Science Olympiad-Astronomy Objects and Systems (DSO) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
T Tauri
answer
Variable star in the constellation Taurus, the prototype of the T Tauri stars. It was discovered in October 1852 by John Russell Hind. Very young, only about a million years old. Distance from Earth is about 460 light years. Apparent magnitude varies unpredictably from 9.3 to 14.
question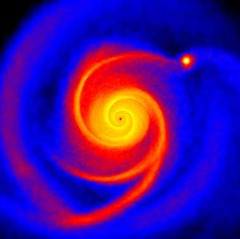
HL Tauri

answer
Very young T Tauri star in the constellation Taurus, approximately 450 light-years from Earth in the Taurus Molecular Cloud.
question
AB Aurigae
answer
A star in the Aurigae constellation. It is better known for hosting a dust disk that may harbor a condensing planet of brown dwarf. The star could host a possible substellar companion in wide orbit.
question
HAT-P-11b
answer
An extrasolar planet orbiting the star HAT-P-11. This planet was discovered by the transit method and submitted for publification on 2 January 2009.
question
51 Pegasi b (Bellerophon)
answer
An extrasolar planet approximately 50 light-years away in the constellation of Pegasus. 51 Pegasi b was the first planet to be discovered orbiting a main-sequence star, which marked a breakthrough in astronomical research.
question
WASP-43b
answer
A transitioning planet in orbit around the young, active, and low-mass star WASP-43 in the constellation Sextans. The planet is a hot Jupiter with a mass twice that of Jupiter, and a radius equal to Jupiter's.
question
WASP-18b
answer
An extrasolar planet that is notable for having an orbital period of less than one day. It has a mass equal to 10 Jupiter masses, just below the boundary line between planets and brown dwarfs, about 13 Jupiter masses.
question
HD 106906b
answer
Directly imaged planetary-mass companion and candidate exoplanet orbiting the star HD 106906, in the constellation Crux at about 300 light-years from Earth.
question
WISE 0855-0714
answer
Sub-brown dwarf that is 2.31 +- 0.08 parsecs from Earth. This dwarf has the third-highest proper motion after Barnard's Star and Kapteyn's Star. Also has the fourth-largest parallax of any known star or brown dwarf, meaning it is the fourth closest extrasolar system to the Sun.
question
2MASSJ22282889-431026
answer
A brown dwarf planet that was observed by the Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes. These indicate that this brown dwarf is marked by wind-driven, planet-sized clouds.
question
M42 (Messier 42) (Orion Nebula)
answer
A diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation in Orion. One of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. Located at a distance of 1,344 +- 20 light years and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth.
question
Barnard 68
answer
A molecular cloud, dark absorption nebula or Bok globule, towards the southern constellation Ophiuchus and well within our own galaxy at a distance of about 400 light-years, so close that not a single star can be seen between it and the Sun.
question
55 Cancri (55 Cnc)
answer
A binary star approximately 41 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cancer. The system consists of a G-type star and a smaller red dwarf, separated by over 1,000 AU.
question
Kepler-186
answer
A main-sequence M1-type dwarf star, located 151 +- 18 parsecs away in the constellation of Cygnus. The star is slightly cooler than the Sun, with roughly half its metallicity. It is known to have five planets, including the first Earth-sized world discovered in the habitable zone: Kepler-186f.
question
HD 95086
answer
A-class pre-main-sequence star. It is roughly 5 times as massive as Jupiter and orbits 56-61 AU away from its parent stars. HD 95086 b is a confirmed, directly imaged exoplanet orbiting the young, 17 Myr.
question
GD 165
answer
A system of a white dwarf and a brown dwarf of spectral types DA4 + L4, located in constellation Bootes at approximately 103 light-years from Earth.
question
HR 8799
answer
A young (30 million year-old) main sequence star located 129 light years (39 parsecs) away from Earth in the constellation of Pegasus, with roughly 1.5 times the Sun's mass and 4.9 times its luminosity. It is part of a system that also contains a debris disk and at least four massive planets.



