Lifespan Exam 2 – Pediatric – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Name the domains of development
answer
Gross motor: using large groups of muscles to sit, stand, walk, run, etc., keeping balance, and changing positions. Fine motor: using hands to be able to eat, draw, dress, play, write, and do many other things. Language: speaking, using body language and gestures, communicating, and understanding what others say. Cognitive: Thinking skills: including learning, understanding, problem-solving, reasoning, and remembering. Social: Interacting with others, having relationships with family, friends, and teachers, cooperating, and responding to the feelings of others
question
Early Childhood Special education is delineated in IDEA Part B and applies for children ages 3 - ____ a. 10 b. 12 c. 18 d. 21
answer
d. 21 Provides services for children 3 years old through 21 years of age & provides: Free, appropriate, public education in the least restrictive environment
question
Define Motor skill
answer
A motor skill is a learned sequence of movements that combine to produce a smooth, efficient action in order to master a particular task. The development of motor skill occurs in the motor cortex, the region of the cerebral cortex that controls voluntary muscle groups.
question
What are warning signs of a developmental delay Discuss behavioral, gross motor, and visual
answer
Behavioral daily violent behavior rocks body Gross motor has stiff arms and legs clumsy compared to same age children Visual rubs eyes frequently brings objects too close to eyes to see
question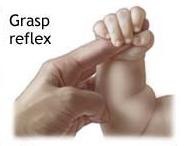
What is the grasphing reflex - when does it integrate (or should it integrate)

answer
Present at birth Seen when a finger is pressed into baby's palm, baby's fingers automatically curl around the person's finger The reflex slowly integrates ; allows the development of more mature grasping patterns - leading to fine motor skills At 4 months, babies will begin to more frequently reach out for toys with arms and hands The reach looks more like a swipe because the baby is learning how to control the arm and hand Over time, babies learn how to make smoother ; coordinated movements with their arms and hands
question
What is IEP
answer
Utilizes the IEP - Individualized Educational Plan Identifies the present level of performance Sets forth a plan for implementation of needed services Identifies who, what ,when, and specific goals and outcomes Services are provided in the educational environment An IEP is an individualized education plan designed to outline a specialized plan for a student according to their special needs in the education environment. It is written by a team of individuals who understand the student's need. Additional assessments may be requested by team members and another meeting is held to discuss results and make adjustments to the IEP as needed. It is a legally binding document. Team members include but are not limited to special education teacher, regular education teacher, parent, child (may or may not attend), psychologist, school administrator, and related service personnel (PT, OT, ST), etc.
question
What is a set of functional skills or age-specific tasks that most children can do at a certain age range that encompasses all domains of development
answer
developmental milestones
question
What pathologies might have crouched gait
answer
Crouched Gait Commonly seen in children with diplegic CP and hamstring contractures. Results in a combination of hip flexion, knee flexion, and ankle equinus
question
Your Pt displays the following signs and symptoms? Asymmetrical hip abduction in flexion Asymmetrical groin or buttock skin folds Clicking or popping of affected hip Apparent femoral shortening on affected side Positive test for hip subluxation What do you suspect
answer
developmental dysplasia of the hip
question
What is important to know about ROM in peds vs adults
answer
Adult ROM values are NOT to be used for comparison with Newborn values. Full term newborns Limited in hip and knee extension Greater dorsiflexion than adults Intrauterine position Flexor muscle tone
question
Upright head posture and walking are examples of what domain of development
answer
gross motor
question
How do children learn new physical skills
answer
Children learn new physical skills by practicing them until each skill is mastered
question
What is important to remember about milestones and their associated age level
answer
Milestones help monitor how a child is developing Although each milestone has an age level, the actual age when a normally developing child reaches that milestone is highly individualized as every child is unique!
question
The domain of the development that concerns itself with interacting with others, having relationships with family, friends, and teachers, cooperating, and responding to feelings of others is the _____ domain a. cognitive b. language c. social d. gross motor e. fine motor
answer
social
question
Spiraling and flexible as to when a child reaches and masters a skill - this describes the developmental milestone process True or False
answer
True
question
Where are the muscles for gross motor skills typically found
answer
Muscles required for gross motor skills are generally found in the arms, legs, back, abdomen & torso Motor skills are deliberate & controlled movements requiring muscle development & maturation of CNS Support Skeletal system must be strong enough to support the movement & weight handling involved in any new activity
question
When would we expect a normally developing baby to hold his/her head steady in sitting a. 3 weeks b. 2 months c. 5 months d. 8 months
answer
2 months - head steady in sitting
question
Reaching and grasping of objects are examples of what domain of development
answer
fine motor
question
True or False Current models of development agree that childhood development is linear, but not necessarily sequential
answer
False, the below is true Current models of development agree that childhood development is sequential, but not necessarily linear Debatable whether one skill in the sequence must be achieved before the next skill may be reached (stair-step)
question
You Pt has the meninges and parts of his spinal cord protruding in a sac at the level of the lesion...obvious abnormality of the spine. What type of spina bifida is this a. meningocele b. acculta or cystic c. occulta d. myelomeningocele e. myositis ossificans
answer
d. Others are described below Occulta (not visible) - No disability usually Acculta or cystic (visible) Meningocele - no disability usually CSF and superficial tissue protrudes from the spine in a sac at the level of the lesion Neurological tissue is rarely involved Myelomeningocele Meninges and parts of spinal cord protrude in a sac at the level of the lesion There is an abnormality of the spine Disability includes paralysis with loss of sensation below the level of the lesion Extent of the disability depends on the level of the lesion and scope of the neurological involvement
question
At what age do we typically see cruising a. 6 months b. 8 months c. 10 months d. 1 year
answer
10 months - cruising
question
This domain of learning is required for large muscle control of the body
answer
Gross motor Abilities required for large muscle control of body Walking, running, sitting, crawling & other activities
question
What is physiologic flexion

answer
Physiologic Flexion Full term babies are born in physiologic flexion Due to confinement & position in the womb Hip, knee & ankle flexion contractures Normal neonatal hip flexion contracture of 30 degrees and knee flexion of 20 degrees; ankle is fixed in DF Q&A: Describe the position of the spine & joints of the extremities
question
At what age would we expect a baby to sit without support a. 3 months b. 6 months c. 10 months d. 1 year
answer
6 months - sits without support
question
Between ages 1 and 3, hip and knee angles change from ____ to ____
answer
varus to valgus
question
Which of the following is not a pediatric neuromuscular disorder a. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy b. Myotonic dystrophy c. Limb-girdle Muscular Dystrophy d. Arthrogryposis e. Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
answer
d.
question
Anticipatory (feed-forward) motor control strategy is typically used by children with what diagnosis?
answer
postural adjustments used by children with cerebral palsy and typically developing children to counteract self-generated motions that disturb balance.
question
What is Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973
answer
Some children may not qualify for services under IDEA yet qualify under section 504 Section 504, a civil rights law, prohibits discrimination on the basis of disabling conditions by programs and activities receiving or benefiting from federal financial assistance. This statute does not require the federal government to provide additional funding for students identified with special needs. Schools must provide these children with reasonable accommodations comparable to those provided to their peers under the rulings of Section 504.
question
Anti-gravity extension

answer
Antigravity Extension Voluntary, active movement against gravity First seen at the neck then the trunk In prone, begins with lifting of the head In prone, extensors strengthen & flexion contractures decrease Active extension movement occurs first as the extensors have been in a lengthened position and are prepared to move before flexors.
question
A child with developmental hip dysplasia is learning how to walk, how might this present in your pt How might this look different in an older child?
answer
A painless waddling limp may be noted as a child learns to walk. If bilateral hip dislocation is present, limping with marked swayback become noticeable during gait. Signs / Symptoms (cont'd) During ambulation in the older child: Trendelenburg gait Decreased hip abduction Thigh pistoning Bilateral DDH Increased lumbar lordosis Swaying (waddling) gait typical of a bilateral Trendelenburg
question
Who is included on the IEP team
answer
Services include: Special education Appropriate related services (; possible members of the IEP team) PT OT ST Transportation Psychological services and counseling Medical, dental, hearing, or optical services needed in support a child's education
question
Older children are normally more flexible than younger children T/F
answer
False
question
When is walking achieved? How does walking pattern evolve
answer
Standing & Walking - 1 to 2 years (usually b/w 9 -15 mos) LEs - Begins with cruising and wide base stance UEs - High Guard Position Stands Independently ~ 10.5 mos. Takes first steps ~ 11 mos. Walks independently ~ 11.5 mos.
question
Anti-gravity flexion
answer
Antigravity Flexion Develops in supine first Foot-play, head lifting The baby has been in a flexed position, but once they spend time in prone, the trunk flexors are now in an elongated (stretched) position and are being strengthened- working to overcome gravity
question
What is Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
answer
Poor alignment of the acetabulum and head of the femur in the developing hip
question
Lateral flexion and rotation
answer
Lateral flexion activity -- Crawling (amphibian) and rotation - rolling
question
Examples of reasonable accommodations include all the following except? a. adapted seating b. additional testing time c. additional time to walk in the hall between classes d. memory foam pillows for nap time
answer
d.
question
At what age can children develop hypotheses and theories (formal thinking)
answer
13-18 years
question
You are working with a 2 year old that sorts objects and turns pages. She cannot match colors. Is this normal development
answer
Yes on the sorting objects and turning pages but not on the inability to match colors
question
Gait pattern begins to resemble adult gait pattern at age
answer
3
question
What is part of the treatment regimen for developmental dysplasia of the hip
answer
Treatment Some physicians will just allow for the process to occur with no intervention (natural course of healing) Monitoring through radiographs Limitation of contact sports Non-weight bearing activities such as swimming are encouraged Use of crutches (non-weightbearing) in more extensive cases Positional splinting (IR/abd) Surgery Bracing & splinting to hold hip in flexion and abduction Children under 9 months usually wear a Pavlik harness which allows for active kicking; promotes strength and mobility and decreases the occurrence of avascular necrosis of the hip Children over 9 months need abduction orthosis that allows for gait Traction & surgery Usually done after 18 months Therapeutic Interventions Measuring and fitting for bracing ROM Strengthening Encourage kicking in infants Encourage transition Sit to quad Pull to stand Encourage pre-gait activities Crawling Creeping
question
By ___ years, gait pattern is assessed like an adult a. 2 years b. 3 years c. 5 years d. 7 years e. 10 years
answer
7 years
question
Gait pattern is like that of an adult at age
answer
8
question
You are doing a skin assessment of your Pt (a baby)...you note hair along their spine...what do you suspect
answer
spina bifida occulta Signs & Symptoms Spina bifida occulta Skin depression, dark tuft of hair, hemangioma, subcutaneous mass Meningocele or myelomeningocele Sac on the back Weakness and paralysis possible if nerves involved Hydrocephalus, often requiring surgery Hypotonia
question
Discuss the difference between how toddlers walk compared to adults...
