Patient Positioning – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
-When possible, position patient prior to anesthesia. (Let the patient decide what is comfortable). -Use supplemental padding/materials to disperse pressure points on body parts & soft tissues. -Many patient positions for surgery can lead to undesirable physiologic consequences.
answer
Positioning considerations
question
Brachial plexus
answer
Most common postoperative nerve injury
question
Multiple contributing factors, i.e. improper position, inadequate tissue perfusion, inflammatory reactions
answer
Definitive etiologies of peripheral neuropathies are unclear.
question
may be related to venous congestion in optic canal d/t prone position.
answer
Position related perioperative vision loss
question
may contribute to spinal cord ischemia and neurologic sequelae.
answer
Excessive spine flexion/extension in anesthetized patients
question
Availability and operational status of equipment Availability of sufficient personnel to safely position the patient Evaluation of joint mobility and integrity of the cervical spine and bones Particular care with the elderly patient Existing medical conditions Risk of cardiovascular or respiratory compromise? Management of pressure points
answer
Major considerations for positioning
question
-Potential for significant cardiovascular and pulmonary compromise. -Vulnerable to additional postural changes. -Blunted or obtunded reflexes prevent patients from repositioning themselves for comfort. -Rendering patients unconscious and relaxed may permit placement in position they may not have normally tolerated in an awake state.
answer
Anesthetic agents blunt natural compensatory mechanisms.
question
Direct compression of neural & soft tissue may result in damage.
answer
Etiological mechanisms
question
stretch, compression and disruption of blood flow.
answer
What are some positioning related causes of ischemia
question
Altered inflammatory response postoperatively
answer
What is a cause of microvascular cause of peripheral neuropathy
question
Opportunistic viral activation associated with central and peripheral neuropathies.
answer
What can immunosuppression lead to?
question
-Depressive effects of anesthetic drugs. -Loss of muscle tone from drugs and position. -Abnormal intra-pulmonic and intra-thoracic pressures. -Abnormal intra-abdominal pressures. -Loss of Autonomic Nervous System control.
answer
Deep planes of anesthesia cause an increase in Respiratory and CV sequelae
question
Positioning devices Preexisting pathology Body habitus Anesthesia technique Length of procedure >2 hours
answer
Risk factors for positioning injuries
question
Table straps Leg solders Axillary Roll Bolsters (Bean bag) Fracture table post Shoulder braces Positioning frames Headrests
answer
Positioning devices
question
Low-flow states Hepatic disease Diabetes mellitus Peripheral neuropathies Alcohol/Tobacco use Limited joint mobility
answer
Preexisting pathology
question
Obesity Underweight Bulky musculature Malnutrition
answer
Body habitus
question
Regional anesthesia Hypotensive technique General anesthesia
answer
Anesthesia technique
question
Elevated diaphragm D/T decreased tone and additional rise of abdominal contents. Additional 15-20% reduction in Functional Residual Capacity (FRC). Chest wall & Lung compliance. Respiratory center depression leading to decreased TV & Increased RR.
answer
Respiratory considerations in the anesthetized patient
question
Direct Myocardial depression. Depression of ANS chemical & pressure receptors.
answer
Cardiac considerations in the anesthetized patient
question
brachial plexus ulnar nerve spinal cord lumbosacral nerve root sciatic and peroneal nerve
answer
Most frequent malposition injuries
question
Patient limitations in movement and strength Preexisting numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation
answer
Documentation should include thorough preoperative evaluation. Includes:
question
Type of position Placement/Check of specific body parts limbs, head, genitals, nose, eyes, etc Padding provided Periodic checks of pressure points
answer
Through documentation includes:
question
Head up favors respiration. Head down favors circulation. Supine best for respiration and circulation as compared to other surgical position.
answer
Favorable positions
question
supine
answer
Which position is most frequently used
question
Patient may be positioned while awake Minimal physiologic insult Easy access to arms, eyes and mouth
answer
what are some advantages of supine positioning
question
consider lumbosacral strain potential stretch/compression of brachial plexus
answer
Supine positioning considerations
question
heels elbows occiput
answer
Potential pressure points while supine
question
prolonged compression can produce hair loss combat this using gel donut
answer
what is a concern with occiput pressure points
question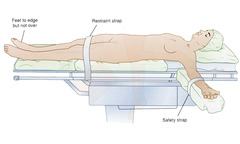

