant. Circulation Time - reduced myocardial pump function leads to reduced cardiac output, which prolongs circ time. Conduction system fibrosis - Conduction fibrosis and loss of SA node cells will increase the incidence of dysrhythmias Incidence of dysrhythmia based on Conduction fibrosis and loss of SA node cells. SA node cell loss Do not replicate properly anymore. vagal tone Increases - decrease in sensitivity of adrenergic receptors leads to decreases in heart rate. Symptoms of diastolic dysfunction
question
These remained unchanged in geriatric cardiovascular: .
answer
-Diastolic BP -Resting systolic function -Excitatory-contraction coupling and -metabolism of ionized calcium are unchanged. -Ionized calcium -cardiac Contractile proteins
question
These decrease in geriatric: cardiovascular :
answer
-Cardiac reserve - Manifested as exaggerated drops in BP -myocardial reserve -Cardiac output - related to the aging process and an increase in afterload. -Maximum cardiac output -Cardiac index - An appropriate response to reduced requirements for perfusion and metabolism that results due to age related atrophy etc. -Resting HR - due to a increase in vagal tone and decreased sensitivity of adrenergic receptors; normal aging loss of one beat per minute for each year over 50. Heart rate - maximum -LV compliance - Based on stiffer (less compliant) myocardial fibers and replacement of these fibers with non-muscle connective tissue. The left ventricle thickens and becomes less elastic with age -Arterial compliance -Stroke volume - a decreased myocardial pump fx leads to decreased stroke volume and decreased cardiac output. -Coronary blood flow -Perfusion to vital organs -Organs with a major blood supply atrophy as you age. Loss of tissue mass in many organs. -Chronotropic and ionotropic response - a decrease in adrenrgic receptor quality. -Baroreceptor function - due to decreased sensitivity of stretch receptors owing to normal aging processes. -Adrenergic sensitivity - a decrease in adrenergic receptor quality.
question
Arterial compliance
answer
Reduced arterial elasticity caused by fibrosis of the media results in a reduction in arterial compliance which may cause an increase in afterload, elevated systolic blood pressure, and eventually left ventricu¬lar hypertrophy
question
Does the heart atrophy?
answer
The heart does not atrophy with age; size and tissue mass increase
question
Because of diastolic dysfunction what are the elderly the elderly more dependent upon?
answer
Age-related diastolic dysfunction causes the elderly to be more dependent on atrial contraction (atrial kick)
question
What increases the incidence of dysrhythmias in the elderly?
answer
Fibrolysis of the conduction system and loss of sinoatrial nodal cells increase the incidence of dysrhythmias in the elderly?
question
Cardiac contractile proteins at the cellular level in the elderly?
answer
There is no change in cardiac contractile proteins at the cellular level
question
Diastolic dysfunction in the elderly can be detected how? What are the symptoms of Diastolic dysfunction in the elderly?
answer
Diastolic dysfunction can be detected with Doppler echocardiography; Symptoms are systemic hypertension, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, and valvular heart disease, especially aortic stenosis
question
What can Diastolic dysfunction lead to in the elderly? .
answer
Diastolic dysfunction results in large increases in ventricular end-diastolic pressure with small changes in left ventricular volume. This may lead to atrial enlargement with subsequent atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure
question
What leads to exaggerated drops in blood pressure during induction of anesthesia in the elderly?
answer
Decreased cardiac reserves may result in exaggerated drops in blood pressure during induction of anesthesia
question
How does prolonged circulation time (takes longer) affect intravenous drugs in the elderly?
answer
Prolonged circulation time (takes longer) delays the onset of intravenous drugs, but speeds induction with inhalation agents.
question
How does prolonged circulation time (takes longer) affect inhalation agents in the elderly?
answer
Prolonged circulation time (takes longer) delays the onset of intravenous drugs, but speeds induction with inhalation agents.
question
Elderly patients (and infants) have a diminished ability to increase or decrease heart rate in response to hypovolemia, hypotension, or hypoxia.
answer
Elderly patients (and infants) have a diminished ability to increase heart rate in response to hypovolemia, hypotension, or hypoxia.
question
The elderly have a contracted state of the vasculature that may result in a higher than expected ?
answer
The elderly have a contracted state of the vasculature that may result in a higher than expected plasma concentration of drugs.
question
The elderly have increased or decreased lipid storage sites?
answer
The elderly have increased lipid storage sites that lead to a greater reservoir for lipid soluble drugs.
question
Younger pts. shiver at ____ C , pts over 80 shiver at ____C.
