Thin Layer Chromatography
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
____ a method of separating mixtures into their pure components
answer
Chromatography
question
chromatography: a method of _____
answer
separating mixtures into their pure component
question
Chromatography separates mixtures because the ____ between the various components of the mixture and the stationary phase are different
answer
intermolecular attractions
question
Chromatography separates mixtures because the intermolecular interactions between the ____
answer
various components of the mixture and the stationary phase are different
question
Chromatography is a method of separation using a ___ and a ____
answer
stationary phase; mobile phase
question
separation occurs as the mobile phase ____ the stationary phase
answer
passes over
question
the mobile phase can be ___ or ___
answer
liquid; gas
question
the stationary phase can be ___ or ___
answer
solid; liquid
question
Chromatography-Basic Principle: same basic principle as TLC but now ____ of pressure (_____) to ___ compounds
answer
use gravity; medium to high; elute
question
Chromatography is both a ____ and ____ method
answer
qualitative; quantitative
question
Chromatography is used for _____ the course of a reaction
answer
monitoring
question
Chromatography is used for monitoring ____
answer
the course of a reaction
question
3 types of chromatography used for monitoring the course of a reaction
answer
thin layer chromatography; gas chromatography; high performance liquid chromatography
question
what does TLC stand for
answer
thin layer chromatography
question
what does GC stand for
answer
gas chromatography
question
what does HPLC stand for
answer
high performance liquid chromatography
question
chromatography is used for _____ the components of a reaction
answer
isolating
question
what methods of chromatography are used for isolating the components of a reaction
answer
column chromatography; prep HPLC; Prep TLC
question
Chromatography is both a qualitative and quantitative method used for ___, ___ and ___
answer
1) monitoring the course of a reaction 2) isolating the components of a reaction 3) assisting in the identification of a compound
question
In liquid chromotagraphy ____ is established
answer
equilibrium
question
in the equation for chemical equilibrium what does Xm and Xs stand for
answer
the concentrations of solute molecules in the mobile phase and the stationary phase
question
in the equation for chemical equilibrium what does Sm and Ss stand for
answer
Sm and Ss are for the solvent molecule concentrations
question
in the equation for chemical equilibrium what does the value K represent
answer
the distribution coefficient or equilibrium between the solute and solvent molecules and between the mobile and stationary phases
question
____ values of K will mean a greater capacity to separate
answer
high
question
Interaction at SiO2/Solvent interface: competition exists between _____ and _____ for sites on the _____
answer
polar solvent molecules; polar solute molecules; SiO2 surface
question
Fill in blank on back elute

answer
A mixture of A, B, and C ready to ___ through a column
question
in tlc ______ contains material to be separated
answer
moving phase
question
Separation occurs as ____ passes over the ____. This separation occurs when molecules _____ of the ____ through weak intermolecular forces
answer
moving phase; stationary phase; adhere to the surface; absorbant
question
in moving phase the separation occurs when moleculars adhere to the surface of the absorbant through weak intermolecular forces. These forces are ____ and therefore ____
answer
weak; reversible
question
The eluents can be collected at the _____ as ___
answer
end of the column; individual fractions (cuts)
question
Order of elution: ____ are strongly retained on the ____ and therefore eluted late from the chromatographic columns filled with polar stationary phase
answer
polar compounds; polar stationary phases
question
Order of Elution: polar compounds are strongly retained on the polar stationary phase and therefore are ____ from the ___ filled with ____
answer
eluted; chromatographic columns; polar stationary phase
question
Order of Elution: _____ are strongly retained on _____ and therefore are eluted late from the chromatographic column filled with nonpolar (so called ___) phase
answer
nonpolar compounds; nonpolar stationary phases; reversed
question
nonpolar compounds are strongly retained on nonpolar stationary phases and therefore eluted late from the chromatographic column filled with _____
answer
nonpolar (so called reversed) phase
question
Draw thin layer chromatography where A is more polar than B

answer
(Mobil phase moves upwards)
question
If A is more polar than B. ___ will elute later from a column with polar stationary phase in column chromatography and will _____ with a polar stationary phase (having a lower ____)
answer
A; stay at the origin of the thin layer chromatography plate; Rf
question
what does Rf stand for
answer
retention factor
question
if something has a higher retention factor then in mobile phase it sill ___
answer
not move as far
question
How do you make a capillary pipet
answer
take a capillary tube. Place middle part in flame, rotate until soft. Remove from flame and pull. Score lightly in center of pulled section. Break in half to give two pipets
question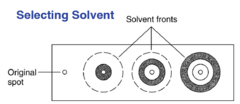
See back page for question? 1st: not polar enough 2nd: satisfactory 3rd: too polar

answer
Which of these solvents is satisfactory?
