Surgery: The Breast – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion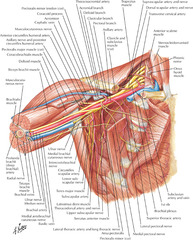
Name the boundaries of the axilla for dissection. a. superior boundary b. posterior boundary c. lateral boundary d. medial boundary

answer
a. axillary vein b. long thoracic nerve c. latissiumus dorsi muscle d. lateral to, deep to, or medial to pectoral minor muscle, depending on level of nodes taken
question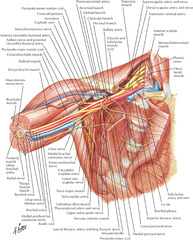
What 4 nerves must the surgeon be aware of during an axillary dissection?

answer
long thoracic nerve thoracodorsal nerve medial pectoral nerve lateral pectoral nerve
question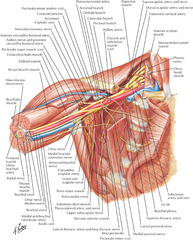
What nerve courses along the lateral chest wall in the midaxillary line, on the serratus anterior muscle? What does it innervate?

answer
long thoracic nerve innervates serratus anterior muscle
question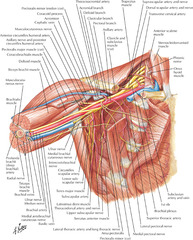
What nerve courses lateral to the long thoracic nerve, on the latissimus dorsi muscle? What does it innervate?

answer
thoracodorsal nerve innervates latissimus dorsi muscle
question
What nerve runs LATERAL to or through the pectoral minor muscle, actually lateral to the lateral pectoral nerve? What does it innervate?
answer
medial pectoral nerve • innervates the pectoral minor and pectoral major muscles
question
What nerve runs MEDIAL to the medial pectoral nerve? What does it innervate?
answer
lateral pectoral nerve • innervates the pectoral major • names describe orientation from the brachial plexus
question
Damage to which nerve causes "winged scapula"?
answer
long thoracic nerve "winged scapula" is the name of the deformity if you cut the long thoracic nerve in the axillary
question
What is the name of the cutaneous nerve that crosses the axilla in a transverse fashion?
answer
intercostobrachial nerve • Many surgeons try to preserve this nerve.
question
What is the name of the large vein that marks the upper limit of the axilla?
answer
axillary vein
question
What is the lymphatic drainage of the breast (2)?
answer
lateral - axillary lymph nodes medial - parasternal nodes that run with internal mammary artery
question
What are the levels of the axillary lymph nodes? a. Level I (low) b. Level II (middle) c. Level III (high)
answer
a. lateral to pectoral minor b. deep to pectoral minor c. medial to pectoral minor In breast cancer, a higher level of involvement has a worse prognosis, but the level of involvement is less important than the # of positive nodes
question
What nodes are located between the pectoralis major and minor muscles?
answer
Rotter's nodes • not usually removed unless they are enlarged or feel suspicious intraoperatively
question
What are the suspensory breast ligaments called?
answer
Cooper's ligaments
question
What is the mammary "milk line"?
answer
the embryological line from shoulder to thigh where "supernumerary" breast areolar and/or nipples can be found
question
What is the name of the breast tissue that tapers into the axilla?
answer
"tail of Spence"
question
Which hormone is mainly responsible for breast milk production?
answer
prolactin
question
What is the lifetime risk of breast cancer (the incidence)? What percentage of women with breast cancer have no known risk factor?
answer
12% 75%
question
What are the major breast cancer susceptibility genes (2)?
answer
BRCA 1 BRCA 2
question
What is the "triad of error" for misdiagnosed breast cancer?
answer
more than 75% of cases of misdiagnosed breast cancer have these characteristics: 1. age < 45 years 2. self-diagnosed mass 3. negative mammogram
question
What are the history risk factors for breast cancer?
answer
"NAACP" Nulliparity Age at menarche (younger than 13) Age at menopause (older than 55) Cancer of the breast (in self or family) Pregnancy with first child (older than 30)
question
What are the physical/anatomic risk factors for breast cancer?
answer
"CHAFED LIPS" Cancer in the breast Hyperplasia Atypical hyperplasia Female Elderly DCIS LCIS Inherited genes (BRCA) Papilloma Sclerosing adenosis
question
What is the relative risk of developing breast cancer from hormone replacement therapy?
answer
1-1.5
question
Is fibrocystic disease a risk factor for breast CA?
answer
No
question
What are possible Sxs for breast CA?
answer
No symptoms, or... mass, pain (most are painless), nipple discharge, local edema, nipple retraction, dimple, nipple rash
question
Why does skin retraction occur with breast CA?
