Visual Anatomy & Physiology Ch 5 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
integument
answer
skin
question
integumentary system
answer
skin; includes two major components: cutaneous membrane and accessory structures
question
cutaneous membrane
answer
includes epidermis and dermis
question
functions of integumentary system
answer
1 - protection; 2 - vitamin D3 synthesis; 3 - excretion; 4 - sensation; 5 - temperature regulation; 6 - produce melanin (protection from ultraviolet radiation from sun); 7 - produce keratin (protection from abrasion and serves as water repellent); 8 - stores lipids
question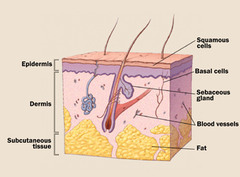
layers of skin

answer
epidermis dermis hypodermis
question
epidermis
answer
several layers (strata) of keratinocytes; consists of stratified squamous epithelial tissue
question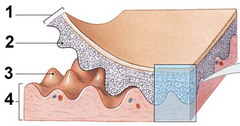
epidermal ridges

answer
deep layers of epidermis that extend into dermis and are adjacent to dermal papillae; increase surface area for binding of dermis to epidermis
question
dermal papillae
answer
upper layers of dermis that project into epidermis; increase surface area for binding of dermis to epidermis
question
thin skin
answer
covers most of body surface; has four layers: stratum corneum, stratum ganulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
question
thick skin
answer
found on palms of hands and soles of feet; has five strata instead of four: stratum corneum, status lucidum, stratum ganulosum, stratum spinosum, and strum basale
question
stratum corneum

answer
uppermost layer of epidermis; exposed surface of skin; 15-30 layers of kerotinocytes; water resistant but not water proof
question
keratin
answer
fluid inside kerotinocytes
question
insensible perspiration
answer
water from interstitial fluid that slowly penetrates to the epidermal surface and evaporates; person does not see or feel this water loss; about 1 pint of water per day
question
sensible perspiration
answer
fluid produced by active sweat glands; person is usually aware of sweating
question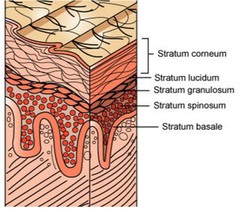
stratum lucidum

answer
"clear" layer of epidermis found only in thick skin under stratum corneum in epidermis; flattened, densely-packed cells filled with keratin and keratonhyalin
question
stratum granulosum
answer
"grainy" layer of epidermis that has 3-5 layers of keratinocytes that have stopped dividing
question
stratum spinosum
answer
"spiny" layer of epidermis that has 8-10 layers of kerotinocytes bound together by desmosomes; also contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells
question
stratum basale
answer
bottom layer of epidermis containing basal cells and Merkel cells
question
basal cells

answer
stem cells found in stratum basale of epidermis that divide to create new kerotinocytes
question
Merkel cells
answer
cells found in stratum basale that are involved with touch sensation
question
papillary layer
answer
upper layer of dermis consisting of areolar connective tissue
question
reticular layer
answer
lower layer of dermis consisting of dense irregular connective tissue
question
hypodermis
answer
also called subcutaneous layer or superficial fascia; separates skin from deeper organs; not part of the integument (skin); consists of areolar and adipose connective tissue
question
touch receptors of skin
answer
convey sensations from the skin; include many different types such as free nerve endings, tactile discs, Meissner's corpuscles, lamellated corpuscles, and Ruffini corpuscles
question
keratinocytes
answer
epithelial cells that produce keratin; continuously produced by stem cell division in deep layers of epidermis and shed at exposed surface of skin
question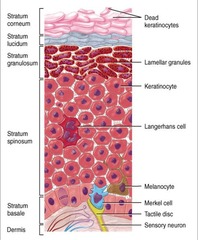
melanocytes