question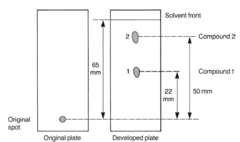
See next page for question Rf(compound 1)=22/65=0.34 Rf(compound 2)=50/65=0.77

answer
What is Rf compound 1? What is Rf compound 2?
question
_____ spots are colored
answer
visualized
question
colorless spots require
answer
I2 vapor; various oxidizing stains such as KMnO4, MoO3, fluorescent indicator in stationary phase (visualized with UV light), special spray reagents
question
What does it mean when Rf=1
answer
spots travel with solvent front
question
Rf=0 what does it mean
answer
spot doesn't move off baseline, undesirable
question
range of Rf values
answer
Rf from 0 to 1
question
what is Rf if spot travels with solvent front
answer
1
question
How to use chromatography to test for purity?
answer
1) Run sample with several solvent systems so that Rf is between 0.2 and 0.5 2) If only one spot appears each time, the sample is probably pure
question
How can we use chromatography to test for identity?
answer
1) run unknown and known with several solvent systems so that Rf is between 0.2 and 0.8 2) if both samples have same Rf each time, they are probably identical
question
The stationary phase is coated on ___
answer
glass or plastic plate
question
The mobile phase flows up the plate by ____
answer
capillary action
question
The ____ flows up the plate by capillary action
answer
mobile phase
question
Binder: ______ is used to help stationary phase stick to plastic or glass surface
answer
hydrogen calcium sulfate
question
Normal phase system: the stationary phase is often ____ or ___
answer
alumina; silica gel
question
in a normal phase system the mobile phase is often ___
answer
organic solvent
question
in a normal phase system the separation mechanism is ___
answer
adsorption
question
4 characteristics of TLC
answer
1) rapid 2) simple 3) requires little sample 4) usually an analytical tool
question
a preparative TLC is not good for ____
answer
separating large (gram) quantities
question
3 uses of TLC
answer
1) purity indicator 2) identification 3) monitoring reactions
question
Why do A, B and C separation
answer
1) chemical nature of A, B, C 2) type of stationary phase 3) mobile phase polarity
question
Different types of chemical nature of A, B, and C which affect separation of compounds.
answer
1) bond-dipoles and polarity 2) hydrogen bonding 3) presence of acidic hydrogens 4) ionic bonds or salts 5) proportion of "polarity" to "grease"
question
What is adsorption?
answer
It is a surface phenomenon. Molecules 'stick' to the surface of a polar solid. "They are said to be absorbed on the surface."
question
adsorption is not the same as ___
answer
absorption
question
Adsorption Chromatography: stationary phase is a ____
answer
solid absorbent
question
3 things which may be used as a solid absorbent
answer
Silica gel (SiO); C18; Alumina (Al2O3)
question
In normal phase chromatography the ___ compound moves faster because ____
answer
least polar; it interacts with the stationary phase to a lesser extent
question
Normal Phase Chromatography: the least polar compound has a ____ retention time and therefore travels ____ the plate. It has a ___ Rf
answer
shorter; farther up; high
question
___ and ___ are common polar stationary phases that will interact strongly via electrostatic interactions with molecules that are ____
answer
SiO2; Al2O3; polar
question
____ is kinda like the opposite of normal-phase chromatography
answer
reverse-phase chromatography
question
In reverse-phase chromatogrpahy ____ interacts strongly with greasy compounds containing lots of saturated and unsaturated _____
answer
C18 backbone; hydrocarbon functionalities
question
R(CH2)nCh3 and other hydrocarbon groups are very ____ functional groups and thus stick to the _____ ,resulting in a ___Rf in reverse phase chromatography
answer
nonpolar; nonpolar stationary phase; Rf
question
In reverse phase chromatography the ____ moves faster, has a____ retention time, travels ___ and has a___ Rf
answer
polar compound; shorter; farther; higher
question
adsorption works because of ____
answer
electrostatic attraction
question
partitioning applies to ___ and ____ chromatography
answer
liquid-liquid; gas-liquid
question
____ applies to liquid-liquid and gas-liquid chromatography
answer
partitioning
question
in ____ compounds distribute between the two immiscible liquid phases
answer
paritioning
question
Solubility differences cause ___
answer
separation
question
_____ cause separation
answer
solubility separation
question
The value ___represents the distribution coefficient or equilibrium of a solute A between the ____
answer
Kp; the two systems Kp=A1/A2 where A1 is amount of A in phase 1 and A 2 is amount of A in phase 2
question
bond dipoles depend on ___, ___ and ___
answer
bond length; charge separation; electronegativity difference
question
a molecular dipole moment is the ____
answer
vector sum of the bond dipole moments
question
____ are heteroatoms with electron pairs, or filled pi-orbitals of double bonds-distribution of electron density can be distorted by a dipole in another molecule (stationary phase)
answer
polarizable groups
question
polarizable groups are _____ with electron pairs, or filled ____ of double bonds. _____ can be distorted by a dipole in another molecule (____)
answer
heteroatoms; pi-orbitals; Distribution; stationary phase
question
hydrogen bonding may cause a ____
answer
strong interaction w/ a stationary phase
question
in order to have hydrogen bonding an organic molecule must have ____ or ___
answer
N-H; O-H
question
the presence of an ___ hydrogen (_____) contributes to making the molecule polar?
