Spinal Cord Injury and Occupational Therapy – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
___________________ is currently the most frequent neurological category followed by ____________________, _______________________, and ____________________________________.
answer
Incomplete tetraplegia is currently the most frequent neurological category followed by incomplete paraplegia, complete paraplegia, and complete tetraplegia.
question
In the 70's, common SCI causes of death were things like
answer
sepsis from UTI or wounds.
question
What level innervates most of the breathing
answer
C4
question
If someone's level is a X, that is the level that
answer
WORKS. THIS IS SUPER IMPORTANT.
question
C4: Key muscles and functions
answer
Diaphragm, trapezius: Respiration;
question
C5: Key muscles and functions
answer
Biceps: Elbow Flexion; Deltoids
question
C6: Key muscles and functions
answer
Radial wrist extensors: Wrist extension; tenodesis after time and therapy
question
Early in therapy with a C6 injury . . .
answer
you might use a universal cuff or hook something to the hand, because they do have the wrist extension. They haven't developed tenodesis grasp yet, which takes a lot of time and effort.
question
C7: Key muscles and functions
answer
Triceps, elbow extension
question
______ is a great activity for C7 SCI, because ______
answer
transfers! They have tricep extension and can work on scooting themselves over (versus just locking their elbows)
question
C8: Key muscles and functions
answer
Flexor digitorum: Finger flexion (makes a claw hand)
question
L2: key muscles and functions
answer
Psoas Major: Hip Flexion
question
L3: Key muscles and functions
answer
Quadriceps : Knee extension
question
L4: Key muscles and functions
answer
Tibialis Anterior: Ankle Flexion
question
S1: Key muscles and Functions
answer
Gastroc: Plantarflexion
question
S3-S5: key muscles and functions
answer
Bowel & bladder
question
In AIS A
answer
Complete: No motor or sensory function is preserved S4-S5
question
In AIS B
answer
Incomplete: Sensory function is preserved below level of injury (including S4-5)
question
In Ais C
answer
Incomplete: At least ½ key muscles below level of injury <3/5
question
In Ais D
answer
Incomplete: At least ½ key muscles below level of injury >3/5
question
In Ais E
answer
Normal: Motor and sensory function is normal
question
A c5 asia D is most likely
answer
a central cord patient -> arms don't work, legs do!
question
What are common precautions and complications of SCI?
answer
Fracture Respiration Spasticity Thrombus Decubiti Orthostatic Hypotension Autonomic Dysreflexia Heterotrophic Ossification Neurogenic Bowel & Bladder
question
When do you hold therapy s/p fracture?
answer
Surgical consult pending Radiological tests pending
question
After operative repair (rods, screws), you need to be aware of
answer
Fusion, screws, rods, bone graft Brace Post-op precautions -> don't move them too much!
question
If a person has non-operative conservative treatment
answer
Non-operative "conservative" treatment Immobilize - bedrest Immobilize - brace Spinal precautions Braces don't immobilize the bones completely! They serve mostly as a reminder.
question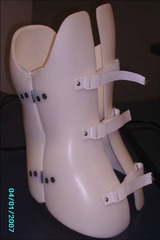
The biggest clue that a patient should not be bending or twisting is

answer
a TLSO!
question
What is a halo?
answer
screwed into the head, rests on your shoulders, stabilizes your neck while you heal, makes you top heavy
question
With splints and braces, it's important to remember that
answer
they can impede function
question
What is BLTS?
answer
No bending, lifting, twisting, or sitting without more than 20 mins at a time without changing position
question
With lesions C4 and above
answer
Damage to phrenic nerve Diaphragm weakness May require ventilator or phrenic nerve stimulator
question
For lesions from C5-C12 (breathing)
answer
Weakness of intercostal, lats & abdominal muscles Impaired respiration
question
What is quad-cough
answer
push on abdomen to help them cough
question
What treatments are available for impaired breathing in SCI?
answer
Quad cough" Suction Trunk strengthening Incentive spirometer
question
One cause of spasticity that can be temporary is
answer
Reflex muscle contraction
question
What are some advantages of spasticity?