answer
epidermal cells that produce melanin; packaged in melanosomes; found in stratum basal
question
dendritic cells
answer
Langerhans cells; cells in stratum spinosum layer of epidermis that defend against microorganisms and superficial skin cancers
question
collagen fibers
answer
dermal cells and fibers that are very strong
question
elastic fibers
answer
dermal cells and fibers that permit stretching
question
skin color
answer
Influenced by presence of pigments, degree of dermal circulation, and thickness and degree of keratinization in epidermis
question
skin color pigments
answer
melanin and carotene
question
melanin
answer
brown, yellow-brown, or black pigment in skin produced by melanocytes; absorbs ultraviolet radiation to cause tanning; skin color is due to level of melanin synthesis rather than due to number of melanocytes
question
carotene
answer
orange-yellow pigment that accumulates in epidermal cells
question
hemoglobin
answer
red pigment found in red blood cells
question
albinism
answer
skin color condition due to genetic lack of melanin; have normal number of melanocytes, but don't produce melanin
question
cyanosis
answer
blue skin color condition due to decreased oxygen in blood; most obvious in lips or beneath fingernails
question
skin cancer
answer
most common type of cancer in people
question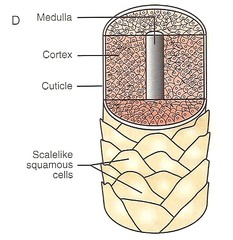
cuticle (hair)

answer
outermost hair layer; consists of daughter cells produced at edges of hair matrix; contains hard keratin
question
cortex (hair)
answer
intermediate hair layer of daughter cells deep to the cuticle; contains hard keratin
question
medulla (hair)
answer
innermost hair layer; consists of daughter cells formed at center of hair matrix; contains soft keratin
question
hair matrix
answer
consists of a layer of basal cells at base of hair bulb and in contact with hair papilla; germinative cells that produce hair; as cells divide, daughter dells are pushed toward surface
question
hair shaft
answer
hair visible on surface of skin; begins deep within hair follicle
question
hair root
answer
portion of hair that anchors it into skin; extends from base of hair follicle to point where hair shaft loses connection to walls of follicle
question
internal root sheath of hair follicle
answer
surrounds hair root
question
external root sheath of hair follicle
answer
consists of epithelial cells, extends from skin surface to hair matrix
question
arrector pili muscle
answer
smooth muscle that contracts to pull hair erect
question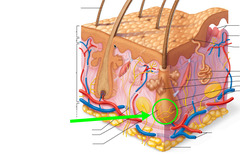
root hair plexus

answer
sensory nerves surrounding base of each hair follicle; allows for felling of movement of hairs
question
hair growth cycle
answer
growing and shedding of hair; active phase - hair grows continuously; resting phase - hair loses its attachment to follicle and becomes a club hair; scalp hair grows for 2-5 years
question
nail body
answer
visible portion of nail; made up of dead, tightly compressed cells packed with keratin
question
nail root
answer
portion of nail lying underneath skin; place where nail production occurs
question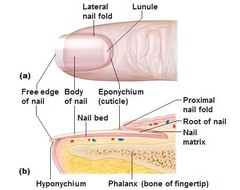
lunula

answer
pale crescent area of nail near root; coloring is caused by obscuring of dermal blood vessels
question
nail bed
answer
epidermis beneath nail
question
eponychium
answer
also called cuticle; part of stratum corneum of nail root that extends over exposed nail
question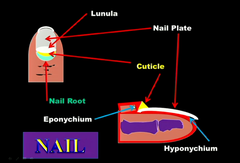
hyponychium

answer
thickened part of stratum corneum that lies underneath the free edge of nail
question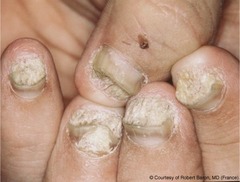
psoriasis

