Ultrasound ch 9 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
attenuation is the result of
answer
absorption, reflection, and refraction, with absorption accounting for about 50% of attenuation. Attenuation is greatest in tissues with a high collagen content and with the use of high ultrasound frequencies. Repulsion is not a cause of ultrasound attenuation.
question
what are the ideal treatment parameters for using ultrasound for teating pressure ulcers?
answer
3 MHz, 0.5 to 1.0 W/cm², pulsed 20% Overall, the studies published so far indicate that pulsed ultrasound may facilitate wound healing, but good evidence of this effect is lacking. The treatment parameters that have been found to be effective for this application are 20% duty cycle, 0.8 to 1.0 W/cm² intensity, 3 MHz frequency, for 5 to 10 minutes.
question
For optimal effect, when should stretching be applied
answer
During heating by ultrasound and be maintained for 5 to 10 minutes after ultrasound application while the tissue is cooling
question
pulsed ultrasound (effect on temperature)
answer
minimizes temperature increase (intensity and frequency stays the same)
question
when using ultrasound for its thermal effects what is the temperature that you should try to achieve?
answer
The minimal therapeutic level is 40° C and should not exceed 45° C.
question
should ultrasound be applied on children?
answer
Although controversial, it is recommended that high-dose ultrasound not be applied over growing epiphyseal plates. Because the age of epiphyseal closure varies, radiographic evaluation rather than age should be used to determine if epiphyseal closure is complete.
question
what are the ideal treatment parameters for using ultrasound before stretching shortened tissues?
answer
1 to 2 W/cm², continuous Continuous ultrasound is the only one that generates thermal effects such as increased tissue extensibility. Pulsed ultrasound has primarily nonthermal effects.
question
To penetrate deeper tissue using ultrasound
answer
Use a lower frequency The lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength of the sound waves, the more readily ultrasound penetrates deeper into the tissue. With a higher frequency, the sound waves have a shorter wavelength and are absorbed more superficially.
question
all of the following are desired effects of ultrasound
answer
increased cell membrane permeability, increased collagen production, increased mast cell degranulation.
question
blood stasis`
answer
adverse effect of ultrasound, as is infection or cross-contamination between patients.
question
how is drug penetration is increased
answer
by ultrasound-induced cavitation and enhanced skin permeability. Since phonophoresis causes drugs to become systemic, a therapist must know what other drugs a patient is taking before treating with phonophoresis.
question
all of the following statements are true about phonophoresis
answer
Hydrocortisone preparations tend to transmit ultrasound poorly a physician must know what other drugs a patient is taking in order to treat with phonophoresis drugs delivered via phonophoresis become systemic
question
depth of penetration and temperature
answer
1 MHz frequency will penetrate deeper than 3 MHz although temperature elevation will be less With 3 MHz ultrasound, as compared to 1 MHz ultrasound, and in tissues with higher collagen content, the depth of penetration is lower, although the maximum temperature achieved is higher. One MHz frequency ultrasound is considered best for heating tissues up to 5 cm deep, and 3 MHz frequency is considered best for heating tissues only 1 to 2 cm deep.
question
how do you determine if ultrasound is reaching therapeutic levels?
answer
Use of appropriate settings does not prove effectiveness. The best way to determine if ultrasound is reaching therapeutic levels is to have a baseline for desired outcome and measure it objectively following treatment. Subjective reporting of sensations is another, more subjective way, of monitoring for effect. Using only one therapy at a time allows that therapy to be observed in a controlled setting.
question
ERA
answer
The effective radiating area is always smaller than the area of the treatment head because the crystal does not vibrate uniformly and must be smaller than the size of the outside of the sound head.
question
Non-thermal effects of ultrasound are believed to be caused by
answer
stable cavitation, microstreaming, and acoustic streaming. Increased tissue extensibility is a thermal effect.
question
what type of heat transfer happens with ultrasound
answer
Ultrasound generates thermal effects indirectly through the conversion of kinetic energy in sound waves into frictional energy within deep tissues, releasing heat in the process. In contrast, conduction and convection transfer heat from one material of higher temperature directly to a material of lower temperature.
question
what is the most common adverse effect of ultrasound
answer
Although adverse effects are rare, the most common adverse effect is a burn. To minimize the risk of burning a patient, always move the ultrasound head and do not apply thermal-level ultrasound to areas with impaired circulation or sensation. Reduce the ultrasound intensity in areas with superficial bone or if the patient complains of any increase in discomfort with the application of ultrasound.
question
what are the ideal treatment parameters for ultrasound to treat inflammation
answer
It is recommended that ultrasound be applied in a pulsed mode at a low intensity (0.5 to 1.0 W/cm²) during the acute phase of tendon inflammation to optimize healing and minimize the risk of aggravating the condition.
question
what are the ideal treatment parameters of ultrasound to treat pain via stimulation of cutaneous thermal receptors?