answer
Younger pts shiver at 36.1°C , pts over 80 shiver at 35°C. Shivering increases O2 consumption 400% which leads to hypoxia, acidosis, and cardiopulmonary compromise.
question
Cardiac function declines by _____%
answer
50% (20-80 years old)
question
Why are arteries less compliant in the elderly? .
answer
Peripheral vasculature has increased wall thickness, increased diameter, and consequent stiffening of the aorta and lg arteries, leading to less ability to vasodilate.
question
T or F Elderly have loss of elasticity throughout arterial tree along with loss of arterial distensibility.
answer
True
question
Systemic hypertension is common in the elderly due ______________?
answer
Systemic hypertension is common due to poorly compliant blood vessels, decreases in CO and increases in peripheral vascular resistance.
question
Myocardial changes in the elderly include: ?
answer
Myocardial changes in the elderly include: increased left ventricular wall thickness, decreased myocardial compliance, and thicjkening of aortic valve cusps, producing midsystolic ejection murmur.
question
Left ventricular hypertrophy results from ?
answer
Left ventricular hypertrophy results from increased afterload, secondary to elevated peripheral vascular resistance.
question
Prolonged circulation time is a result of ?
answer
Prolonged circulation time is a result of impaired myocardial pump function and reduced cardiac output.
question
Increased circulation time has what implications for the elderly? .
answer
Increased circulation time causes a decreased perfusion to vessel rich organs like brain, heart, and liver. Delay onset of drugs and slow onset of effects.
question
When the elderly need an increase in cardiac output they depend on what?
answer
They are more dependent on an increase in end diastolic volume than an increased heart rate to produce an increase in CO. They are more prone to CHF when large volumes of IV fluids are given in the presence of anesthesia induced myocardial depression and hypotension.
question
What happens to the aging myocardium in the elderly?
answer
The aging Myocardium becomes thicker in both systole and diastole, increases in the size (hypertrophy) and number (hyperplasia) of individual myocytes occurs and adipose tissue infiltrates as well.
question
Atrial contraction accounts for ______ of left ventricular end-diastolic volume. Loss of atrial kick will result in decreased BP.
answer
Atrial contraction accounts for 20% of left ventricular end-diastolic volume. Loss of atrial kick will result in decreased BP.
question
T or F There is a decrease in chronotropic and inotropic cardiac function.
answer
True There is a decrease in chronotropic and inotropic cardiac function.
question
How is contractility affected in the elderly ?
answer
Catecholamine effects that enhance calcium ion transport (contractility) are less pronounced in the elderly.
question
Discuss Elderly and increased risk for aspiration: .
answer
Vocal cord stimulation for closure: Increased The stimulus needed for vocal cord closure (protection) is markedly elevated. Airway obstruction - Increased The normal aging process naturally decreases the sensitivity of the need to clear secretions, food, etc. The naturally occurring decrease in laryngeal reflexes compounds the problem. Risk of aspiration - Increased Due to vocal cord stimulation being elevated, thus putting the patient at risk for aspiration. Also, chest wall rigidity increases while muscle strength decreases. The ability to cough is decreased, as is maximal breathing capacity. Pulmonary complications - Increased Aspiration pneumonia is common and life-threatening due to a decrease in protective laryngeal reflexes with age. Also, the decreased ability to cough adds to increased pulmonary complications.
question
Discuss Elderly and Physiologic dead space
answer
Physiologic dead space - Increased Breakdown of alveolar septae reduces total alveolar surface area, increasing both anatomic and physiologic dead space. These changes disrupt the normal matching of ventilation and perfusion within the lungs, increasing both shunting and deadspacing.
question
Discuss Elderly and Work of breathing
answer
Work of breathing - Increased Skeletal calcification and increased airway resistance increase the work of breathing in subjects who are elderly and predisposes them to acute postoperative ventilatory failure.
question
Discuss Elderly and Potential for hypoxia
answer
Potential for hypoxia - Increased The causes are multiple. It starts with decreased elasticity of lung tis¬sues, which reduces alveolar surface area and decreases the effi¬ciency of gas exchange. There is airway collapse, a decrease in normal oxygen tension, ventilation-perfusion mismatch, and increase in preoxygenation time and higher inspired oxygen concentration.
question
Discuss Elderly and FRC
answer
Increase of FRC (modest) - Increased Approximately 30% of alveolar wall tissue is lost between ages 20 to 80 years, diminishing elastic recoil and parenchymal traction that maintains airway patency (loss of interdependence). This produces increased residual volume, closing volume, and functional residual capacity. Like a little oxygen tank that they are carrying around. Elderly need a bigger tank.