answer
3 yrs. of age is when a child's gait pattern begins to resemble that of an adult. Initially there is a wide-based stance with rapid cadence and short steps. Toddlers have a broad-based gait for support, and appear to be high-stepped and flat-footed, with arms outstretched for balance. Legs are externally rotated, with a degree of bowing. Heel strike develops at around 15-18 months with reciprocal arm swing. School-aged children, demonstrate a step length increase and step frequency slows. Adult gait and posture occur around the age of 8 years.
question
At what age would you expect a toddler to be able to run and change direction?
answer
After the age of 2, running and change of direction occur.
question
what is not one of the 4 components of the AAC a. Aids and devices—actual physical devices: handheld devices, computers, and dedicated devices b. Symbol sets—visual or auditory representation of language concepts c. Communication techniques—methods of transmitting messages: access methods, scanning output d. Strategies—methods to increase effectiveness of communication: rate enhancements, role playing e. all of the above
answer
e. all of the above
question
At what age might you see heel strike emerging a. 9 months b. 12 months c. 15 months d. 24 months
answer
24 months
question
Name this pathology Etiology Genetic Problems with the amount ; quality of collagen in the body Presents with fragile bones / low bone density 4 types (Type I, II, III, IV)
answer
Osteogenesis imperfecta
question
Which of the following is not true regarding developmental dysplasia of the hip? a. Usually develops in the last trimester of pregnancy b. May be affected by female homone (relaxin) and tight fetal position in utero, or by breech positioning c. More predominant in males (6 to 8 times) d. Affects the left hip twice as often as right hip e. Can be caused by swaddling and carrying infants with hips in extension and adduction (some cultural practices)
answer
c. it is actually more predominant in females
question
Shaken baby syndrome can result in ++++++ a. cerebral palsy b. traumatic brain injury c. osteogenesis imperfecta d. spina bifida
answer
b.
question
Define steppage gait
answer
Steppage Gait The entire leg is raised at the hip to ensure adequate ground clearance (a foot drop gait). It can be seen with peripheral neuropathies, spina bifida and polio.
question
Distinguish between reflexes vs. primitive reflexes vs. abnormal reflexes
answer
Reflexes Basic unit of movement in the hierarchical theory of motor control Involve the combination of a sensory stimulus ; a motor response Primitive Reflexes Typically present at birth Normal for young infants Usually integrated in the first 9 months of life Abnormal Reflexes Persistent, abnormal, or asymmetrical usually indicate early brain damage and will affect future normal development Contemporary theory recognizes that reflexes alone do not contribute to the dynamic and adaptive nature of early infant motor behavior Fiorintino 1963-81 believed our total postural behavior is the result of interaction of reflexes and the relative strength of each one of them
question
What is not true about emotional development a. plays a role in regulation of muscle tone b. can be a motivation to participate in therapy c. plays role in adherence to performance of activity d. all of the above are true
answer
d. belief in importance of the activity and its relationship to life confidence toward the PTA
question
The following describes a _________ team Discipline specific roles are well defined (role definitions are relaxed) Emphasis on teamwork Therapy services may occur in isolation; however team discusses at regular intervals during team meetings Individuals from different disciplines work together cooperatively to: Plan Implement And evaluate services
answer
interdisciplinary
question
What is necessary to achieve standing skills?
answer
What is necessary to achieve standing skills? Adequate body proportion Adequate ROM Adequate strength, and motor control Coordination of visual, proprioceptive ; vestibular systems for balance (TE-text)
question
What type of child would benefit from AAC
answer
Children born without the ability to communicate or have experienced trauma causing them to loose the ability to communicate, would benefit from some form of Augmentative ; Alternative Communication systerm
question
What pathologies often have a Trendelenburg gait in pediatric patients
answer
Trendelenberg Gait Typically caused by weakness of the hip abductors. The feet, hips and knees are externally rotated, and when weight is borne on one leg, the opposite side of the pelvis drops, rather than rising as normal. Commonly seen in slipped capital femoral epiphysis, Legg-Calve-Perthes disease (idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head), hip dysplasia and inherited myopathies, as well as spina bifida and cerebral palsy. If bilateral sides are affected, the patient exhibits a rolling gait.
question
What is spastic gait? What pathologies typically have this gait pattern?
answer
Spastic Gait Associated with inversion of the foot and foot dragging. It occurs in diplegic and quadriplegic cerebral palsy and stroke
question
What is likely not a major goal for a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta a. Minimize fractures through protective measures Joint protection b. increase running endurance c. Promote bone strength d. Maximize activity ; weight bearing for increased bone strength e. Maximize functional skill
answer
b.
question
The most common physical disability in children, anoxic encephalopathy, is also known as
answer
Anoxic Encephalopathy Brain damage due to lack of oxygen aka
question
What exactly is cerebral palsy
answer
Damage to the cerebrum resulting from: ischemia, hypoxia / anoxia, birth defects, injury or infection CEREBRAL PALSY Most common physical disability of childhood Caused by an insult to the developing brain and resulting in permanent and non-progressive damage Pathology Group of motor disorders caused by cerebral damage during gestation, time of birth, or early childhood Etiology Prenatal Genetic Viral Infections Bacterial infections Drug exposure Etiology Natal Prematurity Low-birth weight Severe jaundice Intra-ventricular hemorrhage Poor nutrition Asphyxia Etiology Post-natal Infection Asphyxia TBI MVA Fall Shaken baby syndrome Child abuse CVA Near drowning Brain tumor
question
CP is diagnosed when a child does not reach motor milestones and exhibits abnormal muscle tone or qualitative differences in movement patterns (i.e. asymmetry) (Campbell, 2006). The degree of severity of CP varies greatly, and the designations of mild, moderate, severe are applied within types. T/F
answer
True
question
Cerebral Palsy effects ____, posture, and ____.
answer
Affects tone, posture, and movement
question
What pathologies typically exhibit toe walking
answer
Toe Walking Habitual toe-walking is not uncommon, and if asked the child can usually walk normally. Persistence of the symptom with failure of heel contact is seen in diplegic cerebral palsy or more rarely, a lysosomal storage disease.
question
What muscle tone may a child with cerebral palsy have
answer
Classified by muscle tone: spastic / high tone, athetoid, ataxic, mixed
question
What is Erb's Palsy
answer
Paralysis or weakness of the muscles of the arm that is caused by damage to the brachial plexus Upper arm paralysis Involving C-5 & C-6
question
What strengthening would be least likely to be included with a Pt that has DDH a. Encourage kicking in infants b. Encourage transition (i.e. sit to quad, pull to stand) c. Encourage pre-gait activities such as crawling and creeping d. Teach caregiver PROM
answer
d.
question
Why is aggressive passive stretching not advised in the patient with JRA
answer
the risk of joint subluxation
question
Define scoliosis
answer
Scoliosis is a lateral curve in the normally straight spine
question
Awareness of potential shunt malfunction must be a consideration for patients with spina bifida hydrocephalus. What are some signs of malfunction (requires emergency response)
answer
Awareness of potential shunt malfunction ~~~SAFETY ISSUE~~~ Signs of malfunction: (may require emergency response) Irritability Headache Vomiting Lethargy Fever Bulging eyes or fontanel Change in behavior or level of alertness Seizure activity Change in coordination
question
What is juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
answer
A group of disorders characterized by inflammation of connective tissue including joints and other systems Classified in children under 16 years of age with condition lasting > 6 weeks Etiology - unknown (may have several contributing factors) Viral or bacterial infection that triggers the auto-immune response May be genetically pre-disposed
question
What is not an appropriate strategy when working with a child and family who have ESL a. Raise your volume to ensure that patient and family member can hear you b. Speak with slightly slower pace so that the patient/caregiver can process the information c. Use natural but animated facial expressions, gestures and body language while looking at the patient d. Use short simple sentences and avoid medical jargon and figurative expressions e. Repeat, paraphrase, and summarize important information
answer
a.
question
A Pt you are treating had a traumatic birth that involved the following....what diagnosis might you expect Excessive stretching of the fetal head and neck in opposite directions during delivery Pulling on the infant's shoulders during the delivery or excessive pressure on the baby's raised arms during a breech (feet first) delivery Two potentially harmful forces during labor: Natural expulsive force of the uterus Traction force applied by obstetrician Labor is typically long and difficult. The infant is usually... High birth weight Sedated Hypotonic Separation of bony segments Overstretching Soft tissue injuries
answer
Erb's Palsy
question
A baby is considered premature at no later than what age a. less than 40 weeks b. less than 37 weeks c. less than 35 weeks d. less than 30 weeks
answer
b.
question
Define motor development
answer
The study of changes in human motor behavior over the lifespan, the process that underlie these changes, and the factors that affect them (Umphred, 2014) All periods of development are valued equally Dynamic, nonlinear process with periods of stability and instability Influenced by intrinsic and extrinsic factors Important as a PTA to understand this process for proper assessment and intervention of impairment/functional challenges encountered at any age stage
question
What happens if primitive reflexes remain present past 6-12 months
answer
Are succeeded by the postural reflexes [inhibited by the frontal lobes] which enable the maturing child to interact effectively with his environment (Goddard, 1996) If present beyond 6 to 12 months of life, they are termed aberrant ; may result in immature patterns of behavior Despite the acquisition of later skills, may cause immature systems to remain Older children or adults with atypical neurology may retain these reflexes IE: patients with cerebral palsy If there is a cluster of primitive reflexes remaining, CNS will be dysfunctional in some way Primitive reflexes may reappear in adults b/c of certain neurological conditions including, but not limited to: Dementia Head Trauma Strokes
question
What is the dynamic system theory
answer
An individual uses all possible strategies to accomplish a task and as physiological systems are modified, the motor behavior changes (Umphred, 2014) A more holistic approach; process rather than product; self-organizing process An interactive model where both intrinsic and extrinsic variables impact motor skill development and acquisition Each subsystem develops at its own rate ; may be a strength or constraint for development of movement Dynamic interaction among the subsystems create modifications in motor behavior (i.e. Musculoskeletal, Neuromuscular, Cardiovascular, Pulmonary and Cognitive systems)
question
Which of the following is not an unaided system of communication a. gestures b. vocalizations c. eye-gaze boards d. sign language e. speech
answer
c. eye-gaze board Unaided systems include: gestures vocalizations speech sign language Aided systems include: physical, mechanical, and electronic devices adapted keyboard communication boards eye-gaze boards computers
question
Babies are born with a curved spine including lumbar curves (True or False)
answer
False 0-12 months Changes from the physiologic flexed ; rounded posture with the emergence of cervical and lumbar curves (lordosis) Provides increased stability of the back and neck 1-6 years Curves continue to increase 1-2 years - standing and walking
question
Growth spurts can cause an elongation of the muscle as the bone grows until the muscle has time to catch up T/F
answer
True Growth spurts can cause an elongation of the muscle as the bone grows until the muscle has had time to catch up
question
What are aided communications
answer
Aided communication uses symbol sets to represent language. These sets follow a hierarchy from concrete to abstract Real objects - actual objects Miniature objects - smaller replica of objects used with children who can't interpret a photo or has limited vision and need tactile feedback Photographs - color or black and white images used to represent objects, verbs, people, activities, or places (cont'd to next slide) Line drawings (color) - used to represent a concept that the child may wish to discuss Line drawings (black and white) Symbols/icons - various types (i.e. Minspeak, Picsyms) Traditional Orthography (written language) - written characters (i.e. Braille, Morse code)
question
What is not a postural reaction a. Righting reactions b. Equilibrium reactions c. Protective reactions d. Associated reactions e. Pusher reactions
answer
e.