answer
condition marked by rapid stem cell division in the stratum basale; can show up as pitted and distorted nails
question
age related changes in integument
answer
1 - fewer melanocytes 2 - epidermis thins and dries out 3 - decreased perspiration 4 - gray/white hairs 5 - diminished immune response 6 - fewer hairs 7 - reduced blood supply 8 - thinning dermis 9 - slower skin repair 10 - altered hair and fat distribution
question
epidermis thins
answer
basal cell activity declines; makes elderly more prone to injury, skin tears, and skin infections
question
decreased perspiration
answer
decreased merocrine sweat gland activity; can lead to easier over-heating
question
epidermis dries out
answer
decreased sebaceous gland secretion
question
fewer melanocytes
answer
melanocytes become less active and skin becomes very pale; causes increased risk of sunburn
question
diminished immune response
answer
decreased number of dendritic cells; may promote skin damage or infection
question
thinning dermis
answer
makes skin weaker and less resilient; causes sag gin and wrinkling especially in areas exposed to sun
question
reduced blood supply
answer
decreased blood flow to dermis can cause person to feel cool even in warm room; combined with reduced sweat gland function, can lessen ability of elderly to lose body heat during exertion and lead to heat exhaustion
question
slower skin repair
answer
extended time needed for skin to heal after injury
question
fewer hairs
answer
decreased number of active hair follicles; decreased melanocyte activity makes hairs grey or white
question
altered hair and fat distribution
answer
as sex hormone levels decline, gender differences n hair and body fat distribution fade
question
circulating hormones that affect integument
answer
1 - glucocorticoids 2 - thyroid hormones 3 - sex hormones 4 - growth hormone 5 - growth factors
question
glucocorticoids
answer
steroid hormone released during times of stress; loosen connections between keratinocytes and reduce effectiveness of epidermis as barrier to infection
question
thyroid hormones
answer
maintain blood flow to subpapillary plexus
question
subpapillary plexus
answer
capillaries supplying dermis with blood flow
question
sex hormones
answer
stimulate epidermal cell divisions to increase epidermal thickness and accelerate wound repair
question
growth factors
answer
compounds that stimulate cell growth and cell division
question
epidermal growth factor
answer
peptide growth factor that effect epithelia throughout body; produced by salivary glands and glands of duodenum (initial segment of small intestine); promotes basal cell division, accelerates keratin production, stimulates epidermal development and repair, and stimulates activity and secretion by epithelial glands
question
growth hormone
answer
stimulates fibroblast activity and collagen synthesis; also stimulates basal cell divisions, thickens epidermis, and promotes wound repair
question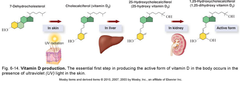
vitamin D production

answer
UV radiation in sunlight → conversion of a steroid into cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) in skin → conversion of cholecalciferol to calcitriol in the liver → absorption of calcium and phosphorus in small intestine to aid in bone growth and maintenance
question
rickets
answer
condition in growing child that results in flexible, poorly mineralized bones; due to lack of sun exposure and vitamin D3 in diet
question
4 phases of skin regeneration after injury
answer
1 - inflammatory phase 2 - migratory phase 3 - proliferation phase 4 - scarring phase
question
inflammatory phase
answer
initial phase of skin regeneration after injury; bleeding occurs at site of injury and mast cells release histamine to cause swelling, redness, heat (warmth), and pain
question
migratory phase
answer
second phase of skin regeneration that occurs several hours after initial injury; blood clot (scab) forms on surface to resist entry of microorganisms → macrophages phagocytize debris and pathogens → cells of stratum divide rapidly and migrate to edges of wound to replace missing epidermal cells; granulation tissue (combination of blood clot, fibroblasts, and extensive capillary network) starts to form if wound is extensive
question
proliferation phase
answer
third phase of skin regeneration that occurs about one week after initial injury; epidermal cells migrate underneath scab to dissolve deeper portions of clot; fibroblasts produce collagen fibers and ground substance in dermis
question
scarring phase
answer
final phase of skin regeneration that occurs several weeks after initial injury; epidermal repair is complete; scar tissue (inflexible, fibrous, noncellular tissue) completes repair process in dermis; tissue is never restored to original condition
question
keloid
answer
raised, thickened mass of scar tissue at site of injury and surrounding area; happen most in people with dark skin; sometimes done intentionally as a form of body decoration
question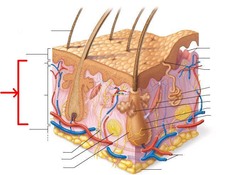
dermis

