Urinary System Vet. Anatomy and Physiology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Urinary System
answer
Removes all soluble waste products from the blood and transports them out of the body
question
Kidneys
answer
Make urine, Help maintain homeostasis by regulating body acid-base and fluid-electrolyte balance
question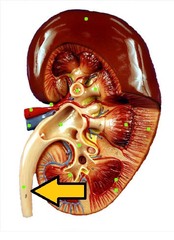
Ureter

answer
Continuously move urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder by peristalsis
question
Urinary Bladder
answer
Collects, stores, and releases urine
question
Urethra
answer
Conducts urine out of the body, Lined with transitional epithelium
question
Nephritis
answer
Inflammation of the kidneys
question
Renal
answer
Refers to the kidneys
question
Main ways the kidneys help maintain homeostasis
answer
Blood filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, fluid balance regulation, Acid-base balance regulation, Hormone production
question
Fluid Balance Regulation
answer
Amount of urine produced is based on the body's needs under the control of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone
question
Diuresis
answer
producing and passing large amounts of urine
question
Oliguria
answer
passing small amounts of urine
question
Anuria
answer
passing no urine
question
Acid-base balance regulation
answer
Removes hydrogen and bicarbonate ions from the blood and excretes them in the urine
question
Hormone production (kidneys)
answer
Influence rate of release of ADH from the posterior pituitary gland, Influence the rate of release of aldosterone, Produce erythropoietin, Produce some prostaglandins
question
erythropoietin
answer
a hormone necessary for red blood cell production
question
aldosterone
answer
a mineralocorticoid secreted by the cortex of the adrenal gland that regulates sodium reabsorption in the nephron and is regulated by the renin-angiotensin system
question
Renin is secreted by the kidney when there is:
answer
low blood pressure in the afferent arteriole decreased sodium concentrations in the blood plasma a decreased osmolarity in the distal tubule stimulation of the sympathetic nerve fibers innervating the afferent arterioles
question
Renin
answer
stimulates the production of angiotensin and aldosterone
question
Angiotensin
answer
a vasoconstrictor that increases blood pressure
question
Aldosterone
answer
causes the kidney to conserve sodium
question
Kidney Location
answer
in the dorsal part of the abdomen, just ventral to and on either side of the first few lumbar vertebrae
question
Horse kidney
answer
right is heart shaped, left is bean shaped
question
Cattle kidneys
answer
is divided into about 12 lobes, giving it a lumpy appearance, do not have a renal pelvis
question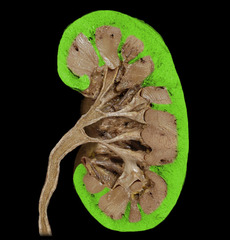
Renal Cortex

answer
Outer portion of the kidney
question
Renal Medulla
answer
Inner portion around the renal pelvis
question
Hilus
answer
Indented area on the medial side of the kidney; area where the blood and lymph vessels, nerves, and ureters enter and leave
question
Renal Pelvis
answer
collection point for tubular filtrate as it leaves the collecting ducts
question
Calyx
answer
A cuplike extension of the renal pelvis into which the medullary pyramids fit, act as funnels that direct fluids into the renal pelvis
question
Nephron
answer
Basic functional unit of the kidney, a filtering, reabsorbing, and secreting system
question
Renal Corpuscle
answer
The first part of the nephron, it is composed of the glomerular capillaries and Bowman's capsule, filters blood at the first stage of urine production
question
Glomerulus (also called Glomerular Capillaries)
answer
tuft of capillaries found in the renal corpuscle, main filtration mechanism of the kidney
question
Bowman's Capsule
answer
Consists of two layers: an inner, visceral layer that lies directly on the glomerular capillaries and an outer parietal layer, Functions as a plasma filter in the process of urine formation
question
Capsular Space
answer
The space between the visceral and parietal layers of Bowman's capsule
question
Glomerular Filtrate
answer
The fluid that has been filtered out of the glomerular capillaries and into the capsular space
question
Glomerular Filtration Rate
answer
The rate at which plasma is filtered into the capsular space Expressed in milliliters per minute Major factor determining GFR is blood pressure
question
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
answer
The first part of the tubular portion of the nephron, its lumen is a continuation of the capsular space of Bowman's capsule in the renal corpuscle, majority of tubular reabsorption takes place from the PCT
question
Tubular Filtrate
answer
The glomerular filtrate after it has passed into the proximal convoluted tubule
question
Loop of Henle
answer
The middle part of the tubular portion of a nephron, Has a descending part that travels from the cortex to the medulla and an ascending part that travels back to the cortex
question
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
answer
The last tubular part of the nephron before it enters the collecting duct
question
Collecting Ducts
answer