question
What is not one of the 3 important elements of motor control a. neural circuit b. motor plan c. the parasympathetic system d. the environment in which the movement occurs
answer
c. Study of how the CNS regulates the musculoskeletal system and environment in regard to movement for the attainment of a specific task 3 important elements of motor control Neural circuit—underlies the processing of input/output Motor plan—effector of output of the neural circuit The environment in which movement occurs—shapes the play between the neural circuit ; the motor plan Stresses task specific learning - all movements are goal oriented Takes into account both neuromuscular control processes ; environmental constraints
question
Name types of primitive reflexes
answer
Palmar ; Plantar grasp Asymmetrical tonic neck reflex [ATNR] Symmetrical tonic neck reflex [STNR] Tonic labyrinthine Galant Babinski Suck / swallow Flexor withdrawal Crossed extension Rooting Stepping Positive Support Moro Startle
question
Your 3 y/o Pt presents with Signs / Symptoms Pain, swelling, stiffness in joints Fever Rash (more common in systemic) Inflammation of the iris of the eye Myalgia Involvement of (more common in systemic): Lymph nodes Heart Liver Spleen Pericardium Lungs What do you suspect
answer
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
question
What is not a type of scoliosis? a. Retrograde b. Congenital c. Neuromuscular d. Degenerative e. Idiopathic
answer
a.
question
What is dissociation
answer
Rotation/Dissociation = balanced control of flexors and extensors ; dissociation between body segments Dissociation - ability to move one body part separate from another associated body part Breaking up of this mass pattern; separating movement in one body part from an associated movement in another body part
question
Anti-gravity flexion...what is the progression
answer
Supine to sit Flexion Progression In Supine: 1. Head ; neck --- 2. lower abdominals / hips------ 3. sitting What muscles must have strength to maintain sitting? Trunk flexors or extensors?
question
What is not a motor control strategy a. feedback b. motor contact c. motor program d. motor plan e. motor skill acquisition
answer
b. Definitions of the motor control strategies are below Motor program - a set of pre-structured muscle commands that end up producing coordinated movement / learned task / carried out without influence of peripheral feedback Motor plan - overall strategy for movement Feedback - afferent information sent by sensory receptors to control centers with constant updates that allow for corrections shaping the ongoing movement ; allows motor responses to be adapted to the demands of the environment Motor-skill acquisition - behavior is organized to achieve a goal directed task with active problem solving needed for the development of the motor program, plan, and learning ; is adaptive to the specific demands of the environment CNS recovery - reorganization is dependent on experience - practice is required to regain lost skills, ; ability to retain ; generalize re-learned skill to other similar tasks or to apply in other environmental contexts Feed-forward - prepares the system in anticipation of responses required for movement and adjusts the system for incoming sensory feedback for future movements Anticipatory (feed-forward) postural adjustments used by children with cerebral palsy and typically developing children to counteract self-generated motions that disturb balance.
question
A Pt presents with Signs ; Symptoms Frequent fractures Scoliosis/Kyphosis Short stature Hearing loss What do you suspect? a. osteogenesis conundra b. SCFE c. osteogenesis imperfecta d. akuna matata
answer
c.
question
What does sit to creep demonstrate
answer
Demonstrates weight bearing, weight shifting, and rotation/disassociation
question
How might a Pt with hemiplegic cerebral palsy ambulate and how would they look
answer
Same side UE ; LE Standing posture (typical) Shoulders in adduction ; IR Elbow ; wrist flexion IR of hip Knee extension Ankle plantar flexion Trunk may also be affected Gait (typical) Asymmetrical gait pattern Circumduction of LE Assistive devices for mobility may include a crutch or cane for balance
question
What do postural reactions do
answer
Assist the child with orienting body in space in the upright position Develop in infancy to early childhood Include: Righting Reactions Protective Responses Equilibrium Responses Emerge as primitive reflexes Emerge to help the infant or child cope with demands of a gravity-based environment Provide the basis for the control of automatic balance, posture and voluntary movement Are complex postural responses that continue to be present throughout adulthood
question
Name this pathology Non-progressive neuromuscular disorder Presents with: Multiple contractures (distally ; proximally) due to decreased fetal movement Dislocation at hips or knees Deformities of joints (fusiform or cylindrical shape) Joint fusion (in some cases) Thinning of subcutaneous tissue Absence or decreased size of muscle groups Absent skin creases a. spina bifida b. juvenila rheumatoid arthritis c. osteogenesis imperfecta d. arthrogryposis
answer
d. Arthrogryposis aka multiplex congenita Etiology Unknown Possible trauma during first trimester Maternal history of a condition that limits fetal movement Fevers during pregnancy MS Myasthenia gravis Myotonic dystrophy Uterine abnormalities
question
What is not a neuromuscular cause for scoliosis a. cerebral palsy b. spina bifida c. bone collapse d. conditions that result in paralysis
answer
c. is a degenerative cause of scoliosis not neuromuscular Congenital - bone abnormality at birth Neuromuscular - abnormal muscles or nerves spina bifida cerebral palsy conditions that result in paralysis Degenerative - results from traumatic injury or illness bone collapse major back surgery osteoporosis
question
At what age do babies have normal physiologic flexion
answer
Basic Principles: ; one year have normal physiologic flexion
question
What is not a thing to consider prior to treatment intervention as it relates to cognitive/social/emotional development: a. patient's cognitive understanding of a task b. attitude toward the activity c. confidence/trust child has in PTA d. all of the above
answer
d. all of the above should understand the cognitive and emotional level at which the patient interacts is not expected to evaluate or analyze motor performance issues but should appreciate their existence and how they impact movement problems should recognize when patient changes behavior or motor responses and if they are better or worse and communicate findings to the PT
question
Righting vs Protective postural reactions
answer
Righting Reactions Orient the head & body in space Involve head & trunk movements Protective Responses Used in response to rapid displacement of the body as a result of an outside force Involve the movement of the extremities in the direction of the displacement
question
What would you not expect of a baby that has cerebral palsy a. increased joint mobility b. motor control problems c. DTR scores of 4 d. extra soft feel to muscles e. decreased activity may lead to obesity
answer
c. I would expect weak or absent reflexes
question
What is IDEA
answer
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act Yielded from 1954 Supreme Court case Brown vs. The Board of Education which was based in the racial inequality of "separate but equal" schools at that time. Later, the findings that "separate was not equal" came to include children with disabilities being denied education In 1975 IDEA was passed and became law. It entitles every child with a disability to have a free appropriate public education (FAPE) designed to meet their needs. "This law governs all special education services and provides some funding to state and local education agencies to guarantee special education and related services for those students who meet the criteria for eligibility in a number of distinct categories of disability, each of which has its own criteria" Council for Exceptional Children, 2002
question
What must be done to determine if a child really has ADHD
answer
Many situations and conditions may trigger symptoms that mimic ADHD but are not ADHD Examples: Death, divorce, learning disability, ear infections, anxiety, depression, undetected seizures, sudden change in lifestyle ***To have a definitive diagnosis of ADHD, the behaviors must appear before age 7 and continue for at least six months. The symptoms must also create a real handicap in at least two areas of the child's life—in the classroom, on the playground, at home, in the community, or in social settings.
question
Name this pathology A group of congenital malformation of the spine, including the vertebrae and the spinal cord Etiology Genetically predisposed Nutritional deficiencies (especially maternal folic acid deficiency) Environmental (i.e. alcohol during first 4 weeks of pregnancy when neural tube closes) Posterior spinous processes of vertebral column does not close during development in utero Gap can permit meninges, spinal fluids ; spinal cord to herniate, neurological impairment results Meningocele - meninges and spinal fluid protrude through bony defect Myelomeningocele - herniation of spinal cord, nerves, meninges, spinal fluid Most serious form Neurologic impairment
answer
Spina Bifida
question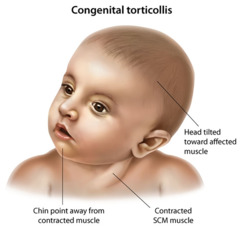
Describe Torticollis

answer
Derived from 2 Latin words Tortus = twisted Collum = neck Describes abnormal neck position Occurs in 2-3% of all live births (Graham), equal male to female (Chan) 3rd most common congenital muscular anomaly in infants 1st = hip dysplasia 2nd = club foot 2 types (Karen Karmel-Ross, 1997) Congenital Muscular Torticollis (CMT) Acquired Torticollis Persistent cervical lateral flexion to one side Generally rotation of the head to the opposite side Most commonly involves sternocleidomastoid muscle More incidences of right torticollis than left (Chan) In 2002, Graham noted more incidence of left torticollis 2° 67% of fetuses descend into birth canal with left occiput transverse
question
If casting was required for your Pt, what will you need to do to help this Pt return to previous level of function (PLOF)
answer
strengthening and stretching
question
How do you name torticollis
answer
Named after which side laterally flexed to i.e. left lateral cervical flexion = left torticollis
question
Why is working with children different from working with adults
answer
One must keep in mind that children are not little adults Stage of development in all domains must be taken into consideration One must be creative ; appeal to the interest of the child One must be able to win the trust of the child ; parent One must involve the parent / family / caregiver at all times One must use a variety of techniques and be flexible One must know how to make treatment "FUN" One must be willing to work as a collaborative team
question
What are etiologic factors of congenital torticollis
answer
Etiology Not always clear More description of presentation than cause Unilateral fibrosis of SCM "Kink" or "crush" to SCM with subsequent ischemia Fetal malposition Increase incidence in twins Bottom vertex fetus (Twin A) more involved (Littlefield et al) Uterine compression Fused cervical vertebrae causing abnormal neck posturing
question
Acquired torticollis is from non-muscular conditions that result how....