answer
supine position
question
Limit abduction of arms to less than 90° in supine, lateral, or prone positions. Avoid rotation and lateral flexion of head to the opposite side. Avoid steep Trendelenburg and shoulder braces; place braces only over acromioclavicular joints with arms tucked at patient's side. Avoid extension of the arm posterior to plane of the torso. Support arms in patients in the sitting position.
answer
prevention of brachial plexus injury
question
the ulnar nerve is very superficial at the elbow and great care must be taken to protect it from injury
answer
What structure is very superficial at the elbow
question
hypotension and hypoperfusion
answer
what factors increase risk of ulnar nerve injury
question
remember s-UP-ination - palm UP
answer
supination
question
Adduction of the arms may be required in many cases. Key: Position with palms facing the outer thigh- "attention" position.
answer
Supine, arms tucked
question
Face straps - prolonged tightness across a patient's face, causing injury to the facial nerve
answer
What causes masking injury
question
Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Mandibular Cervical
answer
branches of the facial nerve
question
Buccal
answer
which branch is most likely to be injured by a face strap
question
head down, knees flexed
answer
Trendelenburg
question
shock/trauma or GYN/lower abdominal surgeries
answer
when would trendelenburg be used
question
Head-down tilt aids blood return from lower extremities, but encourages reflex vasodialation congests vessels in the poorly ventilated lung apices increases intracranial blood volume
answer
what are some negatives associated with trendelenburg
question
Exposure for lower abdominal surgery - used in combination with other positions (ie lithotomy) Access to head and arms. possible decreased aspiration risk. Increases venous return (albeit transient). - c. 1 liter auto-transfusion
answer
Advantages of Trendelenburg
question
Higher inspiratory pressures, may be very difficult to ventilate the pt. Decreased Functional Residual Capacity. Decreased pulmonary compliance. Increased work of breathing. Endotracheal tube displacement. Cephalad shift of the mediastinum. Facial/airway swelling. Increased venous return Increased ICP Increased intraocular pressure
answer
Disadvantages of Trendelenburg
question
Use of shoulder braces can compress the subclavian neurovascular bundle between the clavicle and 1st rib
answer
How does the risk of brachial plexus neuropathy increase with use of Trendelenburg
question
Increased venous drainage in head and neck reduction in intracranial pressure reduced likelihood of passive regurgitation
answer
Benefits of Reverse Trendelenburg
question
Hypotension Increased risk of venous air embolism (VAE) - when surgical site is above the level of the heart
answer
Complications associated with Reverse Trendelenburg
question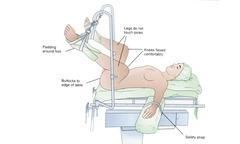
Often used with trendelenburg

answer
Lithotomy
question
Urology and Gyn procedures
answer
Uses of Lithotomy
question
Access to head/airway. Access to arms. Increases circulating blood volume and preload.
answer
Advantages of Lithotomy
question
Multiple opportunities for injury due to excessive rotation of hips. Potential increased with prolonged surgical time Decreasing Tidal Volume and increasing peak pressures. Increases aspiration risk in obese patients
answer
Disadvantages of Lithotomy
question
Obturator Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Common peroneal Brachial plexus is still possible too
answer
What nerves are at risk of injury with lithotomy position
question
Both limbs are simultaneously elevated and separated for surgical exposure and the reverse is true when returned to supine position . This minimizes the torsion stress on the lumbar spine
answer
Why would you need two attendants for positioning legs
question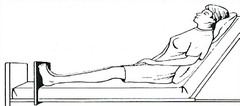