question
Discuss Elderly and Closing volume & closing capacity
answer
Closing volume & closing capacity (dramatic increase) - Increased closing capacity is caused by airway collapse and the distribution of tidal volume to areas of the lung that are less perfused.
question
Discuss Elderly and Alveolar compliance
answer
Alveolar compliance - Increased This increase is caused by the absorption of connective tissue and this results in a loss of "protective netting" to restrict or limit the expansion of the alveoli.
question
Discuss Elderly and Respiratory depression with opioids
answer
Respiratory depression with opioids - Increased Along with the normal respiratory changes due to aging, opioids produce changes ranging from respiratory depression to apnea in a dose-dependent manner.
question
Describe geriatric lung tissue:
answer
Normally sclerotic lung tissue, not very compliant. Have alveoli compliance, blows up readily, but no recoil, not as elastic. Chest wall is not compliant. .
question
Elastin fibers in the elderly?
answer
Elastin fibers (reduced elasticity) Normal process in aging
question
Elderly Chest wall and tissue elasticity.
answer
Tissue elasticity As noted above, and in a tissue-dependent manner, some muscle is replaced with adipose tissue and less-elastic components. Lung recoil - The chest wall is less compliant (stiffer, less elastic); if the chest wall does not expand upward and outward, the lung will not expand fully, nor recoil fully.
question
Ability to cough in the elderly?
answer
Ability to cough - Decreased muscle strength decreases the ability to cough, and it takes more stimulation to cough.
question
Alveolar surface area in the elderly?
answer
Alveolar surface area (functional) - Alveolar wall tissue decreased, and there is a loss of recoil, therefore there is decreased airway patency.
question
Chest wall compliance in the elderly?
answer
Chest wall compliance - Cartilage and connective tissues become stiffer (less compliant). Increased stiffness of the thoracic cage and progressive dorsal kyphosis are accompanied by upward and anterior rotation of the ribs and sternum, which lead to an increase in the anterior-posterior diameter of the chest and restricted chest expansion.
question
Vital capacity, expiratory reserve volume, and inspiratory reserve volume in the elderly?
answer
Vital capacity, expiratory reserve volume, and inspiratory reserve volume - As residual lung volume increases, there is a decrease in vital capacity, expiratory reserve volume, and inspiratory reserve volumes
question
Response to hypoxia & hypercapnia in the elderly?
answer
Response to hypoxia & hypercapnia - There is a decreased respiratory response to hypoxia and hypercapnia.
question
Protective reflexes in the elderly?
answer
Protective reflexes - Laryngeal responses are blunted in the elderly.
question
Cervical spine & TMJ mobility in the elderly?
answer
Cervical spine & TMJ mobility - Inability to flex or extend the neck and a small mouth opening can make intubation challenging.
question
Ease of mask ventilation in the elderly?
answer
Ease of mask ventilation - Often the geriatric patient is edentulous and there is no support for a tight face mask fit.
question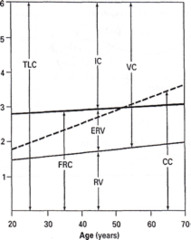
Indicate how the following lung parameters changes with aging .

answer
RV increased ERV decreased FRC increased CC increased IC decreased VC decreased TLC decreased (TV): tidal volume changes minimnally with aging.
question
Elastin and collagen in the geriatric lung? By 70 years of age how much decrease in functional alveolar surface area?
answer
The reduction in elastic tissue along with an increased amount of collagen = 15% reduction of functional alveolar surface area by 70 years of age.
question
The changes in chest wall and lung _________ impair matching of ventilation and perfusion in the elderly?
answer
The changes in chest wall and lung compliances impair matching of ventilation and perfusion. Physiologic shunt is increased and the efficacy of oxygen exchange is reduced at the cellular level.
question
What changes in FEV1 and Forced Vital capacity (FVC) are seen in the elderly. What causes the changes?
answer
Progressive decreases in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) is caused by loss of elastic tissue around the alveoli and alveolar ducts. These changes cause the alveoli to remain more distended at rest (air trapping) and less distensible upon inspiration.
question
What happens during forced expiratory maneuvers in the elderly?? The volume of gas that can subsequently be exhaled is the ________. _____________ is the closing volume plus the residual volume.
answer
During forced expiratory maneuvers, airways begin to close. The volume of gas that can subsequently be exhaled is the closing volume. The closing capacity is the closing volume plus the residual volume.
question
As closing volume increases in the elderly, the greater or less the amount of gas that "remains behind" in the alveoli and airways. .