answer
Non-muscular causes account for 18% of all cases of torticollis Subluxation of C1 on C2 Hematoma in SCM Osteoblastoma Clavicular fracture from forceful delivery Cervical skeletal malformation Subluxation of cervical vertebrae Hemivertebrae Herniated disk Posterior fossa tumor Extraocular muscle paresis Ocular strabismus or nystagmus Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) Prolonged positioning (breastfeeding or bottlefeeding only on one side
question
Which of the following would not be included in your intervention with a patient that has cerebral palsy secondary to hypotonicity a. Support all limbs to prevent injury b. Prevent hyperextension at elbows ; knees c. Vigorous passive and active movement to stimulate increased muscle output d. Promote active weight-bearing to stimulate postural reflexes e. all of the above are true
answer
e. per slide 75
question
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder
answer
A developmental disability resulting in social, communication, and behavioral challenges. Symptoms begin in early childhood and continue throughout the lifespan. A variety of disorders fall under 1 umbrella categorized as ASD. Causes are unknown, can be environmental , genetic, or biological. Motor skills are impaired. Motor coordination, postural control and imitation skills are limited. Planning and completing new motor tasks is challenging. Delayed social skills
question
Signs and Symptoms of Autism
answer
Signs and Symptoms Vary widely, presented in various ways across a spectrum (mild-severe) Typically noticed by parents before a child's first birthday Often times parents notice functional delays by age 2 Starts early in childhood and lasts a lifetime; can be improved with intervention Diagnosis Not a definitive way to diagnosis ASD Assessment tools assist with diagnosis confirmation (i.e. the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, 2nd edition (ADOS- 2), and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R) A child's behavior and specific development must meet certain criteria to receive an ASD diagnosis
question
What are 2 major signs of ASD
answer
2 major signs that indicate a child may have ASD Difficulties in social communication and interaction Examples: avoiding eye contact Enjoys playing alone Lack of social interaction with peers Lack of understanding boundaries and personal space Repetitive speech on a preferred topic or speaks words repetitively A tendency to engage in restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior Examples: Performs self-stimulating behaviors (spinning, rocking, etc.) Irritated by minor changes or upset due to change in normal routine Short attention span Decreased safety awareness Unusual reaction to touch, smell sound, movement or taste Difficulty imitating movements or controlling posture Decreased coordination and balance
question
Hypontonicity in your Pt with cerebral palsy may lead to all the following in regard to gait EXCEPT a. Narrow BOS b. Wide BOS c. Short stride lengths d. Impaired balance
answer
a. Narrow BOS
question
Cephalocaudal development
answer
Development occurs from head to toe Head is disproportionately larger than the other parts of the infant's body Describes the typical direction of development of postural responses Muscular control develops from the head downward First the head & neck Upper body and the arms Lower trunk and the legs Development occurs from the center of the body outward (mid-line first to provide a stable base upon which the head & extremities may move) The head and trunk develop before the arms and legs, and the arms and legs before the fingers and toes Trunk is the stable base Not a cause-and-effect relationship between proximal and distal functions
question
Fine motor movements occur before gross motor movements T/F
answer
False
question
Whole body movements develop before selective movement & before disassociation occurs True or False
answer
True
question
What is muscular dystrophy
answer
Pathology Genetic muscle diseases characterized by progressive weakness & atrophy of skeletal muscles Many types - Duchenne MD and Becker's MD are the most common
question
What is a trans-disciplinary team
answer
Decreases the number of professionals that families must encounter on a regular basis while meeting the needs of the child Professionals committed to teaching, learning, and working with others across traditional disciplinary boundaries Role release Transference of information and skills specific to one discipline to other team members of different disciplines Team members work together to conduct assessments, program plan, develop goals and implement treatment plans
question
When treating a 10 year old child, the PTA should address the a. parent b. 10 year old
answer
b. child
question
What might still be present in your cerebral palsy patient that is hypertonic?
answer
Persistence of primitive reflexes which prevent development of normal movement patterns ATNR STNR TLR
question
What are some intervention strategies when treating a patient who is using aided communication
answer
Work with other team members to ensure a child has a way to communicate, spoken or written, to express their wants and needs Gain an understanding of the child's communication system so that it is used effectively during treatment session Will help minimize patient and therapist frustration Show families that therapist sees the child as a whole and supportive of their additional needs Encourage family/caregivers to allow practice opportunities with the AAC device or communication system across environments to promote carryover Be creative in treatment design incorporating activities that the child can understand and express using their communication style
question
Your Pt fractured their R tibia. This Pt is 3 years old. What assistive device do you give this Pt. a. quad cane b. walker c. crutches d. Lofstrand crutches
answer
b. walker
question
What is the loading response of the gait cycle
answer
loading response --corresponds to the gait cycle's first period of double limb support
question
What is terminal stance
answer
Terminal stance- heel rises from the ground
question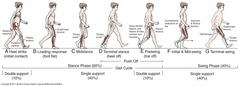
What is pre-swing

answer
Preswing—corresponds to the gait cycle's second period of double limb support
question
Compensations for torticollis include
answer
Compensation for torticollis by production of cervical scoliosis with lateral shift of the head to involved side Spontaneous involuntary compensation for torticollis by elevation of the shoulder on the involved side Leads to head alignment perpendicular to the support surface
question
What is ESL
answer
English as a Second Language
question
What is likely NOT included in treatment of patients with osteogenesis imperfecta a. Construct or provide appropriate orthotic devices Splints b. Body jackets for protection c. Aggressive passive ROM to improve ROM d. Devices to promote WB and to prevent deformity Active stretching
answer
c. Therapeutic Interventions Construct or provide appropriate orthotic devices Splints Orthotics Body jackets for protection Devices to promote weight bearing and to prevent deformity Strengthening exercises ROM Positioning Active stretching SAFETY -- AVOID aggressive passive stretching due to high risk of fracture or joint subluxation
question
Discuss the swing phase of gait
answer
Initial swing begins at toe off and continues until maximum knee flexion (60 degrees) occurs. Midswing is the period from maximum knee flexion until the tibia is vertical or perpendicular to the ground. Terminal swing begins where the tibia is vertical and ends at initial contact.
question
What is the best way to talk about a patient a. my patient with spina bifida b. my spina bifida patient
answer
a. Communicate to families using "People First Language". Put the person before the disability. Disabilities are not persons and they do not define people. Examples: Use - "she has autism"; Don't use - "she's autistic" Use "he has a physical disability"; Don't use - "he's a quadriplegic"
question
Name this pathology A genetic disorder in which babies are born with an extra copy of chromosome 21. The extra copy of chromosome 21 changes the typical development of the baby's brain and the body, causing mental and physical challenges. Occurs in 1 in 800 live births _________may be detected during pregnancy by screening or diagnostic tests. If not detected before birth, it usually is detectable at birth by the baby's physical characteristics, including: Low muscle tone A single deep crease across the palm of the hand A slightly flattened facial profile, and an upward slant to the eyes Smaller size head with flattened neck and nose Mental impairment in varying degrees
answer
Down Syndrome Signs and Symptoms Additional symptoms that develop into adolescence & adulthood include: Poor language development and language use Hearing and visual problems Intellectual disability Compression of the spinal cord and potential misalignment of bones
question
You are treating a child with ESL...what is not an appropriate communication strategy a. Use words, pictures, photographs, charts, media, or any other kind of supplemental information b. Ask "Wh" questions to gather information c. Use open-ended questions d. Use teach back or show me models to ensure patient understands instructions e. Contact translator if previous methods are unsuccessful
answer
c. You should actually use yes/no questions
question
Describe developmental delays that may result from torticollis or why delays may occur
answer
Infants COG unstable & affects ability to move Infants vertical axis is NOT perpendicular to the horizontal axis affecting ability to perform midline activities Developmental skills most affected Righting & postural reactions Prone skills Sitting balance Visual tracking Symmetrical weight bearing both in UE & LE Symmetrical weight shifting Symmetrical transitions
question
Name critical elements of family centered care
answer
Respect for each child and his or her family Honoring racial, ethnic, cultural, and socioeconomic diversity and its effect on the family's experience and perception of care Recognizing & facilitation choice for the child and family even in the difficult and challenging situation Facilitation & supporting the choices of the child and family about approaches to their care Ensuring flexibility in organizational policies, procedures and provider practices so services can be tailored to the needs, beliefs, and cultural values of each child / family Sharing of unbiased and honest information with families on an ongoing basis and in ways they find useful and affirming Providing and enduring formal and informal support for the child and parent and or guardian during pregnancy, childbirth, infancy, childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood Collaborating with families in the care of their individual child at all level of health care including professional education, policy making, and program development. Empowering each child and family to discover their own strengths, build confidence, and make choices and decisions about their healthcare. PT/PTA assessment of patient/caregiver compliance and carryover throughout treatment regimen will assist in optimizing function and producing effective outcomes One must understand that families respond to their child's illness, injury, or condition in different ways which can be impacted by Stress within the home Due to sadness, fear, loss, disappointment, embarrassment Financial / socio-economical issues Relationships / family dynamics Lack of information or ignorance about the condition or about the future of the child Conflicts between health care providers and the family Cultural differences / perceptions The age of the child or the severity of the condition
question
Arthrogryposis is also known as
answer
multiplex congenita
question
Pediatric gait cycle
answer
Still 60% stance phase and 40% swing Refer to (Mansfield/ Neumann) Essentials of Kinesiology for the PTA 2nd Edition Text Ch 11 pg 305 & 12
question
Discuss stance phase of pediatric gait cycle
answer
Loading response begins with initial contact, the instant the heel contacts the ground. Loading response ends with contralateral toe off, when the opposite extremity leaves the ground. Midstance begins with contralateral toe off, ends when the center of gravity is directly over the supporting foot. Terminal stance begins when center of gravity is over the supporting foot and ends when the contralateral foot contacts the ground. Pre-swing begins at contralateral initial contact and ends at toe off.