answer
Semi-supine
question
Used for shoulder surgery and posterior fossa approach for neurosurgery
answer
Uses of beach-chair, sitting, or semi-supine position
question
Yes, it may cause decreased cerebral perfusion, CVA, and brain death
answer
Does beach chair position decrease cerebral perfusion
question
In patients with major cardiovascular disease, due to induced sympathetic reflex hyperactivity
answer
When would you not use sitting position
question
-Peripheral vasodilation leading to decreased CO, increased HR & SVR while CBF falls momentarily and then corrects. -Protect the ulnar and peroneal nerves. -Carefully flex the neck with the chin positioned a finger's breadth from the chest to prevent cervical vein obstruction.
answer
Concerns related to sitting position
question
-Facilitates exposure -Enhances venous drainage -Decreases bleeding -Improved vital capacity, FRC, Diaphragmatic excursion -Decreased facial swelling (beneficial for long surgeries)
answer
Advantages of sitting
question
-Postural hypotension -Edema of Face ; Neck (position dependent) -Flexion of endotracheal tube on the tongue -Midcervical Tetraplegia d/t hyperextension of the neck, can result in vascular compromise and ultimately paralysis below the 5th cervical vertebrae -Sciatic Nerve Injury
answer
Disadvantages of sitting
question
associated with sitting position, although may occur in any position where surgical site is above the right atrium
answer
Venous Air Embolism
question
-TEE (Gold standard) -Doppler -ETCO2 -Esophageal stethoscope
answer
Detection of VAE
question
ETCO2 - changes of even 2 mmHg can be an indicator
answer
Which method of detection for VAE is most convenient and practical
question
Left Lateral Decub + Reverse T-burg Aspiration of Volume of Air from R Atrium
answer
Treatment of VAE
question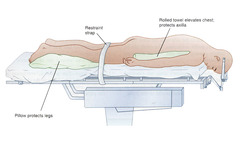
Most difficult to execute

answer
Prone position
question
Rectal, Back, Spine surgery
answer
Uses for prone position
question
-Assure that eyes ; ears are free of pressure. -Keep arm abduction ; 90° or tuck arms at patient's side. -Support the patient at the chest and hips so the abdomen hangs free to limit inferior vena cava obstruction, improve lung expansion. -In the kneeling position, pad knees carefully. -Protect the endotracheal tube, consider a drying agent to decrease oral secretions. -ensure correct position of patient's breasts and genitalia (men)
answer
Prone position concerns
question
every 5 minutes. Consider facial pillow vs turn head to side
answer
How frequently should you check your patient's eyes in prone position
question
ETT - Can't reintubate prone, not prudent to extubate prone either. LMA? Restrictive Respiratory Pattern. Increased peak inspiratory pressures. Barotrauma Increased work of breathing. Obese patients may require positioning that allows the abdomen to hang free. - Improves oxygenation ; V/Q mismatch.
answer
Disadvantages of prone position
question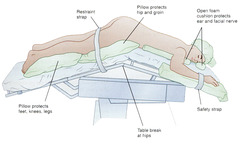
Rectal surgery

answer
Prone - Jackknife
question
Increased Risk w/Prone Position Etiology - Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (89% of cases occur in Prone position) -Decreased Perfusion (increased venous congestion in optic canal) -Increased IOP -Exacerbated by anemia and hypotension
answer
Postoperative visual loss
question
Use of Wilson surgical bed frame Extensive Surgery in Prone Position -Length of surgery Obesity Increased blood loss Male gender Lower percent of colloid administration
answer
Risk factors for postoperative visual loss
question
Used for Thoracic, renal, ; orthopedic procedures Whatever side is down determines the name of position - right lateral decubitus
answer
Lateral Decubitus
question
Maintain good body alignment
answer
Concerns for Lateral Decubitus
question
Dependent Eye and Ear Injury Postoperative neck pain- Support neck to ensure head neutral alignment. Suprascapular Nerve - Circumduction stretch injury in dependent shoulder- Prevent with axillary pad to thorax caudad to axilla. Long Thoracic Nerve - Thought to result from viral neuropathy and lateral flexion of the neck may cause stretch injury.
answer
Disadvantages of Lateral Decubitus
question
Ensure eye is closed, adequate padding of the orb. Ensure pinna is flat and padded.
answer
How would you prevent eye and ear injury in lateral decub position
question
FRC is decreased ; supine. -Decreased FRC in dependent lung. -Increased FRC in nondependent lung. -Increased risk of atelectasis (dep. lung). Gravity causes increased perfusion of the dependent lung, resulting in a V/Q mismatch. -Dependent lung is better perfused and less ventilated than the nondependent lung and vice versa. Difficult to re-intubate.
answer
Respiratory concerns r/t lateral decub
question
BP cuff ; Arterial Line -Make sure that the patient is not lying directly on the EKG leads. -Einthoven's triangle - may not get an accurate EKG reading or increased artifact.
answer
Problems with monitoring devices r/t lateral decub
question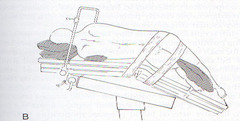

answer
Kidney position