answer
found between epidermis and hypodermic; consists of papillary layer of arelar tissue and a reticular layer of dense irregular connective tissue
question
accessory structures of integumentary system
answer
hair, nails, and exocrine glands, blood vessels and nerve fibers support skin function; also known as epidermal derivatives, because they develop from epidermis during embryonic development
question
cutaneous plexus
answer
network of arteries and veins connected to smaller vessels servicing the tissues of the integumentary system
question
erythema
answer
redness and and inflammation at the surface of the skin
question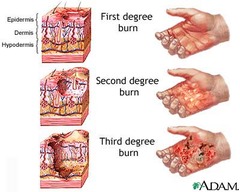
first-degree burn

answer
burn involving only epidermis and causing redness (erythema) and swelling; type of partial thickness burn; includes most sunburns; skin reddens and can be painful
question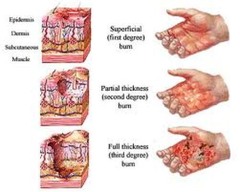
second-degree burn

answer
burn involving epidermis and dermis that usually forms blisters, pain, and swelling; type of partial thickness burn; takes 1-2 weeks to heal
question
third-degree burn
answer
burn involving entire thickness of skin, hypodermis, and subcutaneous tissue, muscle, and bone; causes scarring; less painful than second-degree burns because sensory nerves are destroyed; also called full thickness burn; requires skin grafting
question
Skin functions affected by burns
answer
fluid and electrolyte balance, thermoregulation, protection form infection
question
skin graft
answer
surgical procedure involving tissue transplant; used to treat serious burns
question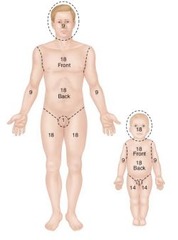
rule of nines

answer
method used to calculate the total surface area involved in burns in which the body surface of an adult is divided into multiples of 9; head is 9%, each upper limb is 9%; trunk is 36%, genitalia are 1%; each lower limb is 18%; modify rule for children because their proportions are different
question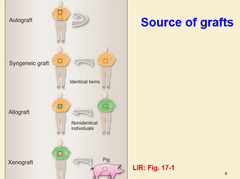
autograft

answer
type of skin graft that uses tissue transplanted from the same person
question
allograft
answer
type of skin graft that uses tissue transplant between members of the same species
question
xenograft
answer
type of skin graft that uses tissue transplant from another species; example: pig skin
question
skin cultivation
answer
recent advance in cell culturing that allows scientists to grow large sheets of epidermal cells for covering burned areas; alternative way to get tissue for skin grafts
question
epithelial columns
answer
cords of epidermal cells that grow into the dermis and allow for development of hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands
question
hair follicle
answer
an accessory structure of the integument that produces body hair; a tube lined by stratified squamous epithelium that begins at surface of skin and ends at hair papilla
question
terminal hairs
answer
Large, coarse, and often dark-colored hairs found on scalp or armpits
question
vellus hairs
answer
Small, short, and delicate hairs found on general body surface
question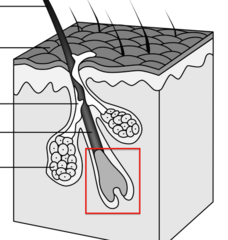
hair bulb

answer
Place where hair growth begins at the expanded base of hair follicle
question
club hair
answer
Hair that loses its attachment to the follicle and will soon be shed and replaced by a new hair
question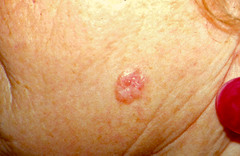
basal cell carcinoma