question
What pathology do you suspect with these Signs & Symptoms Loss of muscular strength, lack of coordination, progressive deformity, eventual disability Muscles become hypertrophied w/ connective tissue Gower's sign Weakness spreads distally and to lungs Start at approximately 2 yrs old and then progresses until death
answer
Muscular dystrophy
question
What is likely not a concern when treating a pediatric Pt who has Down Syndrome a. Hypertonia b. Muscle weakness c. Poor coordination d. Sensory perceptual problems
answer
a. hypotonia is the actual concern...along with resulting joint laxity
question
Your patient is bow-legged and age 14...what are the potential contributing factors
answer
When not a part of normal development, bow-legs are a symptom of a disease or injury such as... Problems with metabolism Problems with nutrition Fractures that heal incorrectly Rickets or Blounts Disease http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HMYSys-T3Rs http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rogGfR5ZENI Genetic bone growth abnormalities Pediatric orthopedic surgeon. (2014)Bow leg and knock knee. Retrieved from: http://www.childrensorthopaedics.com/BowlegandKnockKnees.html
question
What is not one of the 6 stages of adjustment to disability a. Shock b. Anger c. Denial d. Euphoria e. Depression f. Acknowledgement g. Adjustment
answer
d. Euphoria Shock- Overwhelming depersonalization, a sense of loss, or psychological numbness. Produces anxiety, panic, confusion in thinking, fear of death, uncertainty about the future, and purposeless over activity. Denial- a problematic form of coping strategy against painful realization of a long term effect of a disability of disease. Often experiences wishful of unrealistic recovery. Depression- a natural grief reaction to loss associated with feelings of distress, helplessness and hopelessness Anger- characterized feelings of guilt. Can result in self destructive behavior and suicidal ideation. Hostility, often directed toward others or the environment, believed to be responsible for the condition in an attempt to retaliate. Acknowledgement & Adjustment- acceptance phase characterized by the individual's readiness to be realistic about functional limitations and self worth as a person with a disability. Is ready to start making use of new discoveries and potentials for a productive life. These stages will occur when a disease/condition is acquired or even congenital once a child/adolescent realizes that they are different than everyone else or unable to perform as well as their peers.
question
Your PT wtih osteogenesis imperfecta is least likely to do which of the following a. walk b. swim c. run d. navigate in a w/c
answer
c. Therapeutic Interventions Provision of assistive devices for mobility Wheelchairs / customized seating systems Crutches Walkers Low impact endurance activities Swimming Walking Provision of any needed adaptive equipment for ADLs
question
Tell me more about AAC
answer
Often associated with Assistive Technology and communication Team approach is used to conduct AAC assessments; however the SLP is typically the team lead Team includes (OT, PT/PTA, parent, educator, seating specialist-may be a therapist) Team must determine the best device or communication system suited for the child's language capabilities, cognitive and developmental level, seating & positioning needs, motor access, and position for optimal access Used across a variety of settings (schools, rehabilitation facilities, home, etc.) Communication limitations may be permanent or temporary. Children in ICU who have been intubated may have temporary communication issues; where as children with CP or a degenerative musculoskeletal disease may have permanent communication needs.
question
What is augmentative and alternative communication
answer
The American Speech- Language -Hearing Association (ASHA) defines AAC as follows: " an area of clinical practice that attempts to compensate temporarily or permanently for the impairment and disability patterns of individuals with severe expressive disorders" (Angelo, 1997).
question
What is a multidisciplinary team
answer
Multidisciplinary Team Discipline specific roles are well defined Professionals work independently but recognize and value contributions of other disciplines Little or no interaction or ongoing communication occurs among professionals Treatment occurs in isolation for remediation of weaknesses Fragmentation of reporting occurs Overlap and gaps in services may occur and child may not be visualized as a whole
question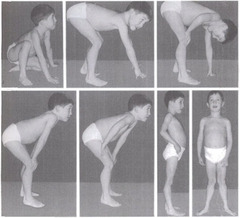
What is Gower's Sign

answer
Gower's sign evident by 4-7 years of age. When a child uses his hands in a walking motion up the thighs to assist while attempting to stand. (hip and knee extensors) Contractures develop in heel cords, TFL, hamstrings and hip flexors.
question
what are some intervention strategies for the child who suffered a fracture
answer
Crutch training or other compensatory strategies Use of a walker if under the age of 5 Strengthening exercises Balance training Endurance exercises ROM/stretching Splinting/casting Pain management
question
What might you advise a parent with a child that has osteogenesis imperfecta as far as diaper changes
answer
Avoid holding baby by ankles during diaper changes. Support head and trunk region and not on long bones of extremities Therapeutic Interventions Parent/family training & education Proper positioning How to safely transfer / handle child Avoid holding baby by ankles during diaper changes How to safely hold and support child Support at the head and trunk region and not on long bones of extremities
question
What is the acronym SMART in relation to pediatric PT
answer
S - Support Families with information, education, understanding , and resources M - Measure The effectiveness of programs through qualitative and quantitative outcome measures A- Ask The right questions. Determine the individual needs of the patient and family. This will decrease the tendency to make biasing generalizations R - Respect That individual differences between the child, family and therapist do occur and that they may be different from our own. T - Train Early on in the health care profession, and recognize that the training is lifelong and ongoing (Taken from page 10 - "Pediatric Physical Therapy" IV'th Edition by Jan Tecklin, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins)
question
Name this pathology The most common life-limiting genetic disorder affecting Caucasians and African-Americans to a much less degree A generalized disorder of endocrine glands producing High sweat electrolyte concentrations Pancreatic enzyme deficiency / GI issues including: Malabsorption Constipation GERD Growth failure due to malnutrition Chronic suppurative pulmonary disease which causes the greatest mortality Median age of survival now is approximately 36 years of age which is an improvement due to newer management strategies and techniques
answer
cystic fibrosis
question
What is not a great communication strategy for children a. engaging the child through play b. utilizing the senses in treatment c. Using a one-page handout in large font, so it's easy to read d. Using visual, auditory, tactile and olfactory techniques during treatment
answer
Engaging the child is critical Creativity is needed to keep the child engaged usually through play Utilizing the senses in treatment to engage the child Visual (seeing) Auditory (hearing) Tactile (touching) Olfactory (smelling)
question
Children who have family involvement clearly have better outcomes T/F
answer
True One must involve the parent as they are with the child most of the time shaping their environment and providing stimulation Parent training and education are crucial for carry over from the clinic to the home and community environments & success Examples of caregiver training Bed mobility skills & transfer techniques Safety skills with ambulation, balance & coordination activities Wheelchair management skills HEP supervision Evidence clearly shows that children who have family involvement clearly have better outcomes.
question
Name settings in which a PTA might treat a child
answer
Medical: Neonatal units Hospitals Rehabilitation centers Outpatient clinics Educational: Early intervention programs Schools Vocational programs
question
What is Part C of Idea
answer
Early Intervention
question
The grasp reflex is present at a. birth b. one month c. 4 months d. 6 months
answer
a. birth
question
What is not true about Part C of IDEA a. Provides services for children under 2 years of age b. Provides for family directed services c. Services occur in the child's natural settings if possible d. Utilizes the IFSP - Individualized Family Support Plan e. Identifies the strengths and needs of the child and family
answer
a. is not true...it's for children under 3! these are also true Sets forth a plan for implementation of needed services Identifies who, what, when, and specific goals and outcomes Services are provided in the child's natural environment (home, daycare, preschool, head-start, or other areas in which children without disabilities are normally seen
question
Postural reactions of infants with torticollis
answer
Upright tilt - NO response on non-involved side Ant./Post. Tilt - asymmetrical axial head to trunk alignment Prone - unable to lift head & rotate to clear airway Supine - ATNR develops toward rotated side only Protective extension Unable to abduct & flex at shoulder of involved side Unable to activate shoulder girdle of involved side for a supported weight bearing response Equilibrium response Difficulty with weight shifting through the pelvis with rotation in the t/s Difficulty with transferring weight with dissociation of the head, to shoulders, to trunk for correct timing & sequencing
question
T/F Boys are typically less flexible than girls
answer
True
question
Walking is normally achieved at what age a. 9 months b. 1 year c. 14 months d. 2 years
answer
b. 1 year
question
Name this pathology Usually self-limiting degeneration of femoral head which causes: Pain Decreased ROM Gait deviations More common in boys 4 to 7 years of age Typically occurs bilaterally 20% of the time Disturbance in blood supply to femoral head Can be the result of: Genetic predisposition Trauma Anatomical variation Generalized disorder of epiphyseal cartilage a. Osgood Schlatter's b. Legg-Calve' Perthes Disease c. DDH d. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
answer
Legg-Calve'-Perthes Disease (LCPD)
question
What does a baby typically use to explore the environment in the first few months? a. hands/fingers b. toes/feet c. eyes d. butt
answer
c. eyes
question
What is the grasp reflex
answer
Seen when a finger is pressed into baby's palm, baby's fingers automatically curl around the person's finger The reflex slowly integrates & allows the development of more mature grasping patterns At 4 months, babies will begin to more frequently reach out for toys with arms and hands The reach looks more like a swipe because the baby is learning how to control the arm and hand Over time, babies learn how to make smoother & coordinated movements with their arms and hands
question
Describe Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
answer
Hip deformity related to slippage of femoral epiphysis Etiology Hormonal influences Genetic predisposition (weak growth plates) Occurs in boys 2 to 3 times more than girls More common in: African-American and Polynesian cultures, children who are tall with delayed skeletal maturity, obese children; children between 9 and 16 years old Can occur bilaterally (25 to 30%) Can be precipitated by trauma
question
All about HIPAA
answer
Provides consumers with important privacy rights and protections with respect to their health information Recognizes circumstances arise where health information may need to be shared to ensure the patient receives the best treatment and for other important purposes, such as for the health and safety of the patient or others. The Rule is carefully balanced to allow uses and disclosures of information—including mental health information—for treatment and these other purposes with appropriate protections. HIPAA defers to state law to determine the age of majority and the rights of parents to act for a child in making health care decisions, and thus, the ability of the parent to act as the personal representative of the child for HIPAA purposes. See 45 CFR 164.502(g). Exceptional situations when parents would not be a minor's personal representative under the Privacy Rule. When a minor consents to care and the consent of the parent is not required under State or other applicable law. When a minor obtains care at the direction of a court or a person appointed by the court. When, and to the extent that, the parent agrees that the minor and the health care provider may have a confidential relationship. However, the parent may have access to the medical records of the minor related to this treatment when State or other applicable law requires or permits such parental access. Parental access would be denied when State or other law prohibits such access. If State or other applicable law is silent on a parent's right of access in these cases, the licensed health care provider may exercise his or her professional judgment to the extent allowed by law to grant or deny parental access to the minor's medical information. A provider may choose not to treat a parent as a personal representative when the provider reasonably believes, in his or her professional judgment, that the child has been or may be subjected to domestic violence, abuse or neglect, or that treating the parent as the child's personal representative could endanger the child.