answer
As closing volume increases, the greater the amount of gas that "remains behind" in the alveoli and airways. .
question
Closing capacity is greater than functional residual capacity in anesthetized elderly patients.
answer
Closing capacity is greater than functional residual capacity in anesthetized elderly patients. More dependent airways are collapsed and more of the tidal volume is distributed to areas of the lung that are underperfused. This combination manifests as atelectasis in dependent lung regions. .
question
Total lung capacity (TLC) and the geriatric pt? Why?
answer
Total lung capacity (TLC) declines about 10% by age 70, reflecting a loss in height due to deterioration of intervertebral disks. .
question
Increase in A-P diameter of the chest and restricted chest expansion in the elderly is due to ?
answer
Increased stiffness (greater elasticity) of the thoracic cage and dorsal kyphosis will cause anterior and upward rotation of the ribs and sternum, leading to an increase in A-P diameter of the chest and restricted chest expansion. .
question
Contributors to a decline in gas exchange in the elderly include:
answer
Other contributors to a decline in gas exchange include: reduction in alveolar surface area, increased alveolocapillary membrane thickness, and reduction in pulmonary capillary blood volume. Taken together, arterial oxygen tension declines with age. .
question
Alveolar-arterial oxygen difference (A-a gradient) increases from ___ mm-Hg at 20 years of age to more than ___ mm-Hg at 70 years of age. .
answer
Alveolar-arterial oxygen difference (A-a gradient) increases from 8 mm-Hg at 20 years of age to more than 20 mm-Hg at 70 years of age.
question
Pa02 decreases ______ per year after 20 years of age. T or F There is a decrease in reactivity of protective airway reflexes, such as coughing and swallowing, due to diminished laryngeal and pharyngeal reflexes.
answer
Pa02 decreases 0.5 mm-Hg per year after 20 years of age. You may need to watch for hypoxia and hypercarbia postoperatively. The elderly may require higher inspired oxygen concentrations because of lower Pa02 levels and reduced efficiency of gas exchange. There is a decrease in reactivity of protective airway reflexes, such as coughing and swallowing, due to diminished laryngeal and pharyngeal reflexes. The risk of pulmonary aspiration increases.
question
Problems with induction in the elderly: .
answer
A difficult fit of the anesthesia mask on edentulous patients may occur. Intubation may be difficult based on limited neck flexion and extension, cervical arthritis, and osteoarthritis.
question
Insulin resistance and the elderly? Why? .
answer
Decreased Pancreatic function declines and diabetes mellitus increases (glucose metabolism is impaired). Mechanisms responsible for elevelated blood glucose: ■ sluggish insulin response to hyperglycemia. ■ resistance to the effects of insulin at peripheral receptors. Frequent intraoperative blood glucose monitoring may be beneficial to patient status.
question
Heat loss and the elderly?
answer
Increases Heat production decreases, heat loss increases, hypothalamic temperature regulating centers may reset to a lower level, predisposing the patient to hypothermia.
question
Heat production and the elderly?
answer
Decreased Heat production decreases, heat loss increases, hypothalamic temperature regulating centers may reset to a lower level, predisposing the patient to hyperthermia.
question
Basal oxygen consumption and the elderly? .
answer
Decreased Basal and maximal oxygen consumption decline as one ages due to general loss of lean body mass
question
Hypothalamic temperature regulation and the elderly? .
answer
Decreased Heat production decreases, heat loss increases, hypothalamic temperature regulating centers may reset to a lower level, predisposing the patient to hyperthermia.
question
Liver mass and the elderly?
answer
Decreased Hepatic blood flow decreases with age, but the hepatocellular function changes very little. Reduced hepatic blood flow and a potential reduction in microsomal enzyme (P450) function impairs the liver's ability to metabolize anesthetics and nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking drugs. Reduced liver tissue mass and blood flow are responsible for inadequate perioperative hepatic function in the geriatric surgical patient. Plasma clearance of drugs metabolized by the liver liver is reduced.
question
Hepatic blood flow and the elderly?
answer
Decreased Hepatic blood flow decreases with age, but the hepatocellular function changes very little. Reduced hepatic blood flow and a potential reduction in microsomal enzyme (P450) function impairs the liver's ability to metabolize anesthetics and nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking drugs. Reduced liver tissue mass and blood flow are responsible for inadequate perioperative hepatic function in the geriatric surgical patient.
question
Liver metabolism and the elderly?