answer
most common type of skin cancer; originates in stratum basal due to mutations caused by overexposure to UV radiation in sunlight; usually not life threatening
question
malignant melanoma
answer
extremely dangerous type of skin cancer; cancerous melanocytes metastasize throughout lymphatic system; survival rate is largely dependent on how early the cancer is found and treated
question
free nerve endings

answer
sensitive to touch and pressure and are found between epidermal cells
question
tactile discs
answer
detect sensations of texture and steady pressure; found in deepest layer of epidermis
question
Meissner's corpuscles
answer
detect sensations of delicate touch, pressure, and vibrations; found in papillary layer of dermis
question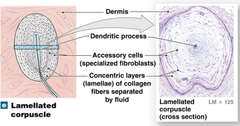
lamellated corpuscles

answer
sensitive to deep pressure and vibration; found in both dermal layers and hypodermis
question
Ruffini corpuscles
answer
sensitive to pressure and stretching of skin; found in reticular layer of dermis
question
lines of cleavage
answer
tension lines or Langer lines; parallel bundles of collagen and elastic fibers that resist forces applied to skin during movement; cut parallel to line of cleavage will have little scarring, whereas cut perpendicular to cleavage line will have considerable scarring
question
skin functions affected by burns
answer
fluid and electrolyte balance, thermoregulation, protection from infection
question
fluid and electrolyte balance
answer
even areas of body with partial thickness burns lose effectiveness as barriers to fluid and electrolyte losses; in full thickness burns, rate of fluid loss through skin may reach five times the normal level
question
thermoregulation
answer
increased fluid loss means increased evaporative cooling; requires expenditure of more energy to keep body temperature within acceptable limits
question
protection from infection
answer
dampness of epidermal surface--resulting from uncontrolled fluid loss--encourages bacterial growth; if skin is broken, infection is likely; widespread bacterial infection (sepsis) is leading cause of death in burn victims
question
sepsis
answer
widespread bacterial infection; rotting of the skin
question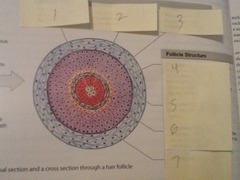
soft keratin

answer
found in medulla or core of hair; flexible
question
hard keratin
answer
found in cortex of hair; thick layers that give hair stiffness
question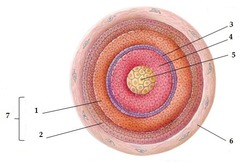
hair follicle structure

answer
includes internal root sheath, external root sheath, glassy membrane, and connective tissue sheath
question
internal root sheath
answer
part of hair follicle that surrounds hair root and deeper portion of hair shaft; produced by hair matrix; cells disintegrate quickly
question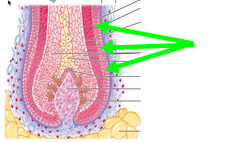
external root sheath

answer
part of hair follicle consisting of epithelial cells; extends form skin surface to hair matrix
question
glassy membrane
answer
thickened, clear basement membrane of hair follicle
question
connective tissue sheath
answer
outermost part of hair follicle
question
exocrine glands
answer
includes sebaceous glands and sweat glands; assist in thermoregulation, excretion of waste, and lubrication of epidermis
question
sebaceous glands
answer
also known as oil glands; discharge an oily, lipid substance (sebum) into hair follicles that coat hair and adjacent area of skin
question
sebum
answer
secretion from sebaceous glands; lubricates hair shaft, moisturizes surrounding skin, and inhibits goeth of bacteria
question
sweat glands
answer
discharge merocrine and apocrine when contractions of myoepithelial cells squeeze the gland
question
apocrine sweat glands
answer
type of sweat glands found in armpits, pubic region, and around nipples; secrete into hair follicles; produce body odor; strongly influenced by hormones
question
merocrine sweat glands
answer
merocrine - found in most areas of skin; important for thermoregulation; secrete directly onto surface of skin
question
nails
answer
thick sheets of keratinized epidermal cells that protect tips of fingers and toes
question
lateral nail grooves
answer
side boundaries (depressions) of nail body
question
lateral nail folds
answer
side boundaries (ridges) of nail body