question
Which of the following is not true about fractures in the pediatric population? a. common etiologic factors are trauma, child abuse, MVA, genetic (osteogenesis imperfecta b. healing takes 6-8 weeks c. fracture patterns are different than in adults due to bones being more flexible and porous d. Children's bones have thicker periosteum than adult bones
answer
b. healing takes 2-4 weeks due to better blood supply Fracture patterns are different due to bones that are more flexible, more porous, and less dense than adult bones Due to thicker periosteum than adults, there is better blood supply therefore healing is faster (2-4weeks) Etiology Trauma Child abuse MVA Genetic (Osteogenesis imperfecta)
question
What is not a common site for a child's bone fracture a. Distal radius b. Tibial shaft c. patella d. Clavicle e. Elbow
answer
c. patella
question
Your Pt presents with the following S and Sx...what do you suspect? Signs & Symptoms Unable to move upper arm Decreased grip strength Unable to externally rotate shoulder Partial or complete arm paralysis Loss of motor and sensory function Lateral proximal upper arm Clinical Manifestation Adduction Internal rotation Elbow extension Forearm pronation Wrist flexion
answer
Erb's Palsy
question
What is typically involved in the treatment of Erb's Palsy
answer
Treatment Rest 7-10 days to allow hemorrhage & edema to decrease Partial immobilization across upper abdomen Physical Therapy Maintain ROM Gentle passive exercises
question
Name S and Sx of bone fracture in the pediatric population
answer
Redness Swelling Pain Heat and deformity of extremity Muscle spasm Crying Not using extremity
question
Name therapeutic interventions in the pediatric population
answer
Crutch training or other compensatory strategies Use of a walker if under the age of 5 Strengthening exercises Balance training Endurance exercises ROM/stretching Splinting/casting Pain management
question
What is a normal progression from rollling to walking
answer
Rolling Creeping Pull to stand Standing Cruising Walking O'Sullivan
question
Describe Duchenne muscular dystrophy including the typical age of development
answer
Duchene MD begins with muscle loss in the pelvis, upper arms, and legs. 1st signs and symptoms of DMD develop between ages 2 to 5 years. Symptoms include: Difficulty walking, such as lateness in learning how to walk (older than 18 months), having a waddling gait, or walking on the toes or balls of the feet Difficulty running or jumping because of weakness in leg muscles Frequent falls, stumbling, and difficulty climbing stairs Difficulty standing from a lying or sitting position Reduced endurance Enlarged calf muscles Mild mental retardation (in some patients)
question
Your Pt presents with the following Signs and Symptoms Limp with ambulation Trendelenburg gait Mild groin pain, or medial thigh or knee Decreased ROM Most noted in hip abduction and internal rotation Leg length discrepancy Disuse atrophy from buttocks, calf, thigh Presents in 2 to 4 stages Initial - failure of femoral head to grow due to decreased blood supply Fragmentation Epiphysis appears fragmented Revascularization of the femoral head is occurring Re-ossification - bone density returns to normal with changes in shape and structure of femoral head and heck Healed stage - femoral head and neck retain deformity from the repair process What might they have
answer
Legg-Calve's-Perth Disease
question
What is not true regarding intervention for the Pt with scoliosis? a. electrical stimulation is not beneficial in preventing progression of scoliosis b. postural education is useful c. stretch the convex side of each curve d. stretch the concave side of each curve
answer
c. is not true Intervention Electrical stimulation, manipulation, and exercise programs are NOT beneficial in preventing the progression of scoliosis however, THEY SHOULD STAY ACTIVE AND FIT! Stretch tissues on the concave side of each curve Strengthen muscles on convex side Bracing Soft tissue mobilization Postural education
question
How is scoliosis treated in a child
answer
Treatment Child is observed at regular intervals Bracing Halts progression of curve Child typically has a 25-40 degree curvature Used if bones are still maturing TLSO—thoracic- lumbo- sacral orthosis is custom made and used to help maintain control of spinal posture. It helps to prevent further curve progression. The Boston brace is the ideal brace for idiopathic scoliosis. It is typically worn 18-23 hrs per day. Surgery Spinal fusion 40- 50 degree curvature Ensures curve does not get worse Will not straighten perfectly Stops growth of fused spine Brace must always be worn
question
Therapeutic interventions for DDH (continued
answer
Therapeutic Interventions (cont'd) Mobility training Gait, stairs, ramps, transfers Functional skill training Patient / parent training for all of the above Brace application Positioning (hips in flexion/abduction) Mechanics of lifting & carrying (maintaining position) Mobility training, home exercise program, etc. Provision of sensory input to promote normal experiences Consultation with teachers to assure mobility and inclusion on campus Promotion of other developmental skills
question
What signs and symptoms might you expect in a patient with the diagnosis slipped capital femoral epiphysis
answer
Intermittent limp Pain in: Groin Buttock Knee Thigh Antalgic gait Trendelenburg (weakened abductors on involved side) LE held in ER Decreased ROM
question
Pediatric ROM
answer
See chart on slide 47 of motor development ppt.
question
What is part of the treatment regimen for someone with SCFE
answer
Treatment Goals include: Minimize or reduce slippage of femoral head on neck Maintain hip ROM & function Minimize possible future degeneration Surgery usually required to pin the hip & prevent further slippage in mild to moderate cases Surgery - Femoral Varus Osteotomy Bed rest / traction may be used to reduce pain & spasm before surgery Therapeutic Interventions Providing appropriate ADs (wheelchair/ crutches) Gait & mobility training ROM (active & passive) Strengthening exercises Assessment of home environment to accommodate mobility and safety Family training for all of the above Consultation with teachers for campus mobility
question
What is the progression in genu development?
answer
Genu varus, genu valgum & the normal growth process Normal children are typically born with genu varus because of their flexed position in the uterus Increases until the age of 18 months, and then the legs straighten on their own. At age three or four, genu valgus develops straightens by about age six, leaving the normal to slightly knock-kneed adult alignment.
question
Automatic movements in babies occur in response to
answer
Occur in response to a stimuli & often involuntarily
question
What is the significance of automatic movements
answer
Significance: Initial appearance demonstrates functioning subcortical primitive centers These early reflexes eventually diminish reflecting maturation of the nervous system with increased control of the cortex
question
Name signs and symptoms of DMD
answer
Signs & Symptoms (cont'd) Skeletal deformities Scoliosis Lumbar lordosis Kyphosis Cardiac myopathy Mild to moderate progressive intellectual impairment Progressive gross motor skill impairment Difficulty walking, such as lateness in learning how to walk (older than 18 months), having a waddling gait, or walking on the toes or balls of the feet Difficulty running or jumping because of weakness in leg muscles Frequent falls, stumbling, and difficulty climbing stairs Difficulty standing from a lying or sitting position Reduced endurance Enlarged calf muscles Mild mental retardation (in some patients)
question
What are primitive reflexes
answer
Largely automatic, consistent, stereotypical A predictable motor response to a specific stimulus Emerge in the fetus & present at birth Provide an indication of the status of the CNS Circuitry is at the spinal cord or brain stem level Carried out w/o involvement of the cortex of the brain Serve some sort of movement purpose Slowly inhibited during the first year of life Ensure the baby's survival in early months of life & provide a training platform for many later voluntary skills Should have a short life-span & should be inhibited or controlled by higher centers of the brain Functionally, contribute to the development of emerging mobility
question
Factoids about scoliosis that is idiopathic
answer
Idiopathic - MOST common form No identifiable cause Strong evidence of condition being inherited Adolescence 10-16 years of age Seen more in girls than boys Progresses through growth spurt Does not usually progress through adults years
question
Name the diagnosis you expect Your Pt presents with the following Signs & Symptoms Related to motor functions: Lack of coordination Exaggerated reflexes Contractures Impaired mobility and strength Developmental delay Speech and swallowing difficulties Seizures Mental retardation The medical history shows that the Pt had an uneventful birth but suffered a TBI shortly after being born
answer
Cerebral Palsy
question
Therapeutic interventions for the Pt with arthrogyposis include
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Provision of UE & LE splints & orthotic devices To maintain or increase ROM Increase function Provision of body jackets and other braces To maintain neutral trunk posture Prevent progression of scoliosis Provision of assistive devises for mobility Canes walkers Standers Gait trainers Adapted strollers Wheelchairs / customized seating systems Therapeutic Interventions Functional & mobility training Rolling Bottom scooting Crawling Gait training Power wheelchair training Strengthening exercises through developmental activities Prone on elbows Sitting Reaching for toys Rolling Kneeling & standing Therapeutic Interventions Parent training / education Daily stretching Positioning ROM Developmental activities
question
How might your Pt with diplegia CP present include posture, position of hips/knees/ankles
answer
Signs & symptoms depend on distribution of motor involvement Both LEs Trunk and UEs to a lesser extent may be affected Standing posture (typical) Crouched with trunk flexion Adduction, & IR at both hips Knees are flexed Ankles are plantarflexed Typically child has spasticity / high tone in both LEs Trunk can also be affected
question
What are inhibition and facilitation techniques
answer
These techniques are specific movements or positioning of the child to decrease or increase the child's sensory motor responses to gravity, position in space, and movement -may include use of toys, hippotherapy etc.
question
Talk to me about ankle foot deformities in the pediatric population
answer
Etiology Congenital deformities In-utero positioning Neuromuscular disorders Myelomeningocoele Arthrogryposis Genetic disorders Classification Metatarsus adductus Talipes Equinovarus Calcaneovalgus
question
What is cerebral palsy dystonia also known as
answer
Mixed tone Fluctuating tone Athetosis
question
What are the 2 most common types of muscular dystrophy a. Guillain and Barre b. Duchenne and Parker c. Duchenne and Becker d. Duchenne and Bernard
answer
c. There are nine major types of MD affecting people of all ages, from infancy to middle age or later. The two most common types of MD that affect children are Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD). Both DMD and BMD affect boys almost exclusively; girls are rarely affected. MD is a sex-linked recessive disease. It typically passes from a mother (who has no symptoms) to her son.
question
What is cerebral palsy dystonia
answer
Characteristics More than one type of tone Can be mild to severe In infancy presents as low tone and changes with maturity Stringy, elastic muscles to the touch Child is usually thin due to extreme expenditure of energy Impaired speech as in hypertonia Poor stability in midline Writhing, athetoid" (worm-like) movements Constant movement within the extremes of available range creating excessive ROM in extreme cases Usually occurs throughout body including face Persistence of primitive reflexes preventing development of normal movement including: ATNR STNR TLR
question
What does gait look like for someone with cerebral palsy dystonia
answer
Gait is only possible to those who have enough stability to stand or walk Gait characterized by: Excessive movements Impaired balance Walker or crutches can be used, but for the most part these children use a wheelchair As children grow and become stronger, they can present as a challenge with management of transfers etc. to their caregivers / family.