answer
Warns of problem Decrease atrophy Promotes circulation Use functionally
question
What are some disadvantages of spasticity?
answer
Impairs function Pain Skin breakdown Seating & positioning limitations
question
Treatments for spasticity include
answer
ROM Splints Medication Baclofen
question
What are some blood clot risks in SCI?
answer
Blood clot - decreased circulation Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) in extremity or Pulmonary Embolus (PE) in lung
question
Symptoms of DVT include
answer
Warm, swollen, pain
question
PE symptoms include
answer
SOB Decreased O2 saturation Chest pain
question
How can we prevent thrombus?
answer
Anticoagulants Sequential Compression Device (SCD) Compression garments(TEDs) ROM & activity
question
What are treatments for thrombus?
answer
Anticoagulants Inferior Vena Cava Filter (IVCF)
question
What are causes of decubitus ulcers
answer
Decreased circulation Immobility Cell death
question
How can you prevent decubitus ulcers?
answer
Position change Skin check Hygiene
question
Stage 1 pressure ulcers
answer
look like red blisters
question
A stage 2 pressure ulcer
answer
skin opens
question
A stage 3 pressure ulcer
answer
goes into subcutaneous fatty layer
question
A stage 4 pressure ulcer
answer
goes into bone/muscle
question
One way to motivate patients that do not want to engage in therapy into doing position changes and hygiene is
answer
to show them pictures of pressure ulcers . . .
question
What is orthostatic hypotension?
answer
Low blood pressure with change of position
question
What is HoTN?
answer
hypotension
question
Symptoms of orthostatic hypotension include
answer
Lightheaded, dizzy Syncope
question
Prevention of orthostatic hypotension include
answer
Slow position change TED hose, abdominal binder
question
Treatment for orthostatic hypotension include
answer
Lie down / recline Elevate LE Progressive activity tolerance Have them kick their legs, move around -> get blood moving back up
question
What is autonomic dysreflexia?
answer
Serious, life-threatening condition! Sympathetic nervous system responds to a stimulus (interpreted as "noxious")
question
Who is at risk of autonomic dysreflexia?
answer
Injuries at or above T6 are at risk
question
What are symptoms of autonomic dysreflexia?
answer
High blood pressure Pounding headache, blurred vision, decreased heart rate, goose bumps, sweating, flushing skin, nasal stuffiness
question
Possible causes of autonomic dysreflexia include
answer
Full bladder Urinary catheter blocked Stool impaction Infection Pressure sore Tight clothes Ingrown toenail ANYTHING that the body feels is a threat!
question
What could happen as a result of autonomic dysreflexia?
answer
Cerebral vascular hemorrhage (CVA - stroke) Myocardial infarction (MI - heart attack)
question
Treatment for autonomic dysreflexia includes?
answer
Sit patient up, or remain sitting. DO NOT LIE THE PERSON DOWN; IT INCREASES THE BP Find the "noxious stimulus" and fix it Nitro paste if necessary
question
Prevention for autonomic dysreflexia includes?
answer
Follow cathing schedule Successful bowel management program Skin checks
question
What is heterotopic ossification?
answer
Abnormal calcification around a joint
question
Where is heterotopic ossification most common?
answer
Most common at shoulder & hip
question
Symptoms of heterotopic ossification include?
answer
Decreased ROM Warm & swollen Febrile
question
Treatment for heterotopic ossification includes
answer
ROM Medication
question
What is neurogenic bowel and bladder?
answer
Decreased voluntary control of bowel & bladder due to neurological injury
question
Bladder management can include
answer
Indwelling foley catheter Intermittent cath Suprapubic cath
question
Bowel management can include
answer
Diet Medication Bowel training program Ostomy
question
How does tenodesis work?
answer
Technique used with C6 injury Use of wrist extension to elicit "grasp" Strengthen wrist extensors Maintain flexor tension
question
At ______ you can usually pronate
answer
c6
question
C6 cannot (extend/flex) the wrist
answer
flex
question
A good thing to work on for ADL's and dressing skills for C6 could be
answer
substitutions movements to get pants on and off, trunk balance; long sitting in bed