answer
acidic; low pKa
question
2 procedure types of column chromatography
answer
gravity; flash
question
3 physical processes for separation
answer
adsorption; partitioning; ion exchange
question
_____ is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds, and is used in chemistry to identify, quantify, and purify the individual components of the mixture
answer
HPLC
question
How does a developing chamber work
answer
You put the solvent in bottom, put the filter paper on the side (solvent goes up the side in order to keep the beaker air full of solvent particles so that none of solvent evaporates off side of filter paper)
question
Why do you use a pencil instead of a pen when drawing the line
answer
b/c if you use pen the ink will spread upwards with the solvent
question
What do you use in order to transfer die onto plate
answer
you use a capillary tube (which makes a small dot)
question
photosynthetic pigments contained in spinach leaves belong to two classes ____ and ____
answer
cartenoids; chlorophylls
question
2 types of cartenoids
answer
cartene; xanthophylls
question
2 types of chlorophylls in experiment
answer
cchlorophyll a and b
question
_____ is the primary pigment that transforms the energy of sunlight into chemical energy oters are ____
answer
chlorophyll a; accessory pigments
question
what do accessory pigments do
answer
help efficiently harvest the light and deliver protons to chlorophyll a
question
_____ via a redox reaction donates an electron into an electron transport chain
answer
accessory pigments
question
____ is chlorophyll lacking the central magnesium ion and serves as a primary electron acceptor and helps initiate the ETC in photosynthesis
answer
phenophytin
question
pheophytin is ____ lacking the _____. It serves as a primary electron acceptor and helps to ___ in photosynthesis
answer
chlorophyll; magnesium ion; initiate the electron transport chain
question
Chlorophyll a has a ____ where chlorophyll b has an ____
answer
methyl group; aldehyde functional group
question
chlorophyll ___ is slightly more polar than chlorophyll __
answer
b; a
question
____ is a hydrocarbon and is therefore very lipophilic and nonpolar
answer
beta-Carotene
question
what is your solvent front?
answer
pretty much how high up the solvent trveled up the paper
question
what might change Rf of same compound
answer
type of solvent u use; temperature
question
when does stationary phase occur for substance
answer
when it is stuck to paper nd not moving
question
when does mobile phase occur for a substance
answer
when it is free moving, not stuck to paper
question
molecules are constantally moving back and forth between free and absorbed stages. What effects this equilibrium
answer
1) polarity and size of moleculle 2) polarity of the stationary phase 3) polarity of the solvent
question
list following from eluted first to last chlorophyll b, chlorophyll a, beta carotene, violaxanthan, zeaxanthin, lutein
answer
beta carotene; chlorophyll a; chlorophyll b; lutein; zeaxanthin; violaxanthan
question
ethanol chemical formula
answer
CH3Ch2OH
question
ethyl acetate chemical formula
answer
C4H8O2
question
hexane chemical formula
answer
C6H14
question
isopropanol chemical formula
answer
C3H8O
question
silicon dioxide chemical formula
answer
SiO2
question
potassium permanganate chemical formula
answer
KMnO4
question
what is elute of part 1
answer
(isopropanol/water 6:1)
question
what is elute part 2
answer
hexane/ethyl acetate (1:1)
question
Why do you add ethanol to the spinach leaves only to extract the ethanol after mixing
answer
because the compounds we are interested in are relatively nonpolar, by adding ethanol we isolate the compounds we want while removing the polar compounds because thanol is polar
question
why do we use hexane/ethyl acetate as a developing fluid?
answer
because it is nonpolar enough to latch onto the compounds and draw them up the page in the mobile phase but not too nonpolar as to latch on to hardly to the compounds and not allow them to enter the stationary phase
question
two phases in chromatography
answer
mobile phase; stationary phase
question
why do we use silicon dioxide in the plate?
answer
because it will latch onto the polar compounds of the molecules nad cause the more polar molecules to move through the plate slower than the less polar ones.
question
liquids with bp below ____ or solids that ____ may vaporize before the plate is visulized
answer
160; sublime
question
what compounds are we eluting in part 1
answer
sudan IV; bismark brown; fast green; rhodamine