answer
Only continuous ultrasound provides significant thermal effects to activate thermoreceptors. The treatment parameters that have been found to be most effective for control of pain are continuous ultrasound at 0.5 to 2.0 W/cm² intensity and 1.5 MHz frequency.
question
what dose of ultrasound should be used for fracture healing?
answer
Numerous studies over the last 25 or more years have demonstrated that low-dose ultrasound can reduce the fracture healing time in animals and humans. There is now a fixed dose ultrasound device available for home use by patients to promote fracture healing.
question
what frequency of ultrasound should be used to penetrate deeper tissues
answer
1 MHz The lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength of the sound waves, the more readily ultrasound penetrates deeper into the tissue. With a higher frequency, the sound waves have a shorter wavelength and are absorbed more superficially.
question
How many hertz are in ultrasound?
answer
20,000 Hz. Just over what we can hear.
question
intensity is measured in
answer
W/cm ^2
question
frequency
answer
MHz
question
duty cycle
answer
percentages (default is 20%)
question
ERA
answer
effective radiating area cm^2 is usually smaller than the head or transducer
question
BNR
answer
Beam Nonuniformity Ratio - difference between spatial peak intensity (top) and spatial average intensity (bottom) sort of like margin of error. ideally 3:1 BNR.
question
Thermal effects of ultrasound
answer
-caused by continuous waves -increased tissue temperature due to absorption coefficient (affected by tissue type), Intensity, frequency, -same properties as other heating agents : increase vascularization, healing, pain relief, tissue extensibility.
question
Nonthermal effects of ultrasound
answer
-does not retain heat because of duty cycles -due to cavitation, microstreaming, acoustic streaming - increased intracellular calcium -promotes cell function
question
indications for ultrasound
answer
soft tissue shortening, pain control, dermal ulcers, surgical skin incisions, tendon and ligament injuries, bone fractures, carpal tunner syndrome, phonophoresis
question
Ultrasound effects on inflammation
answer
-enhance reabsorption of interstitial fluids, -increase intracellular calcium levels, -promote macrophage responsiveness and fibroblast activity in acute inflammation -non-thermal mechanisms increase tissue permeability
question
Ultrasound effects on pain
answer
-raises pain threshold - thermal properties -completing stimulus - gate theory - postulated selective absorption by Ad and C fibers (change nerve transmission possibly due to changes in sodium channel function)
question
ultrasound effects on subacute inflammatory edema
answer
thermal US is contraindicated if edema is due to inflammation (okay if arterial or lymphatic) -reduces old residual edema with thermal and nonthermal properties
question
ultrasound effects on healing open wounds
answer
thermal effects increase blood flow, and metabolism non-thermal effects - increase activity in tissue repair cells (fibroblasts and satellite cells), protein synthesis
question
ultrasound effects on tendon repair
answer
Timing is important- best results are achieved immediately after repair or injury - prolongued use has no effect (>5weeks) non-thermal application is most effective in the acute stage thermal effects are most effective if they're combined with stretching in the chronic stage or with presence of scar tissue
question
ultrasound effects on extensibility of collagenous tissue
answer
-enhanced due to thermal effects -postulated relaxation of peptide bonds -selective absorption by collagen tissue -sustained stretch during US and for 5-10 min post - CW 3MHz, .5-1.0 W/cm^2 -CW 1MHz, 1.5 - 2.5 E/cm^2
question
intensity and frequency
answer
are inversely proportional if frequency is high, intensity must be low if frequency is low, intensity must be high
question
Contraindications for the use of ultrasound
answer
malignancy, pregnancy, CNS tissue (not even crossing over). joint cement, plastic, pacemaker, thormbophlebitis, eyes and reproductive organs
question
precautions for the use of ultrasound
answer
acute inflammation, epiphyseal plates (must be fully closed), fractures, breast implants,
question
Adverse effects of ultrasound
answer
burns (always move the sound head), standing waves (interaction of oncoming ultrasound waves with those reflected back from a tissue interface- creates risk of tissue cavitation)- cause blood stasis (keep head moving,)c cross-contamination/infection
question
application technique
answer
evaluate the patient determine appropriateness and safety apply ultrasound transmission medium, select sound head, select treatment parameters (som US machines will only let you do this if the head is already in contact with the skin circling), turn on machine, move sound head, document
question
treatment parameters
answer
area treated ultrasound frequency ultrasound intensity ultrasound duty cycle treatment duration if underwater response to intervention
question
treatment for soft tissue shortening
answer
Thermal - CW (100%)- -3 MHz (1-2cm) - .5 W/cm^2 -5-10 min/2 x ERA -1MHz (5cm) -1.5 - 2.0 W/cm^2 -5-10 min/2 x ERA
question
treatment for delayed tissue healing and prolongued inflammation
answer
Nonthermal - PW (20%) -3MHz (1-2cm) -.5- 1.00 W/cm^2 -5-10 min/2 x ERA -1MHz (5cm) -.5 - 1.00 W/cm^2 -5-10 min/2 x ERA
question
treatment for fracture healing
answer
Nonthermal - PW (20%) -3MHz (1-2cm) -.2 W/cm^2 -5-10 min/2 x ERA -1MHz (5cm) -.2W/cm^2 -5-10 min/2 x ERA
question
dosage of ultrasound depends on
answer
-intensity and time -time depends on size of treatment area -for thermal at least 3-5 minutes (consider frequency) - maximum physiological effects are achieved in 10 min. - patient should feel mild warmth within 2-3 min (sooner if using 3MHz)
question
number of treatments of ultrasound
answer
depends on goals should have some detectable effect within 1 to 3 treatments -total RX duration depends on goals (wound healing takes longer) -thermal should only be used for subacute or chronic -nonthermal can be used for acute daily is common -no research for phonophoresis?