question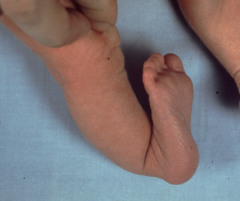
What does calcaneovalgus look like

answer
(dorsiflexion of foot with eversion or valgus of hind-foot)
question
What is involved in the treatment of muscular dystrophy
answer
Treatment No known successful cure has been developed yet; possibility of stem cell therapy Orthopedic devices ; surgery to address deformities Medications if necessary to address seizures and infections as needed Maintain strength and function as long as possible, while avoiding overexertion Equipment and adaptive device consultations, changing as disease progresses Team approach with OT and SLP
question
What AD would you recommend for a Pt with diplegic cerebral palsy and what gait pattern would you anticipate
answer
Gait (typical) Poor disassociation between trunk and legs Body rotates during gait UEs held in the "high guard" position for balance Assistive devices for mobility may include Loftstrand crutches Walker Wheelchair
question
Summary of purpose of primitive reflexes etc

answer
Serve some sort of movement purpose Slowly inhibited during the first year of life Ensure the baby's survival in early months of life & provide a training platform for many later voluntary skills Should have a short life-span & should be inhibited or controlled by higher centers of the brain Functionally, contribute to the development of emerging mobility See Supplemental Handout on Primitive Reflexes
question
Signs and symptoms of children with ankle/foot abnormalities
answer
Signs/Symptoms Obvious deformities Gait abnormalities Delay is gross motor and mobility skills Treatment Serial Casting Surgery
question
When stretching a pt who has ankle foot deformities, what should avoid while stretching the gastroc/solus
answer
Stretching To supplement splinting or bracing for minor deformities To counter the deformity CAUTION - it is important to stretch the gastrocnemius/soleus while avoiding the mid-foot ligaments
question
What are developmental delays
answer
There are many types of developmental delays. Some areas include problems with: language or speech vision movement -- motor skills social and emotional skills thinking -- cognitive skills
question
Name some interventions for the child with ankle/foot deformitites
answer
Sensory stimulation (when out of cast) To promote normal sensory sensitivity and proprioception awareness Promotes motor output Types of sensory input Rubbing with textured material Water play Sand play Massage Weight-bearing
question
You are treating a Pt who has cerebral palsy and resulting hypertonicity...what gait pattern do they likely have
answer
Children have difficulty with LE dissociation during gait. A scissoring gait pattern is often seen in these paients.
question
Talk to me about therapeutic interventions for the Pt who has cerebral palsy hypertonicity
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Stretching / ROM (prevention of contractures) Positioning Passive Active or active-assistive Positioning to inhibit strong reflexive extension Position hips and knees in > 90 degrees of flexion Use midline, symmetrical positioning to inhibit abnormal reflexes Therapeutic Interventions Use gentle, rhythmic movement to encourage controlled movement Promote active weight-bearing with aligned limbs & trunk to allow optimal independence in motor skills Use tone techniques that result in calming and relaxation
question
What are characteristics of cerebral palsy ataxia
answer
Ataxia is distributed throughout body Characteristics Poor balance Wide base of support and "high-guard arm position" during gait Tremors Low postural tone Poor visual tracking ROM usually normal or excessive due to low tone Hyporeflexia of DTRs, with weak primitive reflexes Muscles have a soft doughy feel to the touch
question
Mobility before stability
answer
Margaret Rood presented the concept of mobility before stability, followed by controlled mobility, followed by emergence of skill
question
Kinesiologic concepts
answer
Mobility = Movement Stability = Holding a posture Postural Control = relationship b/w mobility & stability Proximal Stability = Ability to stabilize in anti-gravity positions which leads to: Functional Mobility Symmetry = position/posture characterized by correspondence in relative position of parts on opposite sides of the body Present at birth to ~ 4 months Asymmetry = a lack of this correspondence Co-contraction = Balance between flexors & extensors allows for higher level of function
question
Common secondary complications from spina bifida
answer
Meningitis Hydrocephalous Orthopedic deformities: Club feet Bowed long bones Hip flexion contracture Hip dislocations Scoliosis / kyphosis Cleft palate Obesity Orthopedic cont'd. Osteoporosis Incontinence of bowel and bladder (above S2) Skin breakdown due to impaired sensation Learning problems Visual / perceptual problems Hyperverbal behavior Seizures Developmental delays Abnormal tone (usually flaccid below level of lesion) Tethered cord
question
What are therapeutic interventions for someone with cerebral palsy ataxia
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Encourage midline, symmetrical posture for maximal function Provide sensory input to encourage special orientation Tactile Proprioceptive Auditory Visual Therapeutic Interventions Try weighted vest or belts to increase proprioceptive feedback and improve balance Use aids to assist with balance Weighted walker, crutches, canes.
question
What are the 4 major components of motor learning
answer
"The study of how individuals acquire, modify, and retain motor memories so they can be used, reused, and modified during functional activities" (Umprhed, 2014). Four major points of motor learning Learning is a process of acquiring the capability for skilled action Learning results from practice or experience Learning can't be measured directly Learning produces relatively permanent changes in behavior Ex. Of functional motor memory patterns (rolling, sit to stand, walking , feeding, etc.) Learning isn't measured but inferred based on an individual's behavior Alterations of short-term movement patterns aren't considered motor learning. Motor learning occurs with emergence of interaction between the need to perform/complete a task and the environment in which the task should be performed
question
More on motor learning
answer
Can be modified to adapt to a situation based on sensory feedback ; conditions Generalization of skills occurs ; child is able to use previously learned skills to decrease time and effort needed to learn a needed task 3 stages of motor learning Cognitive stage/acquisition of a motor skill Associative stage/refinement Autonomous stage/retention
question
How is hippotherapy useful to the pediatric population
answer
The use of a horse for habituation or rehabilitation Different from therapeutic riding which focuses on riding skills for disabled riders Defined as the use of a horse as a tool to address impairments, functional limitations, and disabilities in patients with neuro-musculo-skeletal dysfunction The mobile surface of the horse is used to: Promote relaxation Increased ROM Strengthening Proximal control Usually no saddle is used but rather a blanket to promote the sensation of warmth from the animal to the child The therapist must be trained in this specialty Part of the treatment may actually include activities relating to the care of the horse to promote: Cognitive ability Following commands Sequencing activities Memory Psychosocial element Sensory-motor stimulation
question
What is not an indication for hippotherapy? a. abnormal tone b. impaired balance c. heterotrophic ossification d. flexible postural asymmetries e. abnormal reflexes
answer
c. The following are Precautions / Possible Contraindications Abnormal fatigue Allergies Arnold Chiari Malformation Cardiac condition Diabetes Heterotrophic ossification Precautions / Possible Contraindications (cont'd) Hip Dislocation Subluxation Dysplasia with significant restriction of hip abduction History of breakdown of grafting over bony/weight -bearing areas Any child 2-4 yrs of age Hydrocephalus Precautions /Possible Contraindications (cont'd) Incontinence Osteoporosis Peripheral vascular disease Recent surgery Recent dorsal rhizotomy Sensory deficits Shunts Spinal fusion Substance abuse Tethered cord Contraindications Orthopedic: Acute herniated disc Atlanto-axial instability Coxal arthrosis (degeneration of the hip joint) Excessive kyphosis or lordosis Hemivertebrae Severe osteoporosis Contraindications Orthopedic: (cont'd) Pathologic fractures (osteogenesis imperfecta) Spondylolisthesis Structural scoliosis greater than 30 degrees Unstable spine Medical: Acute arthritis Acute multiple sclerosis Agitation with severe confusion
question
Fetus is considered viable at ______ weeks
answer
22-23 weeks
question
What are indications for hippotherapy
answer
Indications Abnormal tone Abnormal reflexes Flexible postural asymmetries Impaired postural control Impaired balance Impaired coordination Flexible proximal malalignment
question
A child must develop levels of competency working against gravity to gain higher level functional motor skill acquisition When tone is insufficient or too high, a child is unable to establish a good foundation for postural control against gravity True or False
answer
True
question
Children with CP may have secondary impairments...those might include
answer
Mental retardation (50 - 75%) Seizures (30%) Hearing impairment (10%) Visual impairment (50%) Other sensory deficits Speech/language deficits or delays (50%) Visual-motor deficits & perceptual problems Oral-motor disorders Behavioral disorders Orthopedic disorders
question
Discuss interventions for someone with cerebral palsy dystonia
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Encourage midline, symmetrical posture to minimize effects of abnormal reflexes Use gentle, rhythmic movements to encourage controlled motor output Allow abnormal movement if they contribute to functional skills Encourage child to problem solve motor difficulties
question
Treatment interventions for a Pt with cerebral palsy
answer
Medications based upon characteristic of the disease Surgery for tissue release, dorsal rhizotomy, intrathecal baclofen Team approach including therapists, physicians, and teachers is very important Goal is to maximize independence and potential through strengthening, stretching, and mobility with use of assistive devices if appropriate.
question
Optimization of function in a Pt with CP may include all the following except a. Elongate shortened muscle groups b. Promote static movement in place of dynamic c. Inhibit primitive reflexes d. Facilitate optimal muscle tone e. Promote weight-bearing
answer
b. You should promote dynamic movment
question
What medications and surgical treatment might you see in a Pt that has the diagnosis of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
answer
Treatment Medications NSAIDS Slow acting anti-rheumatic drugs (SAARDS) Corticosteroids Immunosuppressive and cytotoxic agents Cyclosporing or methotrexate Surgical treatment: Synovectomy Soft tissue releases Osteotomy Joint fusion Total joint replacement
question
Righting Reaction (a type of postural reaction)
answer
Thought to be mediated at midbrain level in response to signaling from several different sensory receptors including: Proprioceptors, cutaneous receptors, eyes and labyrinth of the ears Realigns the head or trunk with each other or with an outside stimulus 1) Neck Righting, 2) Head Righting, 3) Trunk Righting Named to describe the body part responsible for the realignment & often mechanism for sending the signal 1) Optical Head Righting, 2) Labyrinthine Head Righting Stimulus eliciting the response is the effect of gravity or position of the eyes regarding gravity
question
Equilibrium Reactions
answer
Adjust for change in the body's orientation in space Comprised of righting reactions of head ; trunk Protective extension responses of the extremities Include: Tilting reaction Protective responses in sitting ; standing
question
Talk to me about specialized equipment for the Pt with cerebral palsy
answer
Utilization of specialized equipment for positioning and function (adaptive) Maximize function Visual access Use of UEs for functional tasks Mobility Attention To maximize positioning for: Symmetry Posture Alignment of trunk / pelvis / extremities Head in midline to minimize persistent primitive reflexes Support - which is at the level necessary to achieve stability and withdrawn or lessened as the child gains strength and control.