The tubule system that collects tubular filtrate from the distal convoluted tubules and carries it to the renal pelvis, Not a part of the nephron, Primary site of action of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
question
Renal Artery
answer
Branches off the abdominal portion of the aorta, enters the kidney at the hilus
question
Afferent Glomerular Arterioles
answer
Carry blood into the glomerular capillaries of the renal corpuscle
question
Glomerular Capillaries
answer
A continuation of the afferent arterioles; filter some of the plasma out of the blood and put it in the capsular space of Bowman's capsule
question
Efferent Glomerular Arterioles
answer
They carry the blood that has been filtered by the glomerulus; so it contains less plasma
question
Peritubular Capillaries
answer
Surround the nephron and converge to form venules that in turn converge to form larger veins that eventually become the renal vein
question
Renal Vein
answer
Leaves the kidney at the hilus and joins the abdominal portion of the caudal vena cava
question
(Steps of Urine Production) 1
answer
Blood enters the glomerulus via the afferent glomerular arteriole
question
(Steps of Urine Production) 2
answer
High blood pressure in the glomerular capillaries forces some plasma out of the capillaries and into the capsular space of Bowman's capsule (The fluid is called glomerular filtrate)
question
(Steps of Urine Production) 3
answer
The balance of the plasma not forced out of the glomerular capillaries leaves the glomerulus via the efferent glomerular capillaries and enters a peritubular capillary network around the rest of the nephron
question
(Steps of Urine Production) 4
answer
When the tubular filtrate travels through the tubules of the nephron, some of its constituents are reabsorbed back into the peritubular capillaries
question
(Steps of Urine Production) 5
answer
Waste products are secreted from the peritubular capillaries into the tubular filtrate as it travels through the tubules
question
(Steps of Urine Production) 6
answer
The tubular filtrate reaches the collecting duct and then travels to the renal pelvis, where it is called urine
question
Ureters
answer
Tubes that exit the kidneys at the hilus and connect to the urinary bladder near the neck of the bladder; a continuation of the renal pelvis (except in cattle)
question
Ureters 3 layers
answer
Outer fibrous layer Middle smooth muscle layer Inner layer of transitional epithelium
question
Urination
answer
micturition, uresis: expulsion of urine from the urinary bladder into the urethra for elimination from the body
question
Muscular Sac (UB)
answer
Lined with transitional epithelium that stretches as the bladder becomes filled with urine
question
Neck (UB)
answer
Extends from the sac to the urethra
question
Urine accumulation (1)
answer
When the pressure of urine in the bladder reaches a trigger point, stretch receptors are activated
question
Muscle contraction (2)
answer
Spinal reflex is activated that returns a motor impulse to bladder muscles to contract, which signals the sensation of having to urinate
question
Sphincter muscle control (3)
answer
Can be controlled temporarily, When the limit is reached, urine will be released
question
Urine production
answer
does NOT stop when the bladder is full
question
Female Urethra
answer
Short and straight and opens on the floor of the vestibule of the vulva
question
Male Urethra
answer
Long and curved and runs down the center of the penis
question
Vas deferens and accessory reproductive glands
answer
enter the urethra so that spermatozoa and seminal fluid can enter it during ejaculation and be pumped out as semen
question
Uremia
answer
Urine in the blood; waste materials, especially nitrogen wastes, build up in the blood and become toxic
question
Prerenal Uremia
answer
decreased blood flow to the kidneys, waste materials cannot be adequately removed, ie) dehydration, shock, congestive heart failure
question
Renal Uremia
answer
Inability of the kidneys to adequately regulate urine production due to lack of functional nephrons, so waste materials cannot be adequately removed
question
Postrenal Uremia
answer
Associated with an obstruction that prevents urine from being expelled from the body
question
Diabetes mellitus
answer
Insufficient insulin production by the pancreas causes high blood glucose concentrations, Excess glucose is removed in the urine, Renal threshold of glucose is the maximum amount of glucose that can be reabsorbed into the bloodstream
question
Glucosuria
answer
glucose in the urine
question
Osmotic diuresis
answer
abnormally high urine production
question
Polydipsia
answer
drinking increased amounts of water
question
Polyuria
answer
increased volume of urine production
question
Diabetes insipidus
answer
A deficiency in antidiuretic hormone; causes the collecting ducts to not reabsorb enough water, causing polyuria
question
Uroliths
answer
Abnormal mineral masses in the urinary system: May result from bacterial urinary tract infections Uroliths in the urinary bladder may cause hematuria (blood in the urine) and dysuria (painful urination) May lodge in the urethra and cause obstruction