answer
Decreased Hepatic blood flow decreases with age, but the hepatocellular function changes very little. Reduced hepatic blood flow and a potential reduction in microsomal enzyme (P450) function impairs the liver's ability to metabolize anesthetics and nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking drugs. Reduced liver tissue mass and blood flow are responsible for inadequate perioperative hepatic function in the geriatric surgical patient.
question
Metabolism of benzodiazepines in the elderly?
answer
Metabolism of benzodiazepines in men is decreased. Plasma cholinesterase levels are reduced in elderly men.
question
Synthesized plasma cholinesterases and the elderly?
answer
Decreased Plasma cholinesterase levels are reduced in elderly men.
question
Basal oxygen consumption and the elderly?
answer
Decreased
question
Gastric pH and the elderly?
answer
Gastric pH rises (more alkaline), gastric emptying is prolonged and decreased, concern for full stomach.
question
Biotransformation and the elderly?
answer
Decreased Liver function is dereased.
question
Albumin production and the elderly?
answer
Decreased
question
Cerebral cortex neuron loss CSF Degeneration of peripheral nerve cells Spinal duration of action Sensory block with spinals in the elderly. Epidural volume cephalad spread •
answer
Cerebral cortex neuron loss CSF Degeneration of peripheral nerve cells Spinal duration of action Sensory block with spinals Epidural volume cephalad spread • T8 for turp
question
Proprioception threshold Hearing threshold Temperature threshold Touch threshold in the elderly?
answer
Proprioception threshold Hearing threshold Temperature threshold Touch threshold Vision threshold
question
Skeletal muscle in the elderly
answer
skeletal muscle atrophy
question
Intracranial volume Gray matter Brain mass in the elderly.
answer
Cerebral blood flow Intracranial volume Gray matter Brain mass
question
Skeletal muscle steadiness, Skeletal muscle strength and Skeletal muscle control in the elderly?
answer
Skeletal muscle steadiness Skeletal muscle strength Skeletal muscle control
question
Dose for general anesthetics* Dose for locals * Epidural segment dosing * Duration of epidural action * Epidural motor blocks * in the elderly. .
answer
Dose for general anesthetics* Dose for locals * Epidural segment dosing * Duration of epidural action * Epidural motor blocks *
question
What level for a turp?
answer
T-8
question
Cerebral blood flow autoregulation in the elderly? .
answer
No change in Cerebral blood flow autoregulation.
question
Cerebral blood flow and brain mass increase or decrease about ____ with age, neuronal loss prominent in cerebral cortex, especially frontal lobes
answer
Cerebral blood flow and brain mass decrease about 20% with age, neuronal loss prominent in cerebral cortex, especially frontal lobes
question
Intracranial volume increases or decreases from 92% to 82%, most rapid reduction in gray matter and greatest increase in cerebral ,spinal fluid.
answer
Intracranial volume decreases from 92%-82%, most rapid reduction in gray matter and greatest increase in cerebral spinal fluid.
question
Neurons and nerve conduction in the elderly?
answer
Some neurons decrease in size and lose some synapses. Nerve conduction velocity decreases by 0.15 m/ sec/yr. Skeletal muscle strength, control, and steadiness decrease by 20%-50%.
question
Neurotransmitters and receptors in the elderly? .
answer
Synthesis of some neurotransmitters and the number of their receptors are reduced
question
Decreased CNS activity is related to a decrease in neuronal density, decrease in cerebral metabolic oxygen consumption, decrease in blood flow, decrease in neurotransmitters receptors and decrease in the rate of neurotransmitters synthesis .
answer
Decreased CNS activity is related to a decrease in neuronal density, decrease in cerebral metabolic oxygen consumption, decrease in blood flow, decrease in neurotransmitters receptors and decrease in the rate of neurotransmitters synthesis
question
Review general surgery, spinals, epiduals and local anesthesia for the elderly. .
answer
Spinal anesthetics have a longer duration of action Sensory block increase with spinals; Decrease segmental dose for epidurals Epidural volume tends to result in more extensive cephalad spread of anesthetics, but accompanied by a shorter duration of analgesia and motor block. Doses for local and general anesthetics are reduced. Mac decreases Dosing decreases for local anesthetics, opiods, barbituates, benzodiazepine, and many other agents
question
True or False Cerebral auto-regulation of blood flow is preserved.
answer
Cerebral auto-regulation of blood flow is preserved.
question
Dosing increases or decreases for local anesthetics, opiods, barbituates, benzodiazepine, and many other agents
answer
Mac decreases Dosing decreases for local anesthetics, opiods, barbituates, benzodiazepine, and many other agents
question
Post-op delirium and postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly. .
