Thoracic Trauma
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Angle of Louis
answer
Junction of the manubrium and sternal body. Identifies 2nd intercostal space.
question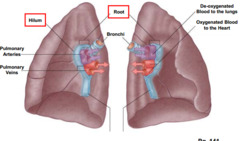
Pulmonary Hilum

answer
Where pulmonary arteries enter and pulmonary veins exit and is the lung's sole fixation point in the thoracic cage.
question
Apneustic center
answer
Located in pons turns off inspiration.
question
Pneumotaxic center
answer
Located in upper pons moderates activity in apneustic center and provide further fine tuning of respiratory patterns
question
Vagus nerve
answer
Parasympathetic innervation of thoracic and abdominal viscera
question
Pericardium
answer
Lines the heart
question
Epicardium
answer
Heart's outer surface
question
Blunt Trauma
answer
Injury from kinetic energy force transmitted through tissues. Blasts, Crush, Deceleration.
question
Blast injuries
answer
Explosive chemical reaction that creates a pressure wave traveling outward. Causes tissue disruption by dramatic compression and decompression as the wave passes. Particularly damaging to hollow air filled structures.
question
Crush injuries
answer
Body is compressed between an object and a hard surface.
question
Traumatic asphyxia
answer
If victim is pinned between two object, significant restriction in ventilation and venous return may occur
question
Rhabdomyolysis
answer
Breakdown of muscle fibers and release of degrade muscle fibers contents into circulation. Highly toxic to kidneys.
question
Deceleration injury
answer
Causes blunt chest wall injury while internal thoracic organs continue in motion. Organs and structures impact with the internal thoracic cavity surface
question
Paper bag syndrome
answer
Rapid chest compression against a closed glottis may cause alveolar and tracheobronchial rupture and pneumothorax
question
Pediatric thoracic injuries
answer
Less significant injury signs, few rib fractures and a greater incidence of serious internal injury
question
Low energy penetrating trauma
answer
Arrows, knives, hand funs and slow moving objects. Injury caused by direct contact and limited temporary cavity creation.
question
High energy penetrating trauma
answer
Caused by military and hunting rifle that fire at high velocity. Creates shock wave as passes through tissue and tissue movement. Extensive tissue damage perpendicular to the projectile's track.
question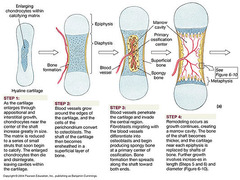
Cavitation

answer
Temporary cavity caused by high energy penetrating trauma.
question
Diaphragm
answer
Separates abdomen from thoracic cavity. Major muscle of respiration. Inhalation: contracts downwards. Exhalation: Relaxes upward.
question
Sternocleidomastoid
answer
Raises upper rib and sternum
question
Intercostal muscles
answer
Increase depth of respiration. Contract to elevate ribs and increase thoracic diameter.
question
Parietal Pleura
answer
Lines inside of thoracic cavity
question
Visceral Pleura
answer
Covers lungs
question
Dead Space Volume
answer
Amount of air in tidal volume that remains in air passage. Avg: 150 mL.
question
Surfactant
answer
Lowers surface tension and prevents the collapse of alveolus at the end of exhalation. Decreased by, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, ards, drowning.
question
Blast
answer
Pressure waves causes tissue disruption. Tear blood vessels and disrupt alveolar tissue and tracheobronchial tree
question
Crush Injury
answer
Body is compressed between an object and a hard surface. Direct injury of chest wall and internal structure
question
Deceleration Injury
answer
Body in motion strikes fixed object. Blunt trauma to chest wall. Internal structures continue in motin.
question
Pediatric Thorax
answer
More cartilage = absorbs forces
question
Geriatric Thorax
answer
Calcification and osteoporosis = more fractures
question
Low Energy Trauma
answer
Arrows, knives, hand guns. Injury caused by direct contract and cavitation
question
High Energy
answer
High energy cavitation. Military, hunting rifles and high powered hand guns
question
Shotgun Trauma
answer
Based upon the distance between the victim and shotgun and caliber of shot.
question
Contusion
answer
Most common result of blunt injury. Signs: ecchymosis, dyspnea, pain on breathing, ecchymosis, limited breathing sounds, hypoventilation, crepitus, paradoxical chest movement
question
Sternal Fracture
answer
Caused by direct blow. Causes myocardial contusion, pericardial tamponade, cardiac rupture, pulmonary contusion.
question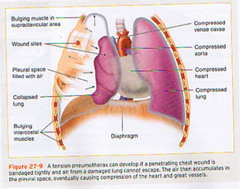
Tension Pneumothorax

answer
Build up of air under pressure in the thorax. Air is unable to escape from pleural space. Tachyapnea, atelectasis, hyperresonance, hyperinflation, hypoxemia
question
Hemothorax
answer
Neck veins flat, breath sounds absent cyanosis
question
Pulmonary contusion
answer
Soft tissue contusion of the lung.
question
Hemoptysis
answer
Coughing up blood
question
Commotio Cordis
answer
Ventricular fibrillation is induced by a direct chest blow