answer
tumor involvement of Cooper's ligaments and subsequent traction on ligaments pull skin inward
question
What are the signs of breast cancer?
answer
Mass (1 cm usually the smallest that can be palpated) dimple nipple rash edema axillary/supraclavicular LAD
question
What is the MC site of breast cancer?
answer
upper outer quadrant
question
What are the major types of invasive breast carcinoma?
answer
invasive ductal carcinoma (90%) invasive lobular carcinoma (10%) inflammatory carcinoma
question
What is the MC type of breast cancer?
answer
Infiltrating ductal carcinoma
question
What is the DDx of breast cancer / mass?
answer
fibrocystic dz of breast fibroadenoma intraductal papilloma duct ectasia fat necrosis absccess radial scar simple cyst
question
How does the edema of the dermis in inflammatory carconima of the breast appear?
answer
Peau d'orange (orange peel)
question
What are the screening recommendations for breast cancer? a. breast exam recommendations? b. mammograms?
answer
a. self-exams monthly; exam every 2-3 years for 20-40 yo; exam annually for those over 40 b. baseline betwen 35-40 years; mammogram annually or every other yr for 40-50 yo; annual after 50
question
When is best time for SBEs?
answer
one week after menstrual period
question
What is the classic picture of breast CA on mammogram?
answer
spiculated mass (stellate)
question
Which radiographic option is best to evaluate a breast mass in a women under 30?
answer
breast ultrasound
question
What type of biopsy is performed when a nonpalpable breast mass is seen on mammogram?
answer
sterotactic (mammotome) biopsy or needle localization biopsy
question
What is a needle loc biopsy (NLB)? What is a mammotome Bx?
answer
needle localization by radiologist, followd by Bx. Checked by mammogram to be sure all of lesion has been excised mammogram-guided computerized sterotactic core biopsies
question
Workup for breast mass?
answer
1. clinical breast exam 2. mammogram or breast U/S 3. FNA, core Bx, or open Bx
question
What is the preop staging workup in a pt with breast cancer?
answer
bilateral mammogram CXR (check for lung mets) LFTs (check for liver mets) serum Ca level, alkaline phos (if they indicate bone mets, do bone scan) head CT if pt has focal neurologic deficits for brain mets
question
What hormone receptors must be checked for in the biopsy specimen of suspected breast CA?
answer
estrogen and progesterone receptors -- this is the key for determining adjuvant treatment ***
question
What staging system is used for breast CA? What stage is distant metastases? What stages are candidates for lumpectomy + radiation?
answer
TMN (tumor, metastases, nodes) IV I, II (tumors < 5 cm)
question
What are the sites of breast CA metastasis?
answer
lymph nodes (MC) lung/pleura liver bones brain
question
What are the indications for modified radical postmastectomy radiation therapy?
answer
> 4 lymph nodes, plus chest wall involvement by tumor
question
What is the Tx of inflammatory CA of the breast?
answer
Chemotherapy first! Then often followed by radiation, mastectomy, or both
question
What is the major absolute CI to lumpectomy and radiation?
answer
pregnancy Others: prior radiation to chest, positive margins, collagen vascular dz, extensive DCIS
question
After a mastectomy, at what drainage level are drains removed?
answer
< 30 cc/day drainage or post op day 14 whichever comes first
question
Why shouldn't the pt be paralyzed during an axillary dissection?
answer
Bc the nerves (long thoracic/thoracodorsal) are stimulated with resultant muscle contraction to help ID them They can be stimulated w/ a forceps, which results in contraction of the latissimus dorsi (thoracodorsal nerve) or anterior serratus (long thoracic nerve)
question
What do you do with a mammatome biopsy that returns as atypical hyperplasia?
answer
Open needle loc Bx as many will have DCIS or invasive CA
question
How does tamoxifen work?
answer
It binds estrogen receptors
question
What is the Tx for local reccurrence in breast after lumpectomy and radiation?
answer
"salvage" mastectomy (axillary dissection already completed)
question
Can tamoxifen prevent breast cancer? What are the SEs of tamoxifen?
answer
Yes In high risk women, tamoxifen for 5 yrs will lower risk by up to 50% (but with an increased risk of endometrial cancer and clots) Endometrial cancer**, DVT, pulmonary embolus, cataracts, hot flashes, mood swings
question
What are common options for breast reconstruction? (3)
answer
TRAM flap (transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap) implant latissimus dorsi flap
question
What type of chemo is usually used for breast CA?
answer
CMF (cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, 5-FU) CAF (cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, 5-FU)
question
What makes a breast tumor high risk?