answer
Post-op delirium and postoperative cognitive dysfunction is a factor with the elderly.
question
BUN in the elderly
answer
BUN - 3. Serum creatinine level is unchanged, owing to a decrease muscle mass and reduced creatinine production. BUN gradually increases.
question
ADH function in the elderly?
answer
ADH response to hypertonic saline load - Elderly release large amounts of ADH in response to hypertonic saline loads. Watch your fluids!!
question
Hyperkalemia and hypokalemia in the elderly. .
answer
Ability to develop hyperkalemia Ability to develop hypokalemia
question
Serum Creatinine in the elderly?
answer
Serum creatinine level is unchanged, owing to a decrease muscle mass and reduced creatinine production. BUN gradually increases. .
question
Kidney mass, Muscle mass, Decreased renal (nephron) mass, Renal blood flow. Renal plasma flow, Renal function (GFR and creatinine clearance) in the elderly.
answer
Kidney mass - kidney mass decrease with age Muscle mass, More prominent in cortex of kidney, which is replaced by fat and fibrotic tissue Decreased renal (nephron) mass Renal blood flow - decreases 50%, about 10% per decade. Renal plasma flow - decreases Renal function (GFR and creatinine clearance) is reduced. GFR - decreases
question
Fluid handling, Sodium handling, Concentrating ability, Response to ADH, Response to aldosterone, Response to aldosterone, and Creatinine production in the elderly? .
answer
Elderly patients may experience impaired sodium handling, concentrating ability, and diluting capacity, predisposing them to dehydration or fluid overload. Fluid handling - decreases Sodium handling - decreases Concentrating ability - decreases Response to ADH - decreases Response to aldosterone - decreases Response to aldosterone - decreases Creatinine production - decreases
question
_____________ is the most sensitive indicator of renal function in the elderly.
answer
Creatinine clearance is the most sensitive indicator of renal function in the elderly
question
Elderly patients may experience impaired sodium handling, concentrating ability, and diluting capacity, predisposing them to ______________________?
answer
Elderly patients may experience impaired sodium handling, concentrating ability, and diluting capacity, predisposing them to dehydration or fluid overload.
question
May develop acute renal failure postop due to ? .
answer
May develop acute renal failure postoperatively due to reduced renal blood flow and decreased renal (nephron) mass
question
As renal function declines, what happens to ability to excrete drugs?
answer
As renal function declines, so does the ability to excrete drugs.
question
Hypokalemia and hyperkalemia in elderly patients, Why? .
answer
Predisposed to develop hypokalemia and hyperkalemia
question
Why would you monitor serum electrolytes, cardiac filling pressure, and urinary output?
answer
Monitor serum electrolytes, cardiac filling pressure, and urinary output.
question
Elderly and: Circulation time? Body fat? Vd for lipid-soluble drugs? Recovery from volatile anesthetics?
answer
Circulation time Body fat - (lipid fraction increases) Vd for lipid-soluble drugs Recovery from volatile anesthetics
question
Elderly and: Extracellular fluid volume Plasma volume Red cell mass
answer
Extracellular fluid volume Plasma volume Red cell mass Response to muscle relaxants
question
Elderly and: Basal metabolic requirements Body heat production Core body temperature .
answer
Basal metabolic requirements Body heat production Core body temperature
question
Elderly and: -Total body water: Progressive decrease in muscle mass (greater in males) -Increase in body fat (lipid fraction increases) result in -decreased total body water (TBW). -Vd for water-soluble drugs -Dosing for barbiturates, opioid .
answer
Total body water - Progressive decrease in muscle mass (greater in males) and increase in body fat (lipid fraction increases) result in decreased total body water (TBW). Vd for water-soluble drugs Dosing for barbiturates, opioid antagonists, and benzodiazepines.
question
Elderly and Mac?
answer
MAC decreases in the elderly.
question
Elderly and muscle mass?
answer
Progressive decrease in muscle mass (greater in males)
question
Elderly and body fat?
answer
Increase in body fat (lipid fraction increases)
question
Elderly and TBW, volume of distribution for water-soluble drugs,
answer
Decreased TBW results in smaller volume of distribution for water-soluble drugs and may lead to a concentrated drug and quick effects.
question
Elderly and volume of distribution for lipid-soluble drugs?
answer
An increased volume of distribution for lipid-soluble drugs can lower their plasma concentration and decrease the rate of elimination
question
***MAC is reduced by ___ per decade of age over 40 years.
answer
MAC is reduced by 4% per decade of age over 40 years.
