Science Olympiad Astronomy 2018 Answers – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Stellar Evolution
answer
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime.
question
small star
answer
Lives longer than large star
question
red giant
answer
A star that expands and cools once it runs out of hydrogen fuel
question
planetary nebula
answer
a ring-shaped nebula formed by an expanding shell of gas around an aging star.
question
white dwarf
answer
hot, extremely dense core; shine for billions of years; lower left on H-R diagram
question
large star

answer
a very big star that turns into a black hole
question
red super giant

answer
The later stage of a high-mass star. Heavy metals form inside it.
question
supernova
answer
a gigantic explosion in which a high-mass star throws its outer layers into space
question
neutron star
answer
dense core of a neutron that remains after a supernova
question
Black hole
answer
An object whose gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
question
stars chemical composition
answer
of most stars is 73 percent hydrogen , 25 percent helium, 2 percent other elements by mass
question
luminosity
answer
the actual brightness of an object such as a star
question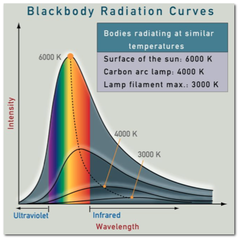
blackbody radiation

answer
A solid object emits visible light when it is heated to about 1000 K
question
star color index

answer
A measure of a star's color, which tells scientists how hot the star's surface is.
question
H-R diagram
answer
a graph relating the surface temperatures and absolute brightness of stars.
question
HII regions
answer
emission nebulae composed of hydrogen
question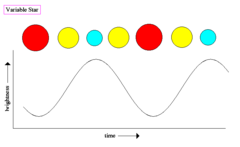
cepheids

answer
Stars whose luminosity that varies periodically over time
question
hypergiants
answer
The largest stars are.... (100x mass of the sun)
question
wolf-rayet stars
answer
hotter than almost all other stars
question
magnetars
answer
a neutron star with an extremely strong magnetic field.
question
pulsars
answer
highly magnetised, rotating neutron star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation
question
stellar mass black holes
answer
small than supermissive
question
eclipsing binaries
answer
a system in which one star periodically blocks the light from the other star
question
X-ray binaries

answer
X-ray binaries are a class of binary stars that are luminous in X-rays.
question
Type II supernovas

answer
results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least 8 times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun
question
Kepler's law
answer
developed using Brahe's measurements and sophisticated math
question
Hubble's law
answer
the observations that the father away a galaxy is the faster it is moving away.
question
RCW 103
answer
it is a supernova remnant with right ascension It is approximately 2000 years old and is 10,000 light years away in the constellation Norma
question
IC 443
answer
is a Galactic supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Gemini. On the plan of the sky, it is located near the star Eta Geminorum. Its distance is roughly 5,000 light years from Earth.
question
Alpha Orionis
answer
is the ninth-brightest star in the night sky and second-brightest in the constellation of Orion.
question
Hr 5171 A
answer
HR 5171, also known as V766 Centauri, is a triple star system in the constellation Centaurus, around 12,000 light years from Earth. It is either a red supergiant or recent post-red supergiant yellow hypergiant, and one of the largest known stars.
question
SN W49B
answer
The highly distorted supernova remnant shown in this image may contain the most recent black hole formed in the Milky Way galaxy.
question
ASASSN-15lh
answer
is a bright astronomical transient discovered by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN). It was first detected on June 14, 2015, located within a faint galaxy in the southern constellation Indus.
question
AG Carinae
answer
is a star in the constellation Carina. It is classified as a luminous blue variable and is one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way.
question
S Doradus
answer
is one of the brightest stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a satellite of the Milky Way. It is a Luminous Blue Variable and one of the most luminous stars known
question
SN 1987A
answer
first naked eye SN since Kepler 1604was a supernova in the outskirts of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud (a nearby dwarf galaxy). It occurred approximately 51.4 kiloparsecs (168,000 ly) from Earth
question
Geminga
answer
is a neutron star approximately 250 parsecs from the Sun in the constellation Gemini.
question
NGC 6357
answer
NGC 6357 is a diffuse nebula near NGC 6334 in the constellation Scorpius.
question
M82 X-2