question
Frequency considerations (1 MHz vs 3 MHz)
answer
-depth of penetration -temperature increase -3 MHz is absorbed 3x faster than 1 MHz -3 MHZ has faster thermal effects more superficially -Greater heat effects in a smaller volume of tissue because it does not penetrate as far). -Studies have shown it takes avg. 3 min for significant -temp rise w 3 MHz at 2.0 W/cm^2 (10 for 1MHz) -use lower intensities when using 3 MHz
question
Target intensities
answer
-chronicity of condition -goal of RX -thickness of tissue -1 MHz: 1.5 - 2.0 W/cm^2 -3 MHz: .5 W/cm^2 (may increase intensity) -ultimate determinant is patient feedback -non-thermal US requires prescribed intensity
question
Pulsed Wave protocols
answer
PW- <50% duty cycle usually will not produce heat but may be intensity dependent (10 - 20% will not produce heat) -stimulates tissue regeneration (ulcers) -stimulates repair process (tendon repair) -increase metabolism (wounds) -increase membrane permeability (acute inflammation, phonophoresis) For wounds: - 3 MHz: .8 - 1.0 W/cm2 : 20% -brief durations 30 - 60 s/ERA (5-10 min total) -daily or every other day -wound bed (gel sheet) or periwound
question
Continuous wave to raise tissue temperature
answer
-will have non-thermal effects with both -ntensities of .5 to .8 W/cm^2 may not produce heat -extensibility of collagen structures (prior to stretching) -decrease joint stiffness (OA) -Increase blood flow (spasm, healing) -decrease pain (raise pain threshold) -produce mild inflammatory response like other thermal agents
question
US for tendon rupture repair
answer
-Frequency depending on depth (1 for deep 3 for shallow) -continued or pulsed depends on the stage of healing - .5 - 2.5 W/cm^2 3-5 min (because area is small)
question
acoustic streaming
answer
steady circular flow of cellular fluids induced by ultrasound -larger in scale than microstreaming -alters cellular activity by transporting material from one part of the ultrasound field to the other
question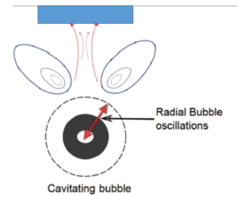
microstreaming

answer
microscale eddying that takes place near any small vibrating object (around gas bubbles set into oscilation by cavitation)
question
cavitation
answer
formation, pulsation, growth, of gas bubbles they get smaller during compression and larger during rarefaction. if cavitation is stable - bubbles do not burst if cavitation is unstable - bubbles grow over a # of cycles and suddenly implode -may alter cell membrane permeability
question
ultrasound definiiton
answer
high frequency sound wave that can be described by intensity, frquency, duty cycle, effective radiating area and beam uniformity ratio. (heats smaller deeper areas than superficial heating agents) amont of energy being delivered depends on time of application
question
duty cycle
answer
proportion of treatment time that the ultrasound is on 20% - 2 milliseconds on 8 milliseconds off continuous is on 100% of the time
question
BNR
answer
peak intensity of the ultrasound output over the area of the transducer to the average intensity of the ultrasound output over the area of the transducer ratio. 3:1 is acceptable- means that some areas penetrate up to 3 cm even if we chose only 1.
question
attenuation
answer
It is the result of absorption, reflection and refraction. -Higher in tissues with high collagen content and with the use of high frequencies.
question
absorption coefficient
answer
materials with high AC allow heat to travel deeper but the heat is not as spread out (opposite for low AC) - the same amount of energy is being deposited but the absorption coefficient alters the distribution
question
temperature that yields the fastest rate of heating
answer
25 C of 77F Applying ultrasound in water cools the superficial skin applying ice before ultrasound may cause loss of sensation so it should be done cautiously
question
phonophoresis
answer
can be done with both thermal and non-thermal provides high drug concentration at delivery site avoids gastric irritation and first pass metabolism by liver should be avoided if patient is already taking medication by another means