answer
> 2 cm lymphatic / vascular invasion nuclear grade (high) S phase (high) ER negative
question
DCIS... a. What does it stand for? b. What is it also known as? c. Describe it. d. SSx? e. Mammographic findings? f. How is diagnosis made? g. What is the most aggressive histiologic type?
answer
a. ductal carcinoma in situ b. intraductal carcinoma c. cancer cells in the duct w/o invasion (not penetrating basement membrane) d. usually none (usually nonpalpable) e. microcalcifications f. core or open bx g. comedo
question
What is the major risk with DCIS?
answer
subsequent development of infiltrating ductal carcinoma in the same breast
question
What is a total (simple) mastectomy?
answer
removal of breast and nipple without removal of axillary nodes
question
What is adjuvant for DCIS?
answer
Tamoxifen postlumpectomy XRT
question
LCIS... a. What is it? b. SSx? c. Mammographic findings? d. How is Dx made?
answer
a. Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (CA in lobules of breast) b. none c. none d. found incidentally on biopsy
question
DCIS cancer occurs in ____ breast. LCIS cancer occurs in ______.
answer
same either (equal risk in both breasts)
question
What type of invasive breast CA do patients with LCIS develop?
answer
most commonly, infiltrating ductal carcinoma with equal distrbution in the contralateral and ipsilateral breasts
question
What is Tx of LCIS?
answer
close follow up (or bilateral simple mastectomy in hi risk patients)
question
What is the MC cause of bloody nipple discharge in a young woman?
answer
intraductal papilloma
question
What is the MC breast tumor in patients younger than 30 years?
answer
fibroadenoma
question
What is Paget's dz of the breast?
answer
scaling rash / dermatitis of the nipple caused by invasion of skin by cells from a ductal carcinoma
question
List the risk factors for male breast cancer?
answer
increased estrogen radiation gynecomastia from increased estrogen estrogen therapy Klinefelter's syndrome (XXY) BRCA2 carriers
question
What type of breast cancer do men develop?
answer
ductal carcinoma (men don't usually have breast lobules)
question
What is the MC cause of green, straw-colored, or brown nipple discharge?
answer
fibrocystic disease
question
What is teh MC cause of breast mass after breast trauma?
answer
fat necrosis
question
What is Mondor's dz?
answer
thrombophlebitis of superficial breast veins
question
What must be ruled out with spontaneous galactorrhea (+/- amenorrhea)?
answer
prolactinoma (check pregnancy test and prolactin level)
question
Fibroadenoma... a. What is it? b. What is clinical presentation? c. How is it diagnosed? d. Tx? e. what is its claim to fame?
answer
a. benign tumor of breast consisting of stromal overgrowth, collagen arranged in swirls b. solid, mobile, well-circumscribed** round breast mass, usually < 40 years c. negative needle aspiration looking for fluid; u/s; core Bx d. surgical resection for large or growing lesions; small can be observed closely e. MC breast tumor in women <30yrs old
question
Fibrocystic dz a. What is it? b. SSx? c. Dx? d. Tx for symptomatic dz?
answer
a. common benign condition; fibrous (rubbery) and cystic changes in the breast b. breast pain or tenderness that varies w/ menstrual cycle; cysts; fibrous "nodular" fullness c. breast exam, Hx, aspirated cysts (usually straw-colored or green fluid) d. STOP CAFFEINE! Pain meds (NSAIDs), Vit E, evening primrose oil
question
Mastitis... a. What is it? b. In what circumstance does it most often occur? c. What bacteria are MC cause? d. Tx? e. Why closely follow up this pt?
answer
a. superficial infection of breast (cellulitis) b. breastfeeding c. staph aureus d. stop breastfeeding; use breast pump instead; apply heat; Abx e. to be sure she doesn't have inflammatory breast CA
question
What are the causes of breast abscess? What is MC bacteria?
answer
mammary ductal ectasia (stenosis of breast duct) and mastitis nursing = staph aureus nonlactaing = mixed infection
question
What is the Tx of a breast abscess?
answer
Abx (e.g., dicloxacilln) needle or open drainage with cultures taken resection of involved ducts if recurrent breast pump if breastfeeding
question
What is lactational mastitis?
answer
infection of the breast during breastfeeding - MC caused by S. aureus. Tx with Abx and follow for abscess formation
question
What must be ruled out with a breast abscess in an nonlactating woman?
answer
breast cancer!
question
What are the 5 causes of male gynecomastia? What is the major differential diagnosis in the older patient? What is the treatment?