answer
M82 X-2 is an X-ray pulsar located in the galaxy Messier 82, approximately 12 million light-years from Earth
question
Circinus X-1
answer
Constellation. Meaning: the pair of compasses.Brightest star: α Circini. Visible in June.
question
NGC 6888
answer
The Crescent Nebula (also known as NGC 6888, Caldwell 27, Sharpless 105) is an emission nebula in the constellation Cygnus, about 5000 light-years away from Earth. It was discovered by Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel in 1792. A Emission nebula
question
SXP 1062
answer
Pulsar in SMC, Supernova created it, maybe Accreting Magnetar A supernova remnant
question
cephei
answer
VV Cephei, also known as HD 208816, is an eclipsing binary star system located in the constellation Cepheus, approximately 5,000 light years from Earth. It is both a B[e] star and shell star.
question
a yellow super giant
answer
A yellow supergiant star is a star, generally of spectral type F or G, having a supergiant luminosity class (e.g. Ia or Ib). They are stars that have evolved away from the main sequence, expanding and becoming more luminous.
question
NP 0532
answer
The Crab Pulsar (PSR B0531+21) is a relatively young neutron star. The star is the central star in the Crab Nebula, a remnant of the supernova SN 1054, which was widely observed on Earth in the year 1054? M1
question
heart of the scorpion
answer
Bright reddish Antares - also known as Alpha Scorpii - is easy to spot on a summer night. It is the brightest star - and distinctly reddish in color - in the fishhook-shaped pattern of stars known as the constellation Scorpius the Scorpion.
question
NGC 3582
answer
Nebula/Stellar Nursery
question
IC 1396/The Elephants trunk nebula
answer
he Elephant's Trunk nebula is a concentration of interstellar gas and dust within the much larger ionized gas region IC 1396 located in the constellation Cepheus about 2,400 light years away from Earth.
question
cas A
answer
Cas A is a supernova remnant (SNR) in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest extrasolar radio source in the sky at frequencies above 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately 11,000 light-years (3.4 kpc) away within the Milky Way. a type IIn sup. nova
question
Cygnus X-1

answer
- nearest black hole to earth - about 6,070 light years distant from earth First proposed black hole
question
PSR J0108-1431
answer
Very old Solitary Pulsar/ Neutron Star, in Cetus, 2nd faintest pulsar
question
microquasar
answer
A microquasar, the smaller version of a quasar, is a compact region surrounding a black hole with a mass several times that of our sun, and its companion star
question
LHa115-N19
answer
-LHa115-N19: A complex of star formation about 200,000 light years from Earth. With its millions of stars and relatively close proximity, the Small Magellanic Cloud offers astronomers a chance to study phenomena across the stellar life cycle
question
Large Magellanic Cloud
answer
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of 50 kpc ≈163,000 light-years, the LMC is the third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way
question
V838 Mon

answer
V838 Mon is a red variable star in the constellation Monoceros about 20,000 light years (6 kpc) from the Sun.
question
SN 2010JL
answer
A Supernova
question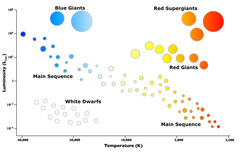
HR diagram

answer
A graph relating the surface temperature and absolute magnitude of the stars.
question
Population II Cepheids
answer
Type II Cepheids are variable stars which pulsate with periods typically between 1 and 50 days. They are population II stars: old, typically metal-poor, low mass objects
question
Pulsating star
answer
Artist's impression of the eclipsing binary system, including a pulsating star called a Cepheid variable.
question
SRA
answer
Small-amplitude giants
question
SRB
answer
Poorly-defined periodicity
question
Protostar
answer
Earliest stage of a stars life
question
molecular cloud
answer
a large, cold cloud made up mostly of molecule hydrogen and helium in which stars are born
question
CNO cycle

answer
the cycle of reactions by which intermediate and high mass stars fuse hydrogen into helium
question
pulsar
answer
-a rapidly spinning neutron star that emits rapid pulses of radio and optical energy -soft gamma rays repeaters
question
the proper order of luminosity
answer
Giants-Bright Giants- Supergiants-Hypergiants
question
OB association
answer
an unbound group of very young, massive stars predominantly of spectral types O and B
question
Hayashi track
answer
The Hayashi track is a luminosity-temperature relationship obeyed by infant stars of less than 3 M
question
Stellar-mass black hole
answer
-Also known as a Collapsar -stellar-mass black hole is a black hole formed by the gravitational collapse of a massive star
question
Kerr-Newman metric
answer
he Kerr-Newman metric is a solution of the Einstein-Maxwell equations in general relativity that describes the spacetime geometry in the region surrounding a charged, rotating mass
question
minkowski space
answer
n mathematical physics, Minkowski space or Minkowski spacetime is a combination of three-dimensional Euclidean space and time into a four-dimensional manifold where the spacetime interval between any two events is independent of the inertial frame of reference in which they are recorded
question
Schwarzschild radius
answer
a measure of the size of the event horizon of a black hole
question
Reissner-Nordstrom metric
answer
In physics and astronomy, the Reissner-Nordström metric is a static solution to the Einstein-Maxwell field equations, which corresponds to the gravitational field of a charged, non-rotating, spherically symmetric body of mass
question
The Eddington limit
answer
he natural limit to the luminosity of stars, or the radiation generated by accretion onto a compact object, is named in his honour
question
Magnetohydrodynamic
answer
A generator that uses a fluid a a moving conductor is a ____?
question
Chandrasekhar limit
answer
the maximum mass of a white dwarf above which it collapses. Approximately 1.4 solar masses.
question
General Relativity
answer
Gravitational attraction between masses is a result of the nearby masses; gravity has waves
question
ZZ Ceti stars
answer
A pulsating white dwarf is a white dwarf star whose luminosity varies due to non-radial gravity wave pulsations within itself. Known types of pulsating white dwarfs include DAV, or ZZ Ceti
question
Proper classes of increasing luminosity
answer
BL Herculis-W Virginis-RV Tauri- Classical Cepheid
question
the hertzsprung progression
answer
a secondary bump in their light curves that appears near light minimum