question
Elderly and Inhalation agent uptake?
answer
Inhalation agent uptake is more rapid if cardiac output is decreased. May also be delayed if there is significant ventilation/perfusion abnormality.
question
Elderly and Recovery from anesthesia with a volatile anesthetic, volume of distribution, hepatic function, pulmonary gas exchange?
answer
Recovery from anesthesia with a volatile anesthetic may be prolonged because of an increased volume of distribution (increased body fat), decreased hepatic function (decreased halothane metabolism), and decreased pulmonary gas exchange.
question
Elderly and dose requirement for barbiturates, opioid antagonists, and benzodiazepineses.
answer
In general, elderly patients display a lower dose requirement for barbiturates, opioid antagonists, and benzodiazepines.
question
Typical eighty year old requires what induction dose of pentothal.
answer
Typical eighty year old requires less than half the induction dose of pentothal.
question
Elderly and Anectine (succinylcholine) and nondepolarizing agents?
answer
Response to Anectine (succinylcholine) and nondepolarizing agents is unaltered with aging. Remember: IV delivery may be prolonged (increased circulation time - takes longer for one whole-body transit).
question
Changes in body composition will reduce basal metabolic requirements during aging by ?
answer
Changes in body composition will reduce basal metabolic requirements during aging by 10%-15%.
question
Elderly and body heat production, core body temperature?
answer
Hypothermia due to decreased body heat production Elderly decrease core body temperature at almost one degree centigrade per hour. This is twice the rate of young people
question
Elderly and Plasma volume, red cell mass, and extracellular fluid volumes?
answer
Plasma volume, red cell mass, and extracellular fluid volumes are normally maintained in physically active elderly patients
question
IV drugs are administered on a schedule adjusted to ? If you give a lipid-soluble drug (inhalational agents, benzodiazepines, barbiturates), you may see what type of recovery?
answer
IV drugs are administered on a schedule adjusted to total body weight. If you give a lipid-soluble drug (inhalational agents, benzodiazepines, barbiturates), you may see a delayed recovery
question
Lipid soluble drugs in the elderly? .
answer
Lipid soluble drugs in adipose tissues will have a prolonged elimination (increased Volume of distribution)
question
Barbituate induction dose in the elderly is reduced ?
answer
Barbituate induction dose is reduced 30-40%.
question
Elderly and benzodiazepines?
answer
Elderly women metabolize benzodiazepines at rates closer to those in young women; men do not.
question
Elderly and benzodiazepines, barbiturates and opiod agonists?
answer
Elderly in general have lower dose requirement for benzodiazepines, barbiturates and opiod agonists
question
Potent inhalational agents in the elderly?
answer
Decrease inspired concentration; MAC down 30%; faster induction and emergence
question
Barbiturates, etomidate, and Ketamine in the elderly?
answer
Use with caution; seizures, hallucinations, mental disturbances
question
Opioids in the elderly?
answer
Marked decrease in initial dose, increased duration of systemic and epidural effects, greater incidence or rigidity, increased res¬piratory depression
question
Fentanyl, Sufenta, alfentanil in the elderly?
answer
Induction dose reduced by 50%, maintenance dose reduced by 30% - 50%
question
Local anesthetics used for in the elderly?neuraxial anesthesia
answer
Small to moderate decrease in segmental dose requirements; anticipate prolonged effects
question
Benzodiazepines in the elderly?
answer
Modest decrease in initial dose, anticipate marked increase in duration (except Versed)
question
Succinylcholine in the elderly?
answer
Slightly reduced dose in elderly men; prolonged block in con¬junction with metoclopramide
question
Nondepolarizing relaxants in the elderly?
answer
Same or slight increase in initial dose; anticipate increased duration (except atracurium or mivacurium)
question
Neostigmine, edrophonium in the elderly?
answer
No change in dose efficacy, though larger doses are often necessary; slightly prolonged effect
question
Atropine in the elderly?
answer
Increased dose for equal heart rate response; anticipate central anticholinergic syndrome
question
Isoproterenol, other beta agonists in the elderly? .
answer
Increased dose for equal cardiovascular responses
question
***Thiopental in the elderly?
answer
• Induction dose reduced by 15% (2.1 mg/kg IV); same maintenance dose
question
***Propofol in the elderly?
answer
Induction dose reduced by 20%; 80 year old = 1.7 mg/kg IV
question
***Midazolam in the elderly?
answer
Sedation/induction dose reduced by 50%; 80 year old = 0.02 -0.03 mg/kg IV; maintenance dose reduced by 25%
question
***Etomidate in the elderly?
answer
Induction dose reduced by 20%; 80year old = 0.2 mg/kg IV
question
...