answer
medications ** illicit drugs (marijuana) liver failure increased estrogen decreased testosterone Male breast cancer Stop medications, correct underlying cause, perform biopsy or SQ mastectomy if refractory to conservative treatment
question
Why is mammography more useful diagnostic tool in older women than in younger?
answer
Breast tissue undergoes fatty replacement with age, making masses more visible. Younger women have more fibrous tissue, which makes mammograms harder to interpret.
question
What are the radiographic tests for breast cancer?
answer
Mammography and breast US MRI
question
What are the methods for obtaining tissue for pathologic examination?
answer
FNA Core biopsy (larger needle core sample) mammotome stereotactic biopsy open biopsy - can be incisional (cutting a piece of the mass) or excisional (cutting out the entire mass)
question
What are the indications for a biopsy?
answer
Persistent mass after aspiration Solid mass Blood in cyst aspirate Suspicious lesion by mammography/US/MRI Bloody nipple discharge Ulcer or dermatitis of nipple Patient's concern of persistent breast abnormality
question
What is obtained first, the mammogram or the biopsy?
answer
Mammogram Tissue extraction may alter the mammographic findings FNA may be done prior because the fine needle usually will not affect the mammogram findings
question
What would be suspicious mammogram findings?
answer
Mass Microcalcifications Stellate/spiculated mass
question
How do you proceed if the mass appears to be a cyst?
answer
Aspirate it with a needle
question
Is the fluid from a breast cyst sent for cytology?
answer
Not routinely, bloody fluid should be sent for cytology
question
When do you proceed to open biopsy for a breast cyst?
answer
1. in the case of a second cyst recurrence 2. bloody fluid in cyst 3. palpable mass after aspiration
question
What stage of breast cancer? Tumor < or equal to 2 cm in diameter without metastases, no nodes
answer
Stage I
question
What stage of breast cancer? Tumor < or equal to 2 cm in diameter with mobile axillary nodes or tumor 2-5 cm in diameter, no nodes
answer
Stage II A
question
What stage of breast cancer? Tumor 2-5 cm in diabeter with mobile axillary nodes or tumor >5 cm with no nodes
answer
Stage II B
question
What stage of breast cancer? Tumor >5 cm with mobile axillary nodes or tumor > 5 cm with fixed axillary nodes, no mets
answer
Stage III A
question
What stage of breast cancer? Peau d'orange or chest wall invasion/fixation or inflammatory CA or breast skin ulceration or breast skin satelite mets or any tumor and + ipsilateral internal mammary lymph nodes
answer
Stage III B
question
What stage of breast cancer? Distant mets including ipsilateral supraclavicular nodes
answer
Stage IV
question
What are the major txs of breast cancer?
answer
Modified radical mastectomy Lumpectomy and radiation (both treatments either with or without postop chem/tamoxifen)
question
What breast carcinomas are candidates for lumpectomy and radiation?
answer
Stage I and II, tumors <5 cm
question
Where are the drains placed with an MRM?
answer
1. axilla 2. chest wall (breast bed)
question
What are the potential complications after a MRM?
answer
Ipsilateral arm lymphedema, infection, and injury to nerves, skin flap necrosis, hematoma/seroma, phantom breast syndrome
question
How can the long thoracic and thoracodorsal nerves be identified during an axillary dissection?
answer
The nerves can be stimulated with forceps which results in contraction of the latissimus dorsi (thoracodorsal) and anterior serratus (LTN)
question
What is a "sentinel" node biopsy?
answer
Instead of removing all the axillary lymph nodes, the primary draining or sentinel lymph node is removed
question
How is the sentinel lymph node found?
answer
Inject blue dye or techetium labeled sufur colloid
question
What follows a positivie sentinel node bx?
answer
Removal of the rest of the axillary lymph nodes
question
What is the tx for DCIS 1 cm?
answer
Remove with 1 cm margins +/- XRT Perform lumpectomy with 1 cm margins and radiation or total mastectomy (no axillary dissection)
question
What is the role of axillary node dissection with DCIS?
answer
No role in true DCIS (without microscopic invasion), some perform a sentinel node dissection for high-grade DCIS
question
What are the common options for breast reconstruction after a mastectomy?
answer
Saline implant TRAM flap
question
a. What is the incidience of BRCA in men? b. What is the average age at diagnosis? c. What are the s/sx? d. Most common presentation? e. How is it diagnosed?
answer
a. <1% b. 65yrs c. Breast mass (most painless), breast skin changes, nipple discharge d. painless breast mass e. biopsy and mammogram
question
What is the treatment of BRCA in men?
answer
1. mastectomy 2. sentinel LN dissection of clinically negative axilla 3. axillary dissection if clinically positive axillary LN