question
Pediatric TBI interventions
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Heighten level of arousal through sensory stimulation Olfactory Gustatory Tactile Auditory Visual Proprioceptive Educate family how to provide sensory stimulation Must be age appropriate stimulus
question
Describe the classifications of JRA oligoarticular/pauciarticular Polyarticular Systemic
answer
Classifications: Oligo-articular (5 joints) Systemic oligoarticular or pauciarticular: affected jts. usually have asymmetrical distribution Polyarticular: jts. Have symmetrical distribution, slow onset ; gradual jt. Pain Systemic: acute onset with high fever, rash on trunk and proximal extremities, possible organ inflammation, can cause disability
question
Interventions for spina bifida
answer
Interventions Family education: Prevention - minimization of deformities Positioning to prevent contractures of hips, knees, and ankles Prevention - fractures Proper handling techniques especially for support of lower extremities due to muscle flaccidity and osteoporosis Therapeutic exercise program to promote development Family instruction in the care of assistive devices and therapeutic intervention for promotion of optimal development in all domains
question
Name some interventions for DMD
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Maintain ROM through: Positioning Splinting stretching Maintain ambulation ; standing skills as long as possible through: Use of assistive devices Splinting, bracing, use of crutches, standing frames, dynamic standers Participation in fun and motivating activities in standing /weight bearing position Maintain functional skills including mobility as long as possible through: Use of assistive devices Power wheelchairs with custom seating Augmentative and alternative communication devices Assistive UE movement devices
question
Patients with spina bifida Meningocele and myelomeningocele are treated surgically and what does PT do to help regain function and improve quality of life for these individuals
answer
Surgically closed after birth Defects can be seen in ambulation, bowel or bladder function PT: developmental skills, strengthening and adaptation using mms that are innervated; possible adaptive equipment or wheelchairs Therapeutic Interventions Maximization of functional skills Strengthening through play ROM / Stretching PRECAUTION - high risk for fractures in patients with paralysis, so stretching should not be aggressive. Provide / fit / teach use of assistive devices Upright positioning devices Cart or scooter for floor mobility Static standers Dynamic standers Wheelchairs with customized seating systems Power mobility
question
What is ADHD
answer
"Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD is a common childhood illness that can be treated. It is a health condition involving biologically active substances in the brain. Studies show that ADHD may affect certain areas of the brain that allow us to solve problems, plan ahead, understand others' actions, and control our impulses." Inattentive children: bore quickly with activities, have difficulty organizing and completing a task or learning something new. They oftentimes forgetful (i.e. not write down a school assignment or bring a book home). Completing certain tasks can be a huge challenge. Hyperactive children: constantly move around, always fidget, squirm, touch or play with whatever is around, or talk continually. Some children wiggle their feet or tap their fingers, and can't sit still in the classroom. An adolescent or adult may appear restless and need to stay constantly busy. Impulsive children often blurt out comments without thinking, display emotions without restraint, and fail to consider the consequences of their actions. They are impatient and dislikes sharing and taking turns with peers. Impulsive adolescents tend to make choices that have a small immediate payoff rather than working toward larger delayed rewards. One of the most common health disorders Affects 5 to 10% of children in the United States Hallmark common symptoms inattention—easily distractible, careless, forgetful, difficulty completing tasks hyperactivity—constantly in motion, restless impulsivity—impatient, lack of restraint These symptoms must be expressed in multiple settings and across numerous functional domains, thus demonstrating the pervasiveness of this condition.
question
Interventions for Pt with spina bifida
answer
Interventions Fitting and use of proper orthotic devices to provide trunk and LE stability to allow greater function and mobility Body jacket Reciprocating gait orthosis HKAFO KAFO AFO Facilitation of functional motor development
question
Name therapeutic interventions for the Pt with JRA
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Splinting to maintain joint ROM Hand & finger extension Knee extension Stretching to maintain soft tissue flexibility Pain control measures Modalities / Physical Agents US *TENS Cold (ice packs) *Moist heat Paraffin Baths *Heat lamps Hyro-therapy with warm water Contrast heat / cold Therapeutic Interventions Construct or provide appropriate orthotic devices Splints Orthotics Body jackets for protection Devices to promote weight bearing and to prevent deformity ROM Positioning Active stretching SAFETY -- AVOID aggressive passive stretching due to high risk of joint subluxation Therapeutic Interventions (Cont'd) Strength and endurance activities / training Education regarding rest and avoidance of joint trauma especially during flares Developmental mobility training - (depending on age and skill achievement) transitions, standing, cruising, walking Patient/family training for all of the above Functional skills Mobility Self-help skills
question
Interventions for Pt with Down Syndrome
answer
Intervention PT can help improve movement with gross and fine motor activities ; activities of daily living PT can help to: Improve strength Improve developmental skills Improve balance and coordination Improve overall physical fitness PT can help assist with additional complications of DS (i.e. developmental delay, obesity, and lower levels of heart or cardiovascular fitness) These children typically function 18-24 months behind age level with a gradual decrease of skills in both static and dynamic balance tests
question
What are some considerations for exercise with the pediatric patient that has asthma
answer
Exercise Recommendations Low impact (aerobics, weight training, stationary bike) Ensure environment is trigger free where exercise is conducted (avoid cold, pollution, etc.) Monitor FEV1/FV ratio before, during, and after physical activity decrease of 10% requires slowing activity drop of 15-20% from exercise Tell patient to take prescription meds properly
question
Name some torticollis impairments
answer
Shortened and fibrosed SCM Weakened contralateral SCM Constantly over lengthened position Disuse 2° pain with rotating or laterally flexing to contralateral side Shortened splenius capitis ; upper trapezius Right tort = left splenius cap short ; right upper trap Can appear as a hemi with visual ; extremity neglect Visually tracking in only 1 direction Plagiocephaly contralateral to involved SCM Since back to sleep campaign in mid 90's - increase in plagiocephaly from 1/300 births to 1/60 Facial asymmetries/ Hemihypoplasia Cervical and thoracic scoliosis Attempts at child bringing his eyes to a horizontal position when cervical motion is limited Found in 5.8% of 85 children after long-term follow-up by Binder et al Right tort = c/s scoliosis convex towards left Developmental Delays
question
Signs and symptoms of cystic fibrosis
answer
Signs & Symptoms (can vary) Productive cough Abnormally frequent and large stools Failure to thrive Recurrent pneumonias Rectal prolapse Nasal polyposis (polyps in the nose) Clubbing of the digits
question
What interventions do expect for the patient with cystic fibrosis
answer
Therapeutic Interventions Provision of and instruction in airway clearance techniques including: Traditional postural drainage techniques (depending on lobe involvement) Diaphragmatic breathing Chest percussion Vibration Positioning Suctioning (if needed) Interventions (cont'd) Instruction for breathing exercises Diaphragmatic excursion Maximal inspiration Forced expiratory techniques (lower lobes) Secretion removal Expiratory ; inspiratory muscle strengthening using simple handheld devices to maintain / increase respiratory muscle strength Interventions Conditioning exercises include: Walking Jogging Cycling Swimming Appropriate sports activities Strengthening exercises ROM - emphasis on thorax ; shoulder girdle Interventions Therapeutic Exercise Considerations Parent -child education: children should participate in vigorous exercise as it is beneficial if they have good lung function Not appropriate for those with advanced lung disease Due to oxygen desaturation, carbon dioxide retention O2 supplementation may be used for those with more advanced disease during exercise to: Be able to exercise for a longer duration Promote higher level of oxygen consumption Decrease 02 desaturation
question
Name this pathology Reversible obstructive lung disease Inflammation and increased muscle reaction of the airway to various stimuli Chronic condition with acute exacerbations Occurs in families 80% of individuals report allergic rhinitis Develop when predisposed people are infected by viruses or exposed to pollutants/allergens
answer
Asthma Extrinsic (allergic)-result of an allergy to specific triggers: usually food or environmental allergens (i.e. smoke, mold, pollen) Intrinsic (non allergic)-no known allergic cause, has an adult onset usually 40yrs of age. Most often secondary to chronic bronchi, sinus, adenoid infections. Categorized in 2 main types based causative factors: Extrinsic (allergic) asthma Result of an allergy to specific triggers: usually food or environmental allergens (i.e. smoke, mold, pollen) Intrinsic (non allergic) asthma No known allergic cause, has an adult onset usually 40yrs of age. Most often secondary to chronic bronchi, sinus, adenoid infections Other categories: Adult-onset Exercised induced Aspirin sensitive Occupational Narrowing of airways, related to exposure in the workplace specific to airborne dust gas, acid, mold, etc. Asperigillus-hypersensitive Risk Factors Environment Hygiene hypothesis-lack of exposure to stimulants or too much exposure to cleaning agents Can occur at any age, typically occurs for first time before age 5 Antibiotic exposure during infancy Prematurity Areas of poverty Obesity Overcrowded living areas with repeated exposure to: Cigarette smoke, dust, cockroaches, and mold **Early exposure to pets, early infections, childcare, may protect against allergic sensitization **3 times more common in and more severe in boys before puberty and evens out in genders afterwards **One study revealed that 32% of obese children and 3% of kids with normal BMI have reduced respiratory function
question
Kinesio concepts WB Dissociation etc.
answer
Weight bearing (WB) Stability in postures permits WB; WB assists in development of stability Weight shifting = one body part stabilizes another part being un-weighted enough to move Rotation/Dissociation = balanced control of flexors and extensors ; dissociation between body segments Dissociation - ability to move one body part separate from another associated body part
question
Treatment of children with ASD
answer
Treatment/Intervention Physical therapists can work with children, families, and educational teams to help children: Improve participation in daily routines in the home and educational environment Acquire new motor skills Develop better coordination and posture Improve reciprocal play skills, such as throwing and catching a ball with another person Develop motor imitation skills Increase fitness and endurance
question
What is Osgood Schlatter's
answer
Epiphysis of the tibial Tuberosity irritated by repetitive running, jumping, pulling of the patellar tendon on the tibial tuberosity Individual must rest. Limit activities.
question
ADHD Treatment Interventions
answer
Treatment/Intervention Provide support to help increase attention span, control their behavior, slow down, and improve self-esteem Establish regular exercise routine Provide family education Encourage child to have a healthy diet Child may also have Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD)in conjunction with ADHD—PT will need to address *** With DCD-children appear clumsy, awkward, have difficulty with everyday activities (i.e. jumping, running, bicycling, writing) ---PT will address: Strength, balance/ coordination, body awareness problems and help improve ADLs and quality of life
question
If a child has little league elbow, what would you advise
answer
rest / limit activities
question
What is aquatic therapy useful for as far as the pediatric population
answer
Warm water therapy is excellent for hypertonic muscular condition Excellent medium for proprioception stimulation Enhanced ability to range joints in fluid patterns of motion Environment that encourages active movement without gravity restriction Proper flotation devices provide a safe environment to challenge functional movement behavior Reaching Grasping Squatting - lunging - walking
question
What variables influence development
answer
Motivation Muscle strength Body weight Level of arousal Complexity & maturation of neural networks Environmental forces
question
Gait considerations in peds
answer
Physical therapy for children with gait problems focuses on implementing mobility and strengthening programs, overseeing orthotic use through open communication with their physician and orthotist, balance training, and gait training