answer
Administration of a water soluble drug may lead to a concentrated drug and quick effects. The volume of distribution is small. However, if you give a lipid soluble drug to the same patient, you will get a lower plasma concentration and a decreased rate of elimination. When you study the age-related changes in the elderly, drug activity must be pondered.
question
Decreased/contracted vascular volume. .
answer
Results in high initial plasma concentration
question
Decreased protein binding
answer
Increased availability of free drug
question
Increased lipid storage sites
answer
Prolonged action of lipid soluble drugs.
question
Decreased renal and hepatic blood flow
answer
Prolonged action of drugs dependent on kidneys and liver for elimination.
question
Which drugs have no change in dosing in the elderly? .
answer
Atracurium, Neostigmine, edrophonium
question
Which drugs have increase in dosing in the elderly? .
answer
Atropine, Isoproterenol, other beta agonists
question
1. Which of the following physiologic changes occurs in the geriatric patient? a. Decreased lung compliance b. Decreased chest wall compliance c. Decreased residual volume d. Decreased closing capacity
answer
b. Decreased chest wall compliance
question
2. Geriatric cardiovascular changes that occur include all except: a. Elevated afterload b. Left ventricular hypertrophy c. Elevated systolic blood pressure d. increased arterial elasticity
answer
d. increased arterial elasticity
question
3. The geriatric population has renal changes. As renal function declines, so does the kidneys ability to: a. Modify the glomerular filtration rate b. Maintain potassium level c. Excrete drugs d. Handle diuretics
answer
a. Modify the glomerular filtration rate
question
4. The principle pharmacodynamic change associated with aging is: a. Arthritis b. Pulmonary changes c. Lipid solubility d. Reduced anesthetic requirements
answer
d. Reduced anesthetic requirements
question
5. The onset of drug action in the elderly is determined mainly by: a. Alveolar ventilation b. Lipid solubility c. Increased circulation time d. Decreased circulation time
answer
c. Increased circulation time
question
6. Aged men have a prolonged effect with Anectine but aged women do not. What explains this? a. Lipid solubility. b. Water solubility c. Lower plasma cholinesterase concentration d. Fewer motor end-plates
answer
c. Lower plasma cholinesterase concentration
question
7. Which MAC number would be appropriate for a 65-year-old person receiving Desflurane? a. 10 b. 9 c. 8 d. 4
answer
d. 4
question
8. The geriatric patient needs special attention while positioning. Which joint is most vulnerable? a. Hip /leg b. Knee c. Arms/brachial plexus d. Neck
answer
d. Neck
question
9. The onset of muscle relaxants in the elderly is prolonged because of: a. Increased cardiac output b. Low muscle blood flow c. Decreased kidney clearance d. Decreased hepatic function
answer
b. Low muscle blood flow
question
10. Which drug would have prolonged action in the geriatric patient? a. Fat soluble drug b. Water soluble drug c. Both fat soluble and water soluble drugs d. Makes no difference
answer
a. Fat soluble drug
question
11. All of the following contribute to increased pulmonary complications in the elderly undergoing surgery EXCEPT: a type of surgery b. duration of surgery c. fat content (obesity) d. age greater than 70 years old
answer
a type of surgery
question
12. A short-term increase in cardiac output in the elderly is due to all of the following EXCEPT: a. increase in heart rate b. increased left ventricular end-diastolic volume c. larger stoke volumes d. decreased pre-load
answer
d. decreased pre-load
question
13. Which of the following statements best describes desflurane in an elderly patient? a. uptake will be slower b. build-up will occur first in the brain c. It works slower because of bradycardia d. It is very blood-soluble.
answer
b. build-up will occur first in the brai
question
14. Choose the correct change in lung parameters in the elderly. FRC Vital Capacity a. Increases Increases b. Increases Decreased c. Decreases Increases d. Decreases Decreases
answer
b. Increases Decreased
question
15. The most sensitive indicator of renal function in the elderly is: a. BUN b. creatinine production c. serum creatinine levels d. Creatinine clearance
answer
d. Creatinine clearance
question
16. Which of the following physiologic changes occurs in the geriatric person? a. decreased lung compliance b. increased chest wall compliance c. decreased residual volume d. increased closing capacity
answer
d. increased closing capacity
question
17. Which of the following physiologic changes occurs in the geriatric person? a. BUN b. Creatine production c. ability to excrete drugs d. ability to handle diuretics
answer
a. BUN



